At its core, brazing creates exceptionally strong and clean joints by using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the parts being joined. This fundamental difference from welding allows it to join dissimilar materials and complex assemblies with minimal distortion. The most advanced form, vacuum brazing, elevates these benefits by performing the process in a contaminant-free environment, resulting in the highest possible joint integrity.
Brazing's primary advantage is its ability to join materials without melting them, which preserves their properties and reduces stress. Vacuum brazing, in particular, offers unparalleled cleanliness and strength by eliminating oxides and the need for corrosive flux, making it a superior choice for complex, high-performance applications.

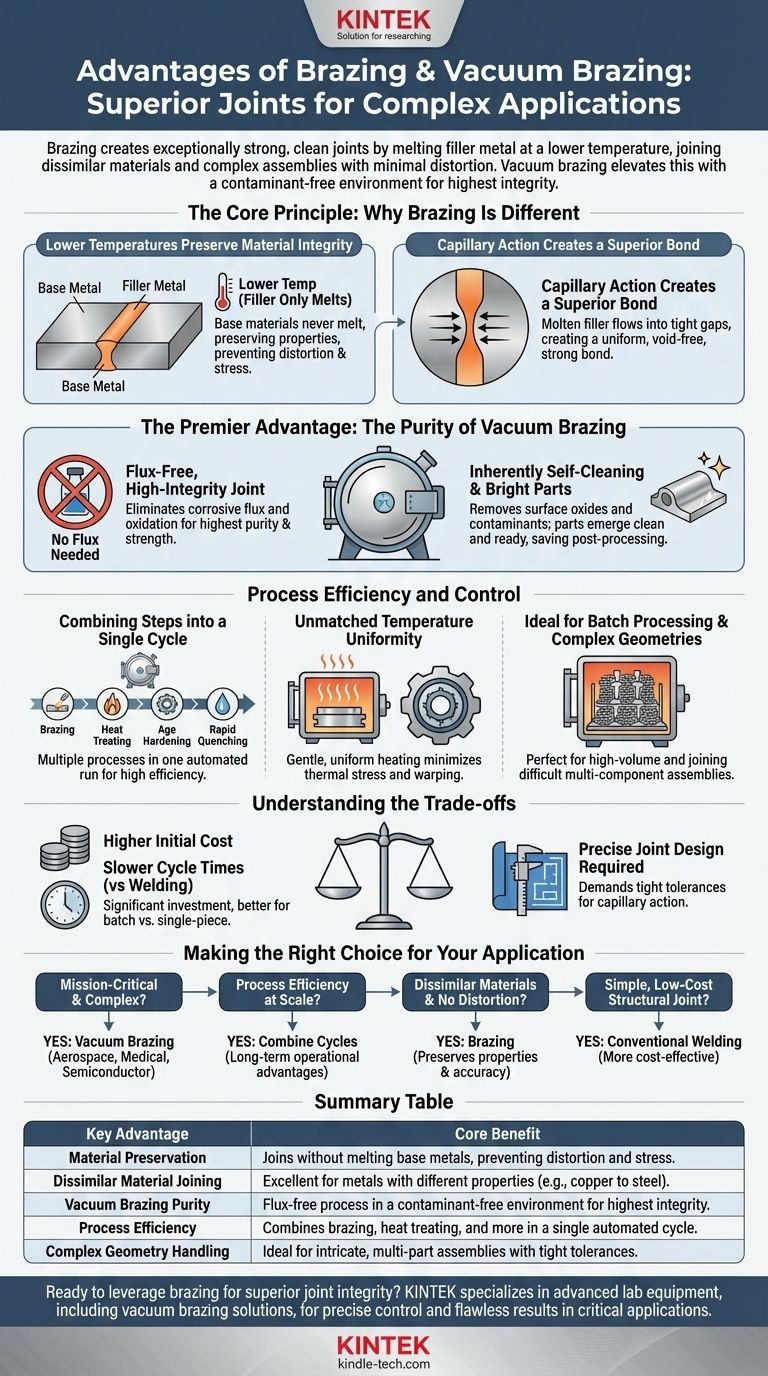
The Core Principle: Why Brazing Is Different
Brazing is a joining process defined by a few key characteristics that set it apart from methods like welding or soldering. Understanding these principles is key to appreciating its advantages.
Lower Temperatures Preserve Material Integrity
The filler metal used in brazing has a melting point that is significantly lower than the base materials being joined.
Because the base materials never melt, their fundamental metallurgical properties remain largely unchanged. This prevents the heat-affected zones, distortion, and residual stress commonly associated with welding.
Capillary Action Creates a Superior Bond
During brazing, the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting gap between the parts through a phenomenon called capillary action.
This ensures the entire joint is completely and uniformly filled, creating a strong, void-free bond that distributes stress evenly.
Joining Dissimilar Materials with Ease
Since the base metals are not melted together, brazing is an excellent method for joining materials with vastly different properties and melting points, such as copper to steel or ceramic to metal.
The Premier Advantage: The Purity of Vacuum Brazing
While all brazing offers benefits, vacuum brazing represents the pinnacle of the technology. The process takes place inside a furnace from which all air has been removed, providing unique and powerful advantages.
Creating a Flux-Free, High-Integrity Joint
Traditional brazing requires a chemical "flux" to clean the metals and prevent oxidation. This flux can become trapped in the joint, leading to corrosion and potential failure points.
Vacuum brazing is a flux-free process. The vacuum itself prevents oxidation and removes contaminants, resulting in joints of the highest possible purity, strength, and integrity.
An Inherently Self-Cleaning Process
The combination of heat and vacuum works to remove surface oxides and vaporize oils or other contaminants on the parts.
This self-cleaning action ensures the filler metal can wet and bond directly to pristine base material, creating a stronger metallurgical bond.
Exceptionally Clean and Bright Finished Parts
Parts emerge from a vacuum furnace bright, shiny, and free of discoloration or residue.
This often eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming post-processing cleaning steps, saving both time and money.
Process Efficiency and Control
Beyond joint quality, vacuum brazing provides significant advantages in process control and manufacturing efficiency, especially for high-volume or complex production.
Combining Steps into a Single Cycle
A vacuum furnace allows for precise thermal management. This means multiple processes can be combined into one automated cycle.
It's common to perform brazing, heat treating, age hardening, and even rapid quenching in a single furnace run, dramatically improving efficiency and reducing part handling.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
Heating within a vacuum furnace is slow, gentle, and incredibly uniform. This ensures the entire assembly, no matter how complex, reaches the target temperature at the same time.
This uniformity minimizes thermal stress, prevents warping, and allows for the joining of parts with tight dimensional tolerances.
Ideal for Batch Processing and Complex Geometries
The controlled environment of a furnace is perfect for processing many parts at once (batch processing). It's also uniquely suited for joining intricate, multi-component assemblies that would be difficult or impossible to join with other methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every situation. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the limitations.
Higher Initial Equipment Cost
Vacuum brazing furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to standard welding equipment. This cost is typically justified for high-volume or mission-critical applications.
Potentially Slower Cycle Times
While combining processes is efficient, the heating and cooling cycles within a furnace can take longer than joining a single part with a welding torch. Its speed advantage lies in batch processing, not single-piece work.
Requirement for Precise Joint Design
Brazing relies on capillary action, which requires a specific, narrow gap between the parts (typically 0.001" to 0.005"). This demands greater precision in part manufacturing compared to some welding processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if brazing is the optimal solution for your goal.
- If your primary focus is joining mission-critical, complex assemblies: Vacuum brazing is unparalleled for its cleanliness, strength, and ability to hold tight tolerances, making it ideal for aerospace, medical, and semiconductor parts.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency at scale: The ability to combine brazing and heat treatment in a single cycle for large batches can offer significant long-term operational advantages.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials without distortion: Brazing's lower-temperature process is superior to welding for preserving the base materials' properties and maintaining dimensional accuracy.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost structural joint: A conventional method like welding may be more cost-effective, as the advanced benefits of vacuum brazing would be unnecessary.
By understanding its core principles, you can leverage brazing to achieve superior joining results that are often impossible with other methods.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Core Benefit |
|---|---|
| Material Preservation | Joins without melting base metals, preventing distortion and stress. |
| Dissimilar Material Joining | Excellent for metals with different properties (e.g., copper to steel). |
| Vacuum Brazing Purity | Flux-free process in a contaminant-free environment for highest integrity. |
| Process Efficiency | Combines brazing, heat treating, and more in a single automated cycle. |
| Complex Geometry Handling | Ideal for intricate, multi-part assemblies with tight tolerances. |
Ready to leverage brazing for superior joint integrity in your lab or production line? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including vacuum brazing solutions, to help you achieve flawless, high-strength joins for complex assemblies in aerospace, medical, and semiconductor applications. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for precise temperature control, batch processing efficiency, and contaminant-free results. Contact us today to discuss how our brazing solutions can enhance your manufacturing process and deliver the reliability your critical applications demand!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















