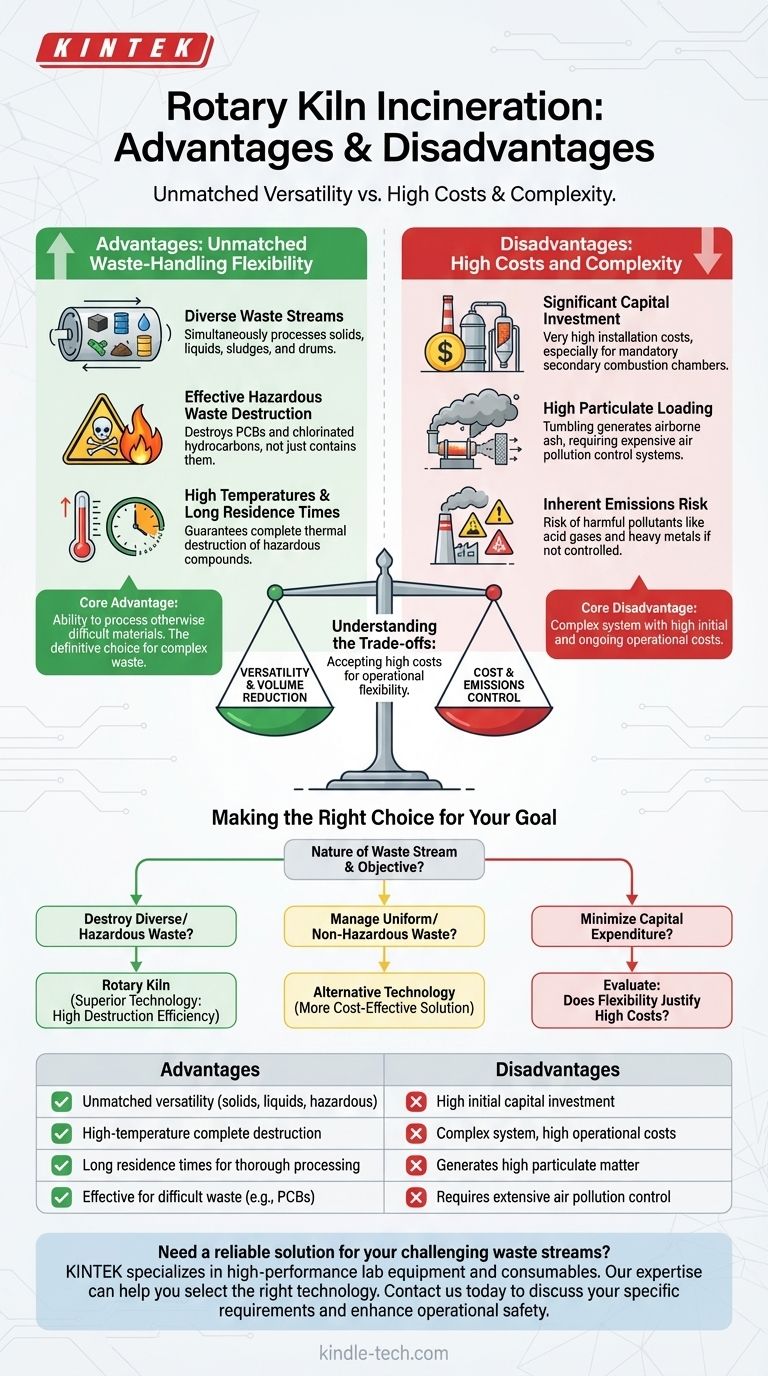
The primary advantage of a rotary kiln incinerator is its unparalleled versatility, allowing it to safely destroy a vast range of solid, liquid, and hazardous wastes that other systems cannot handle. However, this flexibility comes at a significant cost, both in the high initial capital investment for secondary combustion chambers and in managing the high levels of particulate matter it generates.
A rotary kiln is the definitive choice for treating complex, mixed, or hazardous waste streams due to its high-temperature operation and long residence times. The core trade-off is accepting high initial costs and complex operational requirements in exchange for this unmatched operational flexibility.
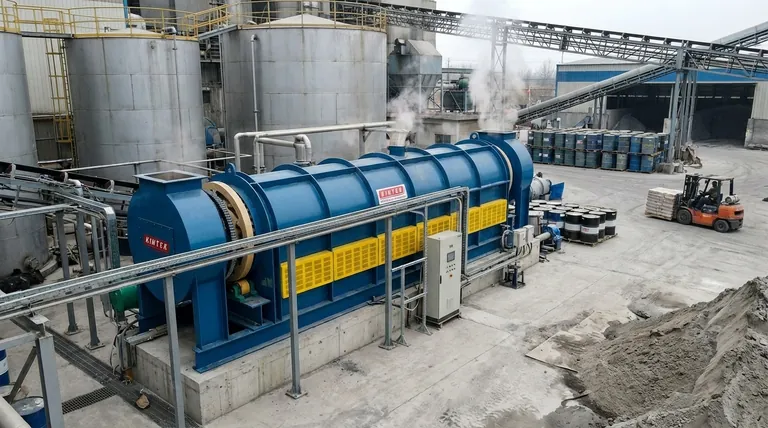

The Core Advantage: Unmatched Waste-Handling Flexibility
A rotary kiln's primary strength lies in its ability to process materials that are otherwise difficult to manage. Its design makes it the preferred technology for the most demanding disposal tasks.
Processing Diverse Waste Streams
The kiln's rotating, cylindrical design constantly tumbles the waste material. This action allows it to simultaneously process solids, liquids, sludges, gases, and even entire drums of waste, making it exceptionally adaptable.
Effective Hazardous Waste Destruction
This technology is increasingly used for the disposal of dangerous materials like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and other chlorinated hydrocarbons. The system's design ensures these materials are destroyed, not just contained.
High Temperatures and Long Residence Times
Rotary kilns operate at very high temperatures and keep waste inside for an extended period. These two factors—high temperature and long residence time—are critical for guaranteeing the complete thermal destruction of hazardous compounds.
The Principal Disadvantage: High Costs and Complexity
The versatility of a rotary kiln incinerator is enabled by a complex and expensive system. These operational realities represent its main drawbacks.
Significant Capital Investment
Rotary kiln systems have very high installation costs. A large portion of this expense is for the mandatory secondary combustion chamber (or afterburner) needed to ensure complete combustion and destruction of pollutants.
High Particulate Loading
The tumbling action that makes the kiln so effective at mixing also generates a large amount of airborne ash and particulate matter. This requires extensive and costly downstream air pollution control systems to capture these particles before they are released.
Inherent Emissions Risk
Like all incineration technologies, rotary kilns convert solid or liquid waste into gaseous emissions. If not properly controlled, these can include harmful pollutants like acid gases and heavy metals, posing a risk to the environment and human health.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a rotary kiln involves a clear set of compromises. Understanding these is essential for making an informed decision.
Versatility vs. Cost
The central trade-off is straightforward: you gain the ability to process nearly any waste stream, but you pay a significant premium for that capability in both upfront and operational costs.
Volume Reduction vs. Emissions Control
The kiln excels at reducing the physical volume of waste, which is a major benefit for landfills. However, it achieves this by converting that waste into gas, which then requires a complex and expensive flue gas treatment system to manage.
Energy Generation vs. Pollutant Risk
While the heat from incineration can be recovered to generate energy, this benefit is always paired with the operational responsibility of managing toxic emissions. Any failure in the pollution control system can turn a benefit into a liability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use a rotary kiln should be based entirely on the nature of your waste stream and your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is destroying diverse or hazardous waste streams: The rotary kiln is the superior technology due to its robust processing capabilities and high destruction efficiency.
- If your primary focus is managing a uniform, non-hazardous waste stream: A less complex and less expensive incineration technology may be a more cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is minimizing capital expenditure: You must carefully evaluate whether the operational flexibility of a rotary kiln justifies its significantly higher initial and ongoing costs.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary kiln is an investment in operational flexibility for the most challenging waste management scenarios.
Summary Table:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Unmatched versatility for solids, liquids, and hazardous waste | High initial capital investment |
| High-temperature operation ensures complete destruction | Complex system with high operational costs |
| Long residence times for thorough processing | Generates high levels of particulate matter |
| Effective for diverse and difficult waste streams (e.g., PCBs) | Requires extensive air pollution control systems |
Need a reliable solution for your challenging waste streams? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise can help you select the right technology for efficient and safe waste destruction. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and enhance your operational safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing



















