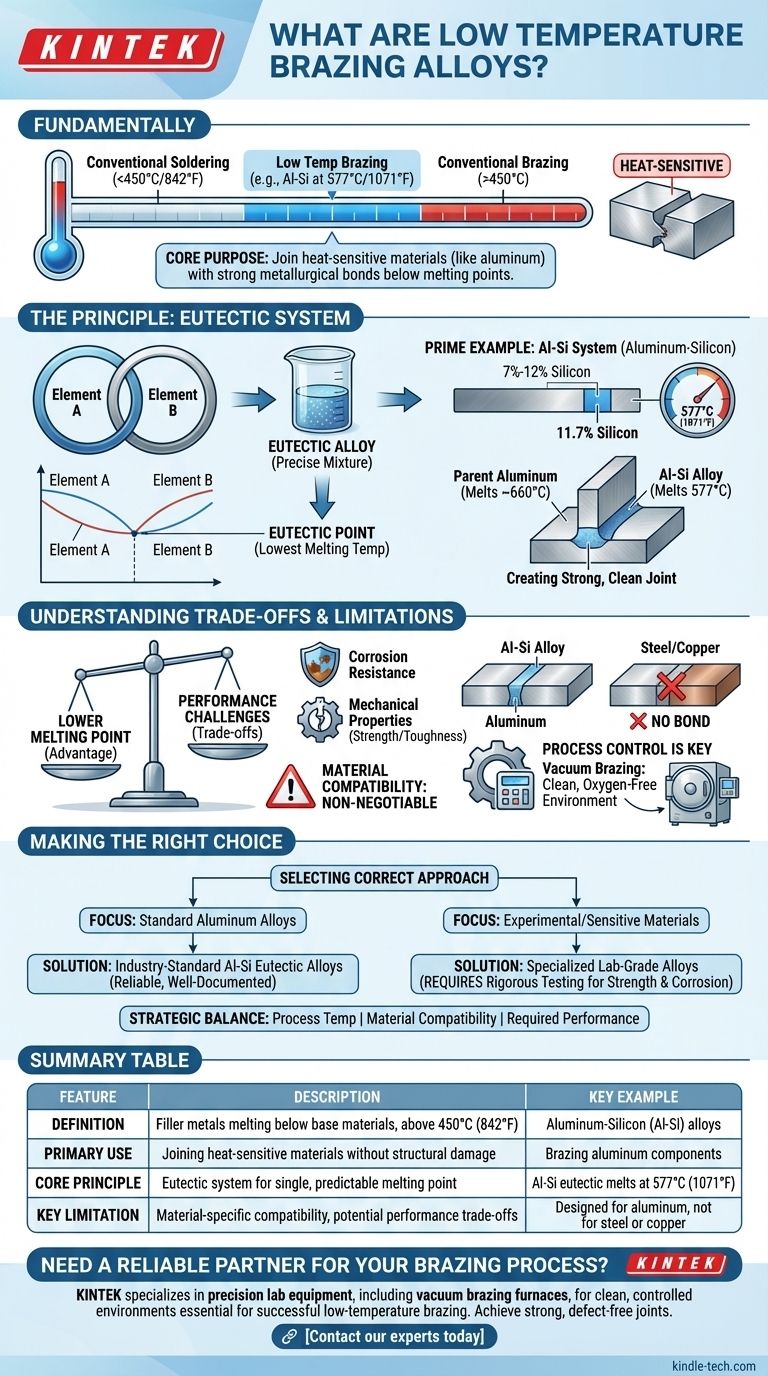
Fundamentally, low temperature brazing alloys are specialized filler metals designed to create strong joints between materials without exposing them to damaging high heat. These alloys melt at a temperature significantly lower than the base materials being joined, but still above the conventional 450°C (842°F) threshold that separates brazing from soldering. The most common industrial example is the aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) system used for brazing aluminum, which has a melting point around 577°C (1071°F).
The core purpose of a low temperature brazing alloy is to enable the joining of heat-sensitive materials, like aluminum alloys, by creating a robust metallurgical bond well below their melting point. The key is to achieve this low-temperature advantage without compromising the final joint's strength or corrosion resistance.

The Principle Behind Low Temperature Alloys
The effectiveness of these alloys is not magic; it is rooted in a specific metallurgical principle known as a eutectic system. Understanding this concept is key to understanding why they work so well for specific applications.
What is a Eutectic Alloy?
A eutectic alloy is a precise mixture of two or more elements that has a lower melting point than any other mixture of those same elements.
When combined at this exact ratio, the elements melt and solidify at a single, sharp temperature, behaving almost like a pure substance. This predictable melting behavior is ideal for a controlled brazing process.
The Al-Si System: A Prime Example
The most prevalent low temperature brazing alloys are based on the aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) system. These alloys typically contain between 7% and 12% silicon.
The eutectic point for this system occurs at 11.7% silicon, which creates an alloy that melts at a precise 577°C (1071°F). This is the standard for brazing many common aluminum alloys.
Why This Matters for Aluminum
Most aluminum alloys melt at temperatures around 660°C (1220°F). The Al-Si eutectic alloy's lower melting point of 577°C creates a crucial temperature window.
This window allows a fabricator to heat an assembly until the brazing alloy melts and flows into the joint, while the parent aluminum components remain solid and structurally sound. This process creates a strong, clean joint with excellent color consistency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While extremely useful, low temperature brazing alloys are not a universal solution. Their specialized nature comes with specific considerations that are critical for success in an industrial setting.
The Challenge of Performance
While standard Al-Si alloys are proven and reliable, more advanced low-temperature alloys developed in laboratories often struggle to meet industrial demands.
These experimental alloys may offer an even lower melting point but can fall short in corrosion resistance and mechanical properties like toughness and strength, making them unsuitable for many commercial applications.
Material Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
Low temperature alloys are designed for specific families of base materials. An Al-Si brazing alloy is engineered exclusively for joining aluminum.
Using it on other metals, such as steel or copper, will not work because the necessary metallurgical interactions will not occur. The alloy must be compatible with the parent materials.
Process Control is Key
Achieving a successful braze requires more than just the right alloy. The process itself is critical.
Techniques like vacuum brazing are often used to ensure a clean, oxygen-free environment. This prevents oxidation of the aluminum surfaces, which would otherwise inhibit the flow of the brazing alloy and result in a weak or failed joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on the materials you are working with and the performance requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is joining standard aluminum alloys: The industry-standard Al-Si eutectic brazing alloys are the most reliable and well-documented choice.
- If your primary focus is joining experimental or highly sensitive materials: You may need to investigate specialized lab-grade alloys, but must budget for rigorous testing to validate their mechanical strength and corrosion resistance.
Ultimately, selecting the right low temperature brazing alloy is a strategic balance between process temperature, material compatibility, and the required performance of the final joint.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Example |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Filler metals melting below base materials but above 450°C (842°F) | Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) alloys |
| Primary Use | Joining heat-sensitive materials without structural damage | Brazing aluminum components |
| Core Principle | Eutectic system for a single, predictable melting point | Al-Si eutectic melts at 577°C (1071°F) |
| Key Limitation | Material-specific compatibility and potential trade-offs in strength/corrosion | Designed for aluminum, not for steel or copper |
Need a reliable partner for your brazing process?
The right equipment is just as critical as the right alloy. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including vacuum brazing furnaces, that provide the clean, controlled environment essential for successful low-temperature brazing. Whether you're working with standard aluminum alloys or advanced materials, our solutions help you achieve strong, defect-free joints.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- How does a benchtop orbital shaker facilitate the production of reducing sugars? Boost Cellulose Hydrolysis Yields
- What are the products of slow pyrolysis? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components
- What is magnetron sputtering method of deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Coatings
- What are the benefits of metallurgy? Achieve Superior Material Performance and Efficiency
- How does thermal treatment equipment enhance biosynthesized ferrihydrite? Unlock High-Performance MRI Contrast Agents
- Why are agate mortars and pestles used for grinding iron oxide? Ensure Sample Purity for XRD Analysis



















