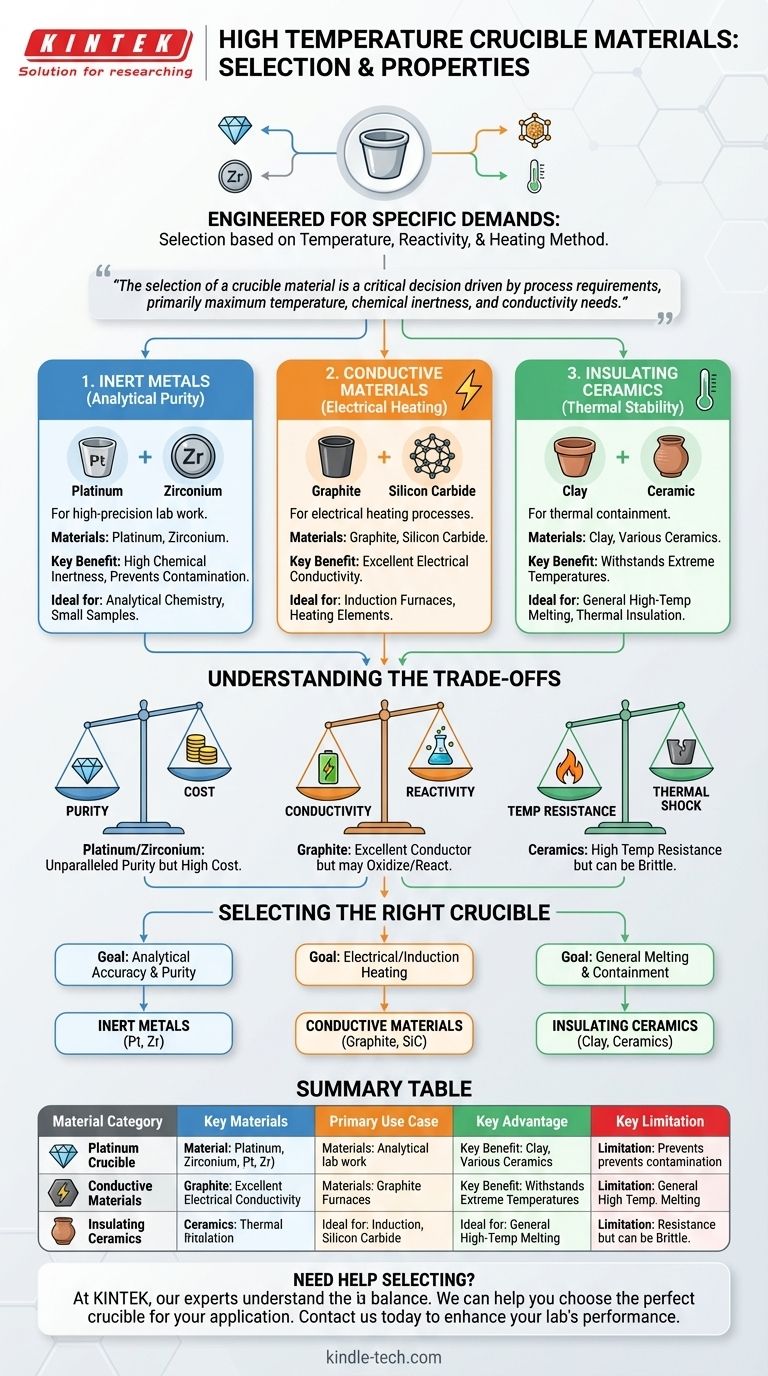
Crucibles for high-temperature applications are not made from a single material. Instead, they are engineered from a select group of substances chosen for their specific properties, including platinum, zirconium, graphite, silicon carbide, and various ceramics. The correct material is always determined by the demands of the application, such as the required temperature, the chemical reactivity of the substance being heated, and the heating method being used.
The selection of a crucible material is a critical decision driven by process requirements. The primary considerations are the maximum temperature, the chemical inertness needed to avoid contamination, and whether the process requires electrical conductivity or insulation.

The Core Categories of Crucible Materials
The most effective way to understand crucible materials is to group them by their primary functional properties. Each category serves a distinct purpose in laboratory or industrial settings.
Inert Metals for Analytical Purity
For high-precision laboratory work, preventing contamination is the highest priority.
Platinum and zirconium are the materials of choice in these applications. Their primary advantage is their high degree of chemical inertness, even at extreme temperatures. This ensures that the crucible itself does not react with or contaminate the sample, which is essential for accurate analytical chemistry.
Conductive Materials for Electrical Heating
Some high-temperature processes rely on electrical current to generate heat.
Crucibles for these applications are made from conductive materials like graphite or silicon carbide. Their ability to conduct electricity allows them to be used in induction furnaces or other systems where the crucible itself is part of the heating element.
Insulating Ceramics for Thermal Stability
The most common and historically significant crucibles are designed for thermal containment.
These insulating crucibles are made from a wide range of ceramic materials, with clay being the traditional choice. Their purpose is to withstand extreme temperatures without melting or degrading while effectively insulating the contents.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible material involves balancing performance against practical limitations. No single material is perfect for every situation.
Purity vs. Cost
Platinum and zirconium offer unparalleled purity and resistance to chemical attack. However, they are exceptionally expensive, limiting their use to applications where analytical accuracy is non-negotiable and sample sizes are small.
Conductivity vs. Reactivity
Graphite is an excellent, cost-effective conductor for heating, but it can be oxidized at high temperatures and may react with certain metals. This requires careful consideration of the atmosphere (e.g., vacuum or inert gas) and the material being melted.
Temperature Resistance vs. Thermal Shock
Ceramic crucibles can often withstand the highest temperatures, but they can be brittle. They may be susceptible to thermal shock, where rapid changes in temperature cause them to crack or shatter.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Goal
Your choice should be guided by the primary objective of your work.
- If your primary focus is analytical accuracy and sample purity: Choose inert metals like platinum or zirconium to eliminate the risk of contamination.
- If your primary focus is a process involving electrical or induction heating: Select a conductive material like graphite or silicon carbide.
- If your primary focus is general high-temperature melting or containment: A durable and cost-effective ceramic crucible is almost always the appropriate choice.
Ultimately, matching the crucible's material properties to your specific thermal and chemical requirements is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Materials | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Metals | Platinum, Zirconium | Analytical Chemistry, High Purity | Maximum Chemical Inertness | High Cost |
| Conductive Materials | Graphite, Silicon Carbide | Induction/Electrical Heating | Excellent Electrical Conductivity | Potential Reactivity |
| Insulating Ceramics | Clay, Various Ceramics | General High-Temperature Melting | High Temperature Resistance, Cost-Effective | Brittle, Thermal Shock Risk |
Need help selecting the perfect high-temperature crucible for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts understand the critical balance between purity, conductivity, and thermal stability. We can help you choose the right crucible material—whether platinum for ultimate purity, graphite for efficient heating, or durable ceramics—to ensure your process is a success.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and let our expertise enhance your lab's performance and accuracy. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- Why use an alumina crucible in a stainless steel autoclave? Ensure Purity in Liquid Lead and LBE Exposure Experiments



















