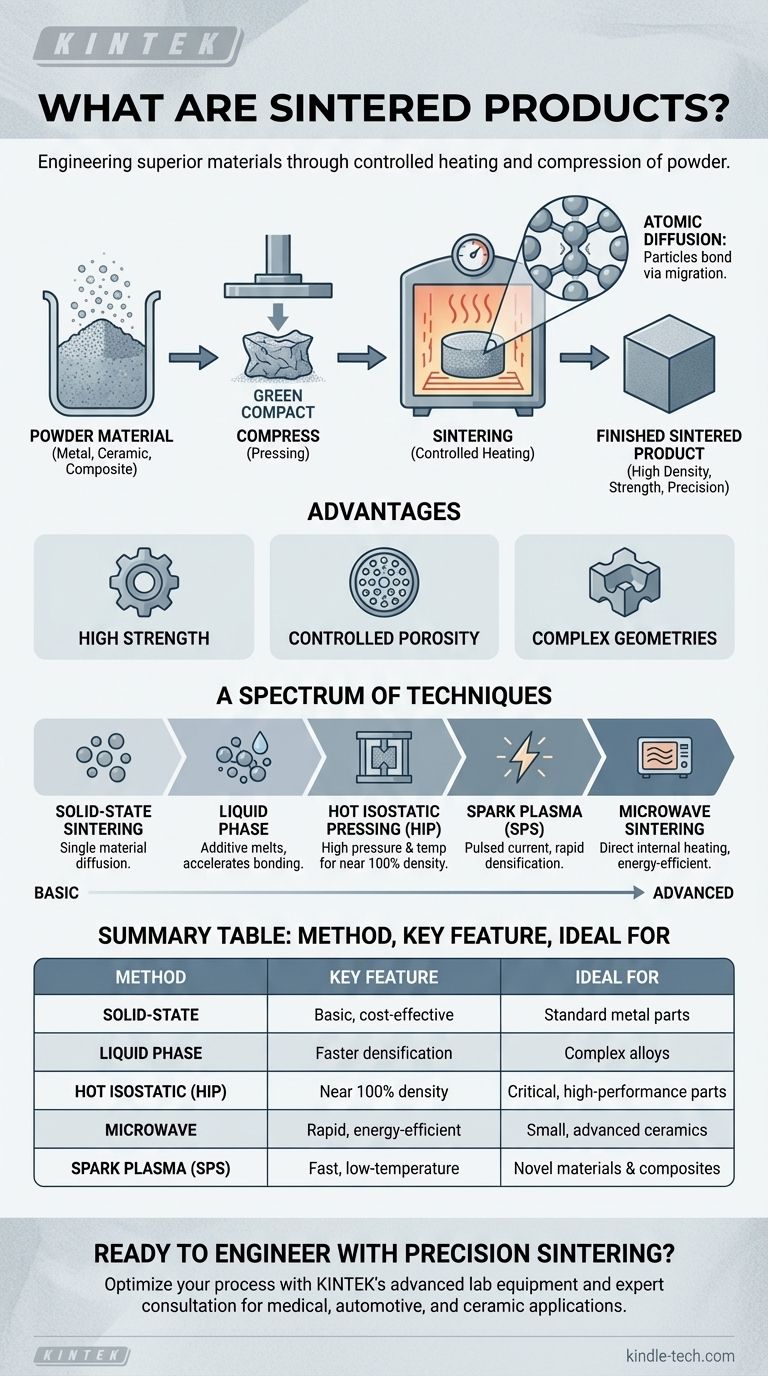
In essence, sintered products are solid objects created by heating and compressing powdered material until the particles bond together. This process, known as sintering, transforms loose powder into a dense, solid part without melting it completely. The technique is used to manufacture everything from high-strength ceramic cutting tools and porous metal filters to automotive gears and medical implants.
Sintering is not simply a method for creating a shape; it is a sophisticated manufacturing process used to engineer materials with specific, often superior, properties like high density, controlled porosity, and exceptional hardness that are difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional melting and casting.
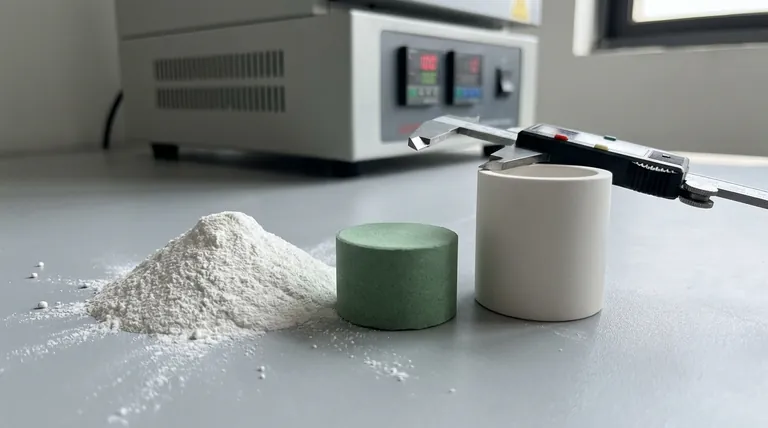

The Core Principle: Fusing Powder into a Solid
Sintering is a thermal treatment applied to a powder compact to impart strength and integrity. The temperature used is below the melting point of the main constituent of the powder.
From Powder to Part: The Basic Process
The journey begins with a fine powder, which can be a metal, ceramic, or a composite. This powder is first pressed into a desired shape, creating a fragile "green compact." This compact is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace, where the sintering process causes the individual particles to fuse together, densifying and strengthening the object.
The Science of Diffusion
At the microscopic level, sintering works through atomic diffusion. As the powder is heated, atoms on the surfaces of adjacent particles migrate across the particle boundaries. This movement effectively creates "necks" or bridges between particles, which grow over time, eliminating the voids between them and turning the loose powder into a solid mass.
Why Not Just Melt It?
Sintering offers critical advantages over melting. It allows for the creation of parts from materials with extremely high melting points (like tungsten or ceramics) that are impractical to cast. It also enables the combination of different materials that wouldn't normally mix in a liquid state, creating unique alloys and composites.
A Spectrum of Sintering Techniques
The specific goals of the manufacturing process—such as achieving maximum density, speed, or unique chemical properties—dictate the type of sintering used.
Foundational Methods
Solid-State Sintering is the most basic form, where a single material's powder is heated just below its melting point, relying purely on atomic diffusion to bond the particles.
Liquid Phase Sintering introduces a small amount of a secondary material (an additive) that melts at the sintering temperature. This liquid phase wets the solid particles, pulling them together through capillary action and accelerating densification before it is driven off.
Advanced, Energy-Assisted Methods
Some techniques use external forces to speed up the process and improve results.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) simultaneously applies high temperature and high-pressure inert gas to the powder. This intense pressure helps collapse internal voids, producing parts that are nearly 100% dense.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) passes a powerful pulsed electric current through the powder while also applying physical pressure. This generates rapid, localized heating at the particle contact points, enabling extremely fast densification at lower overall temperatures.
Microwave Sintering uses microwave radiation to generate heat directly within the material itself, rather than heating it from the outside. This can lead to faster, more energy-efficient processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is a complex process where the chosen method and process parameters present distinct trade-offs.
The Challenge of Full Densification
Achieving a product that is completely free of pores can be difficult. Residual porosity can remain if the process is not perfectly controlled, potentially affecting the final strength and performance of the component. This is why methods like HIP are employed for critical, high-performance applications.
Method-Specific Limitations
No single sintering method is universally superior. Microwave Sintering, for example, is excellent for rapid heating of small ceramic parts and maintaining a fine grain structure. However, it is poorly suited for large-scale production (often processing one part at a time) and is incompatible with certain materials that don't couple well with microwaves.
Process Control is Critical
The final properties of a sintered product are highly sensitive to process variables. Temperature, heating rate, pressure, and the furnace atmosphere (e.g., performing the process in a vacuum to remove gases and prevent oxidation) must be precisely controlled to achieve high hardness, good densification, and stable performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering strategy is entirely dependent on the desired outcome for the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and material purity for a critical application: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) or Vacuum Sintering are the leading choices.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard metal components: Conventional Solid-State or Liquid Phase Sintering provides a reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing of small, advanced ceramic parts: Microwave Sintering is a strong candidate, provided the material is compatible and production volume is low.
- If your primary focus is creating a novel material through a chemical change during heating: Reactive Sintering is the specific technique designed for this purpose.
Ultimately, sintering empowers engineers to build materials from the ground up, achieving properties tailored precisely to the task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State | Basic, cost-effective | Standard metal parts |
| Liquid Phase | Faster densification | Complex alloys |
| Hot Isostatic (HIP) | Near 100% density | Critical, high-performance parts |
| Microwave | Rapid, energy-efficient | Small, advanced ceramics |
| Spark Plasma (SPS) | Fast, low-temperature | Novel materials & composites |
Ready to engineer superior components with precision sintering? The right sintering furnace is critical to achieving the desired density, strength, and performance in your metal or ceramic parts. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert consultation needed to optimize your sintering process. Whether you're developing medical implants, automotive gears, or advanced ceramics, our solutions help you control porosity, enhance material properties, and scale your production efficiently. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific sintering challenges and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Crucible for Phosphorous Powder Sintered
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Sheet
People Also Ask
- How much heat do you need to braze? Master the Brazing Temperature Window for Strong Joints
- Why is Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) preferred for ODS iron-based alloys? Achieve 95% Density and Fine-Grained Strength
- How does HIP furnace post-treatment improve fluoride ceramic optical quality? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density
- Can you vacuum cast metal? Achieve Superior Quality and Detail in Your Castings
- What is the purpose of the sintering process? Transform Powder into High-Performance Solid Parts
- What are the various types of quenching media? A Guide to Water, Oil, Air, and More
- Why can't conduction occur in a vacuum? The Essential Role of Particles in Heat Transfer
- Why is vacuum created in the chamber before thermal evaporation? For High-Quality, Uniform Thin Films



















