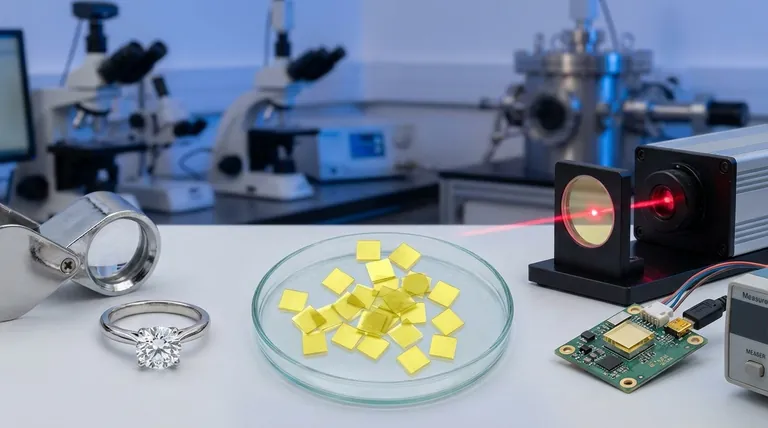
At their core, CVD diamonds have two primary domains of application: fine jewelry and advanced industrial/scientific tools. This is because the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process creates diamonds that are chemically and physically identical to their natural counterparts, but with a degree of control that allows their properties to be tailored for specific purposes, from aesthetic brilliance to extreme technical performance.
The key insight is not just that CVD diamonds are used for jewelry and industry, but why. Their value lies in being a fully engineered material, allowing us to leverage the supreme properties of diamond for either aesthetic perfection or specific high-performance tasks.
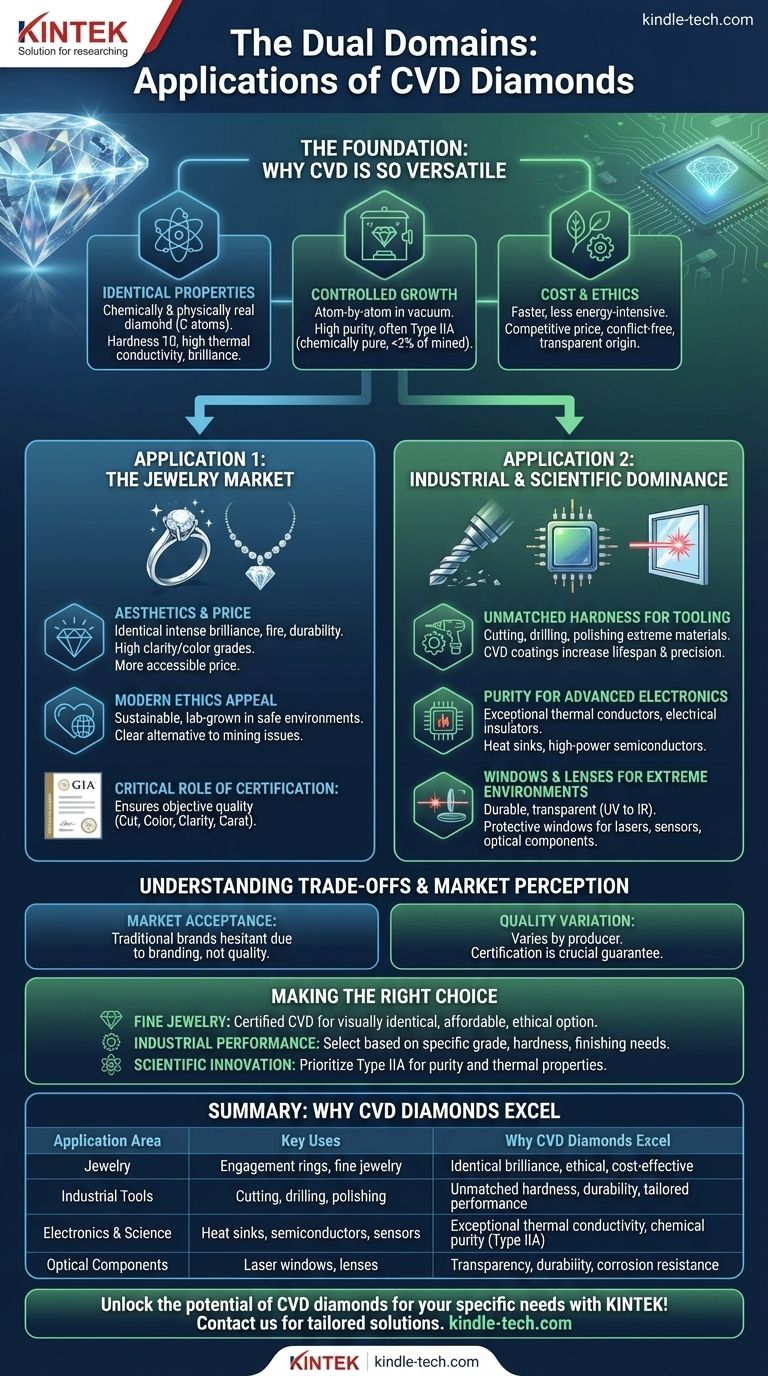
The Foundation: Why CVD Is So Versatile
To understand its applications, you must first understand why the CVD method is so effective. It produces a material that is not a substitute for diamond, but is diamond in its purest form.
Identical Chemical and Physical Properties
CVD diamonds are real diamonds. They are composed of carbon atoms arranged in the same crystal lattice structure as mined diamonds.
This gives them the same essential properties, including a hardness of 10 on the Mohs scale, exceptional thermal conductivity, and the signature brilliance and sparkle sought after in jewelry. They are not simulants like cubic zirconia; they are physically and chemically the same substance.
A Controlled Growth Process
The CVD process involves growing diamond crystals atom-by-atom in a vacuum chamber. This controlled environment allows manufacturers to create diamonds with remarkable purity.
Many CVD diamonds are Type IIA, a category that includes only 2% of mined diamonds. This means they are chemically pure, lacking the nitrogen or boron impurities that can affect color and performance, making them ideal for specialized technical applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Ethics
Compared to the geological processes that form natural diamonds over billions of years, the CVD process is significantly faster and less energy-intensive than mining.
This results in a more competitive price point and sidesteps the ethical concerns associated with diamond mining, offering a product that is both affordable and verifiably conflict-free.
Application 1: The Jewelry Market
The most visible application for CVD diamonds is in fine jewelry, where they compete directly with mined diamonds on the most important metrics.
Aesthetics and Price
Because they are real diamonds, CVD diamonds exhibit the same intense brilliance, fire, and durability that consumers expect. The ability to control the growth process often results in diamonds with very high clarity and color grades.
Combined with their more accessible price, this makes them a compelling value proposition for engagement rings, necklaces, and other fine jewelry.
The Appeal of Modern Ethics
A growing segment of the market prioritizes sustainability and ethical sourcing. CVD diamonds are created in safe, controlled laboratory environments.
This transparent origin provides a clear alternative to the environmental and humanitarian issues historically tied to the diamond mining industry.
Application 2: Industrial and Scientific Dominance
While jewelry is the most public-facing application, the unique properties of CVD diamonds make them a critical material in high-technology and industrial sectors.
Unmatched Hardness for Tooling
Diamond is the hardest known material, and CVD technology makes it available for a range of industrial tools. These are used for tasks where nothing else can survive.
Applications include cutting, drilling, and polishing extremely hard materials. CVD diamond coatings on machine tools dramatically increase their lifespan and precision, with specific grades engineered for "roughing" (rapid material removal) or "finishing" (creating a perfectly smooth surface).
Purity for Advanced Electronics
The chemical purity of Type IIA CVD diamonds makes them exceptional thermal conductors and electrical insulators. This unique combination is crucial for next-generation electronics.
They are used as heat sinks to draw damaging heat away from sensitive processors and in the development of high-power semiconductors that can operate at frequencies and temperatures far beyond the limits of silicon.
Windows and Lenses for Extreme Environments
Because CVD diamonds are both incredibly durable and transparent to a wide spectrum of light (from UV to infrared), they are used as protective windows and lenses in harsh settings.
This includes windows for high-power industrial lasers, sensors exposed to corrosive chemicals, and optical components for scientific research equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Market Perception
While technically equivalent, CVD diamonds face unique challenges in the market that are important to understand.
Market Acceptance and Branding
The jewelry industry is built on tradition, and some renowned luxury brands have been hesitant to adopt lab-grown diamonds. This is largely a matter of branding and market positioning rather than a reflection on the quality of the material itself.
The Critical Role of Certification
Initially, the lab-grown market had few regulations. Today, however, high-quality CVD diamonds are readily available with grading reports from the same independent gemological labs that certify mined diamonds, such as the GIA (Gemological Institute of America) and IGI.
This independent certification is not a "con" but an essential tool for any buyer, as it provides an objective assessment of a diamond's quality (its cut, color, clarity, and carat weight) regardless of its origin.
Quality Varies by Producer
As with any manufacturing process, the quality of CVD diamonds can vary between producers. This variability makes it even more crucial to insist on a reputable certification. The report is your guarantee that you are getting the quality you are paying for.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of diamond should be driven by your specific goal, as CVD technology has broadened the possibilities.
- If your primary focus is acquiring fine jewelry: Seek a certified CVD diamond for a visually identical, more affordable, and ethically sourced alternative to a mined diamond.
- If your primary focus is industrial performance: Select a CVD diamond tool based on its specific grade, hardness, and finishing properties required for your cutting or polishing application.
- If your primary focus is scientific or electronic innovation: Prioritize Type IIA CVD diamonds for their exceptional chemical purity and thermal properties, which are critical for high-performance sensors and semiconductors.
Ultimately, understanding the application begins with recognizing that CVD technology allows us to treat diamond not just as a gemstone, but as a high-performance engineered material.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Why CVD Diamonds Excel |
|---|---|---|
| Jewelry | Engagement rings, necklaces, fine jewelry | Identical brilliance, ethical sourcing, cost-effectiveness |
| Industrial Tools | Cutting, drilling, polishing hard materials | Unmatched hardness, durability, tailored performance |
| Electronics & Science | Heat sinks, high-power semiconductors, sensors | Exceptional thermal conductivity, chemical purity (Type IIA) |
| Optical Components | Laser windows, lenses for extreme environments | Transparency (UV to IR), durability, resistance to corrosion |
Unlock the potential of CVD diamonds for your specific needs with KINTEK! Whether you're crafting exquisite jewelry or developing cutting-edge industrial tools, our high-purity lab-grown diamonds offer unmatched performance, ethical sourcing, and cost efficiency. As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides tailored solutions to meet your precision requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our CVD diamond products can enhance your projects and drive innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What pressure is needed for chemical vapor deposition of diamonds? Master the Low-Pressure 'Sweet Spot'
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What's the difference between CVD and HPHT? Choosing the Right Lab-Grown Diamond Method
- Why is Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MW-PCVD) preferred for BDD? Achieve Ultra-Pure Diamond Synthesis
- Why is MW-CVD preferred for high-purity diamond optical windows? Achieve Zero-Contamination Material Growth
- What are 5 negative impacts of diamond mines on the environment? The Hidden Environmental Cost of Diamond Mining
- What is the temperature of a plasma reactor? Harnessing Stellar Power on Earth
- What is the process of chemical vapor deposition diamond? Grow High-Purity, Engineered Diamonds from Gas


















