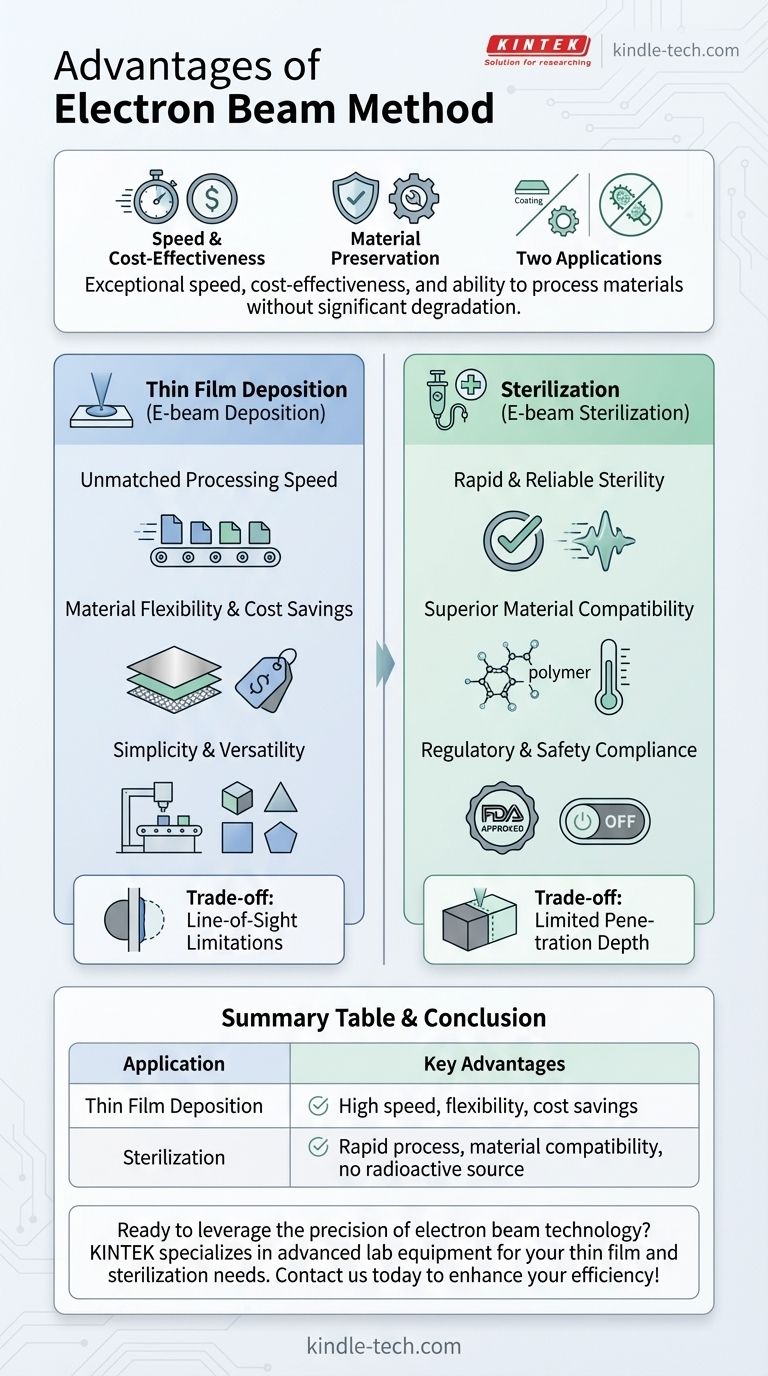
In short, the primary advantages of the electron beam method are its exceptional speed, cost-effectiveness, and ability to process materials without significant degradation. This makes it a highly valuable technology in two distinct fields: creating thin film coatings for industries like optics and electronics, and rapidly sterilizing sensitive products, particularly in the medical device sector.
The core value of electron beam technology is its precision and efficiency. It delivers highly controlled energy for a specific task—be it depositing a molecular layer or sterilizing a device—at a rate that is often faster and less damaging to the underlying material than competing methods.
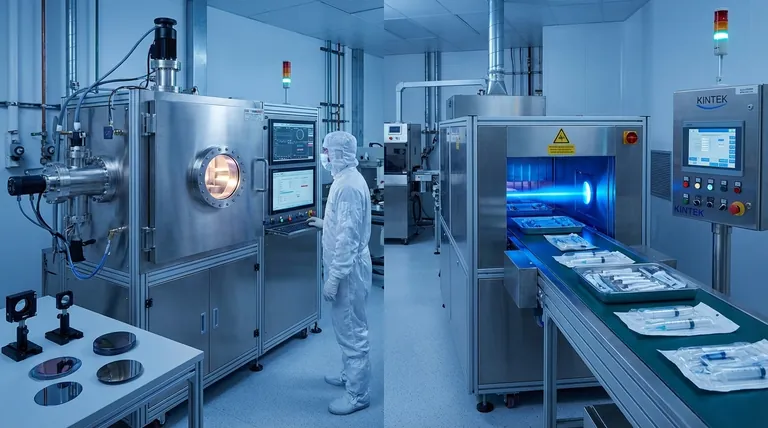

A Tale of Two Applications: Coating and Sterilization
The term "electron beam method" refers to using a focused beam of electrons to achieve a goal. Its advantages are best understood by looking at its two most prominent commercial applications: thin film deposition and product sterilization.
While both use the same fundamental physics, the benefits they deliver are tailored to solve very different industrial problems.
Key Advantages in Thin Film Deposition
When used to create ultra-thin coatings on a surface (a process known as E-beam deposition), the method excels in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Unmatched Processing Speed
E-beam deposition is known for its rapid processing times, especially in batch scenarios.
This high throughput makes it ideal for commercial applications where speed and volume are critical, often outperforming alternatives like magnetron sputtering.
Material Flexibility and Cost Savings
This method is compatible with a wider array of evaporative materials compared to other techniques.
Crucially, these materials are often less expensive than the specialized "targets" required for magnetron sputtering, leading to significant cost reductions in production.
Simplicity and Versatility
The process is noted for its relative simplicity and flexibility.
This is particularly beneficial when applying polymeric coatings, allowing for straightforward and adaptable manufacturing setups.
The Gold Standard for Sterilization
When used for sterilization, a high-energy electron beam inactivates microorganisms on a product, a process trusted by the medical device and pharmaceutical industries.
Rapid and Reliable Sterility
The process delivers a high dose of energy very quickly, ensuring a high Sterility Assurance Level (SAL).
This speed means products can be processed and released for shipment almost immediately, eliminating the long quarantine periods required by gas-based sterilization methods.
Superior Material Compatibility
E-beam allows for precise temperature control during irradiation.
This is critical for protecting the integrity of modern polymers and other sensitive materials, preventing the degradation that can occur with methods like high-heat or gamma irradiation.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
The electron beam sterilization process is internationally accepted and FDA-approved.
A major advantage over gamma sterilization is that it does not use a localized radioactive source (like Cobalt-60). The system can be simply switched off, enhancing operational safety and minimizing environmental impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging the limitations inherent in any method.
Line-of-Sight Limitations (Deposition)
E-beam deposition is a "line-of-sight" process. The material evaporates from the source and travels in a straight line to the substrate.
This can make it challenging to achieve a uniform coating on objects with complex, three-dimensional shapes without sophisticated rotation and manipulation.
Limited Penetration Depth (Sterilization)
While E-beam can penetrate packaging foils, its overall penetration depth is less than that of gamma rays.
This makes it unsuitable for sterilizing very large, dense, or heavily loaded products, which are better served by the deep-penetrating power of gamma irradiation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if the electron beam method is correct for you, anchor your decision in your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of thin films: E-beam deposition offers an excellent combination of speed, material flexibility, and lower operational costs.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive medical devices: E-beam sterilization provides a fast, FDA-approved method that preserves material integrity without the complexities of radioactive sources.
- If your primary focus is treating products with complex shapes or high density: You must carefully evaluate whether the line-of-sight and penetration depth limitations of the electron beam align with your product's specific geometry and composition.
Ultimately, electron beam technology offers a powerful solution when your goal requires speed, precision, and material compatibility.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Advantages | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Thin Film Deposition | High processing speed, material flexibility, cost savings | Optics, electronics, high-volume manufacturing |
| Sterilization | Rapid process, superior material compatibility, no radioactive source | Medical devices, pharmaceuticals, heat-sensitive products |
Ready to leverage the precision of electron beam technology? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable solutions your laboratory needs for thin film deposition and sterilization processes. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Vacuum Cold Mounting Machine for Sample Preparation
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass
















