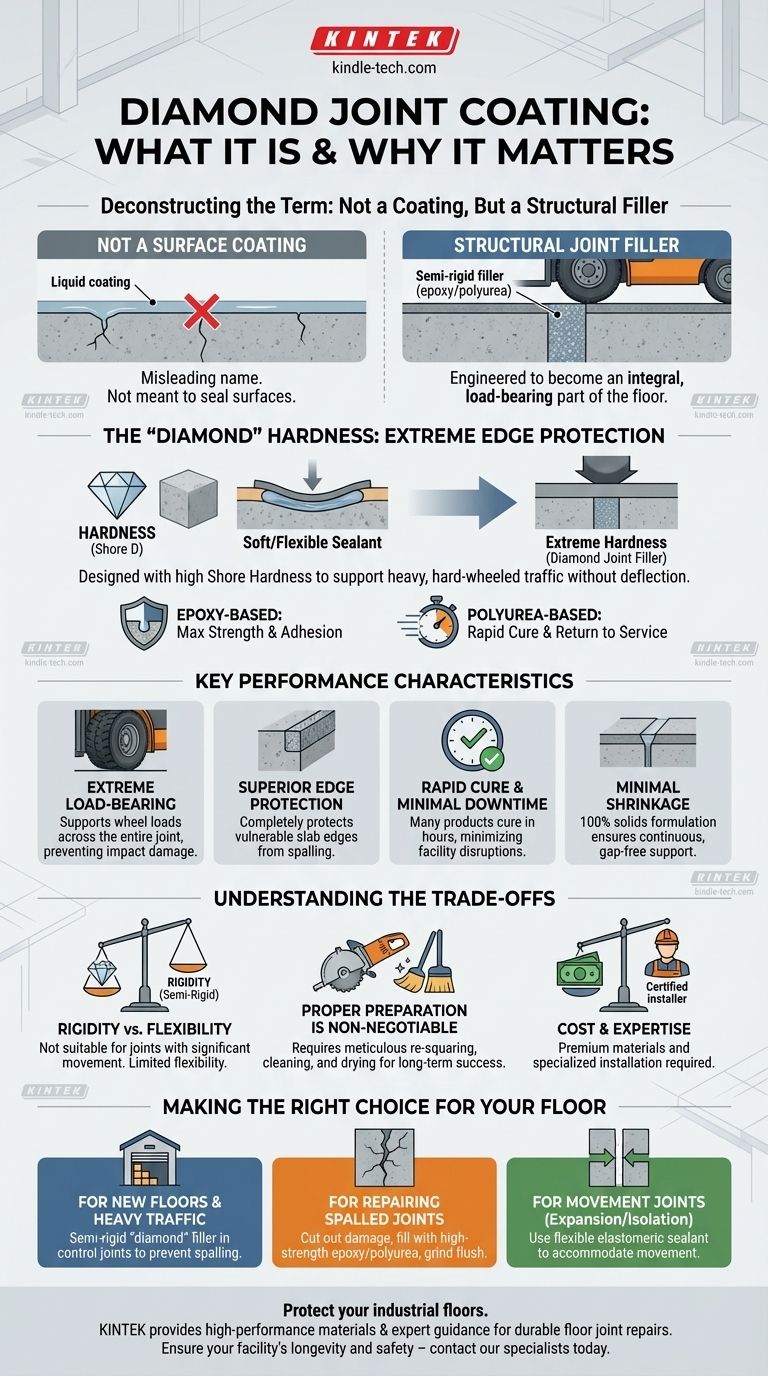
To be precise, "diamond joint coating" is a marketing term rather than a standard industry classification. It typically refers to a high-performance, semi-rigid joint filler, usually epoxy or polyurea-based, that is engineered for extreme hardness and durability. Its defining characteristic is its ability to protect the vulnerable edges of control joints in concrete floors from damage caused by heavy, hard-wheeled traffic.
The core concept to understand is that these are not "coatings" in the traditional sense, but rather structural fillers designed to become an integral, load-bearing part of the floor. Their primary purpose is to eliminate joint spalling by providing uncompromising edge support, prioritizing hardness over flexibility.

Deconstructing "Diamond Joint Coating"
While the name is evocative, the material itself is a blend of specific chemical compounds and aggregates designed for a singular purpose: reinforcing concrete joints from within.
Not a Coating, But a Structural Filler
The term "coating" is misleading. This material does not coat the surface of the floor. Instead, it is poured into a prepared control joint or a cracked area, filling it completely from the bottom up.
Once cured, it becomes a solid, structural component. Its function is to transfer loads from forklift wheels smoothly across the joint, preventing the concrete edges from chipping and breaking down—a failure known as joint spalling.
The "Diamond" Hardness
The "diamond" in the name alludes to the material's extreme hardness. This is achieved by formulating the filler with a very high Shore Hardness (often D-scale), making it nearly as hard as the surrounding concrete.
This hardness is essential for supporting traffic without deflecting. A soft, flexible sealant would simply compress under a wheel, leaving the concrete edge exposed to impact and eventual fracture. These systems often include hard aggregate materials like quartz to increase compressive strength.
The Binder: Epoxy vs. Polyurea
The strength comes from a polymer binder, most commonly an advanced epoxy or polyurea.
- Epoxy-based fillers are known for their incredible compressive strength and adhesive bond to concrete. They form a rigid, unyielding filler that provides maximum edge protection.
- Polyurea-based fillers offer a faster cure time, allowing for a quicker return to service. While still very hard, they can be formulated to have slightly more flexibility than epoxies, though they are still considered semi-rigid.
Key Performance Characteristics
These fillers are chosen for specific, demanding environments where standard sealants would fail.
Extreme Load-Bearing Capacity
Their primary characteristic is the ability to withstand extreme point loads from hard-wheeled vehicles like forklifts and pallet jacks. The filler supports the wheel across the entire joint, preventing impact.
Superior Edge Protection
By filling the joint with a material that is flush and nearly as hard as the concrete itself, the vulnerable top edges of the slab are completely protected. This is the single most effective way to prevent spalling in high-traffic areas.
Rapid Cure and Return to Service
Many products in this category, especially those based on polyurea, are designed to cure in a matter of hours. This minimizes facility downtime, a critical factor in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing plants.
Minimal Shrinkage
These materials are formulated to be 100% solids, meaning they exhibit very little to no shrinkage as they cure. This ensures the joint remains completely full, providing continuous support without separating from the concrete walls.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The extreme hardness that makes these fillers effective also introduces critical trade-offs that must be considered.
Rigidity is a Double-Edged Sword
The primary trade-off is flexibility. These are semi-rigid systems, not flexible sealants. They are designed to allow for minimal slab movement.
If installed in a joint that experiences significant thermal expansion and contraction or differential slab movement, the rigid filler may crack or separate from the joint wall. They are not suitable for isolation joints or true expansion joints.
Proper Joint Preparation is Non-Negotiable
You cannot simply pour this material into a dirty or damaged joint. For a successful, long-term repair, the joint must be meticulously prepared.
This often involves using a concrete saw to "re-square" the joint edges, creating a clean, solid shoulder for the filler to bond to. The joint must also be completely clean and dry.
Cost and Installation Expertise
These are premium, high-performance materials. The initial material cost is significantly higher than that of basic elastomeric or silicone sealants.
Furthermore, proper installation requires training and often specialized equipment. This is not a typical maintenance task; it is a specialized flooring repair. The long-term value comes from preventing costly structural repairs to the concrete slab itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Floor
Selecting the correct joint treatment depends entirely on the joint's purpose and the traffic it will endure.
- If your primary focus is protecting new floors from heavy, channelized forklift traffic: A semi-rigid "diamond" type filler installed in control joints is the definitive solution to prevent future spalling.
- If your primary focus is repairing existing, spalled control joints: The process involves cutting out all damaged concrete, filling the void with a high-strength epoxy or polyurea filler, and grinding it flush with the floor surface.
- If your primary focus is sealing joints designed for significant slab movement (expansion/isolation joints): You must use a flexible elastomeric sealant, not a rigid filler, to accommodate the movement without failing.
Ultimately, matching the filler's mechanical properties to the specific demands of the floor joint is the only way to ensure a successful, long-lasting solution.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Structural filler for concrete control joints, not a surface coating. |
| Key Property | Extreme hardness (high Shore D) for load-bearing and edge protection. |
| Common Binders | Epoxy (max strength) or Polyurea (fast cure). |
| Best For | High-traffic areas with hard-wheeled vehicles (e.g., forklifts). |
| Main Trade-off | Semi-rigid; not suitable for joints with significant movement. |
Protect your industrial floors from costly damage. Diamond joint coatings are a specialized solution for demanding environments like warehouses and manufacturing plants. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-performance materials and expert guidance needed for durable floor joint repairs. Ensure your facility's longevity and safety—contact our specialists today to discuss the right solution for your concrete joints.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance












