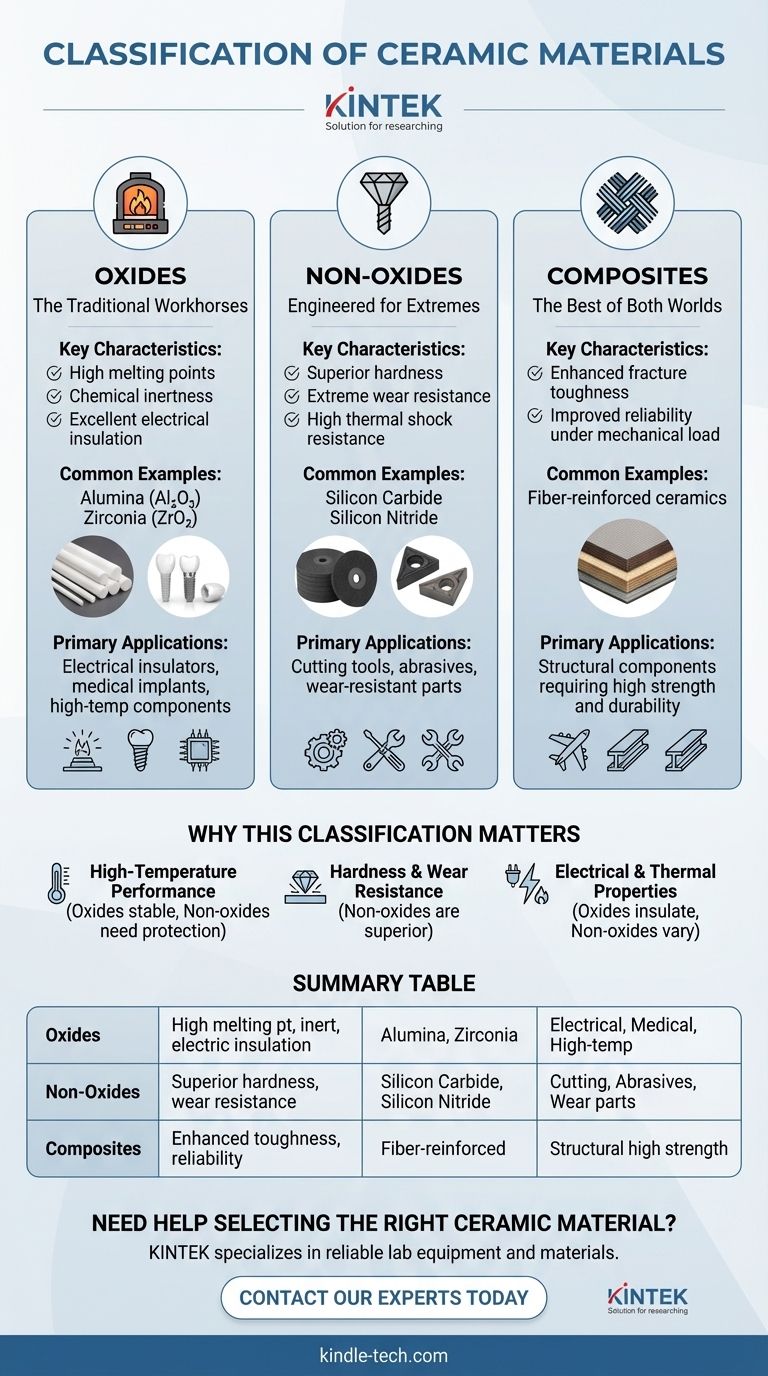
At their core, ceramic materials are classified into three distinct categories based on their chemical composition. These groups are oxides, such as alumina and zirconia; non-oxides, which include carbides, borides, and nitrides; and composite materials, which are engineered combinations of the other types.
The classification of a ceramic is not an academic exercise; it is a direct indicator of its fundamental properties. Understanding whether a ceramic is an oxide, non-oxide, or composite tells you how it will behave under extreme heat, mechanical stress, and chemical attack.

Deconstructing the Ceramic Families
The chemical makeup of a ceramic dictates its atomic structure and bonding, which in turn defines its performance characteristics. This is why composition is the primary method of classification.
Oxides: The Traditional Workhorses
Oxide ceramics are compounds formed between at least one metal and oxygen. They are the most common and historically significant group of advanced ceramics.
Examples include alumina (aluminum oxide, Al₂O₃), a highly versatile material used in everything from spark plugs to medical implants, and zirconia (zirconium dioxide, ZrO₂), known for its exceptional strength and toughness.
These materials are generally characterized by high melting points, chemical inertness, and excellent electrical insulation.
Non-Oxides: Engineered for Extremes
Non-oxide ceramics are materials that do not contain oxygen. They are compounds like carbides (silicon carbide), nitrides (silicon nitride), and borides (titanium boride).
These materials are often developed for applications where oxides fall short. They typically exhibit superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal shock resistance.
Because they lack oxygen, their processing often requires high temperatures and carefully controlled, oxygen-free atmospheres, making them more specialized.
Composite Materials: The Best of Both Worlds
Ceramic composites are engineered materials that combine two or more distinct ceramic materials to achieve properties that are not possible with a single component.
This is often done to overcome the inherent brittleness of monolithic ceramics. By embedding fibers (fiber-reinforced) or particles (particulate-reinforced) of one ceramic within a matrix of another, engineers can significantly improve fracture toughness and reliability.
Why This Classification Matters
Choosing the right ceramic requires matching its inherent properties—which are dictated by its classification—to the demands of the application.
High-Temperature Performance
Oxides like alumina are very stable in oxygen-rich environments, even at high temperatures. Non-oxides, while often having higher melting points, can be susceptible to oxidation if not protected.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
Non-oxide ceramics, particularly silicon carbide and boron nitride, are among the hardest materials known. This makes them the definitive choice for cutting tools, abrasive media, and wear-resistant coatings.
Electrical and Thermal Properties
Most oxides are superb electrical insulators, a property leveraged in countless electronic components. Conversely, some non-oxides, like certain carbides, can be electrically conductive. Their thermal properties also vary widely, from insulating to highly conductive.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The classification helps clarify the inherent compromises you must consider when selecting a ceramic.
Brittleness: The Universal Challenge
A defining characteristic of most traditional ceramics, both oxide and non-oxide, is their low fracture toughness, or brittleness. They fail catastrophically under tension rather than deforming like a metal.
This is the primary driver for developing ceramic matrix composites (CMCs), which are specifically designed to absorb fracture energy and fail in a more controlled, less catastrophic manner.
Processing and Cost
Generally, oxide ceramics are less expensive and easier to produce than their non-oxide counterparts. The high temperatures and controlled atmospheres needed to process non-oxides and composites add significant complexity and cost to manufacturing.
Selecting the Right Ceramic for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the primary performance demand of your project.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose high-temperature stability and electrical insulation: Oxide ceramics like alumina or zirconia are the most reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness, cutting, or wear resistance: Non-oxide ceramics such as silicon carbide or boron nitride are the superior option.
- If your primary focus is overcoming brittleness for structural reliability under load: Ceramic composite materials are specifically engineered to provide enhanced fracture toughness.
Understanding these foundational categories empowers you to select a material based on its fundamental nature, ensuring it is perfectly matched to the challenge at hand.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Characteristics | Common Examples | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxides | High melting point, chemical inertness, excellent electrical insulation | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Electrical insulators, medical implants, high-temperature components |
| Non-Oxides | Superior hardness, extreme wear resistance, high thermal shock resistance | Silicon Carbide, Silicon Nitride | Cutting tools, abrasives, wear-resistant parts |
| Composites | Enhanced fracture toughness, improved reliability under mechanical load | Fiber-reinforced ceramics | Structural components requiring high strength and durability |
Need help selecting the right ceramic material for your lab application?
Understanding material classification is the first step. The next is sourcing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for your research and production processes. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and materials, serving the diverse needs of laboratories.
We can help you navigate the complexities of material selection to ensure your project's success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Sheet
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- Is there an alternative to silver caps? Discover Modern, Natural-Looking Dental Crowns
- What ceramics are sintered? The Essential Process for Creating Strong, Durable Ceramics
- What is the sintering process of advanced ceramics? Transform Powder into High-Performance Components
- What is the strength of dental ceramics? Mastering the Compressive vs. Tensile Force Balance
- What is the new technology for veneers? Discover the Digital Revolution for a Perfect Smile
- Can ceramic withstand high temperatures? Discover the Superior Materials for Extreme Heat
- How much temperature can porcelain withstand? Unlock Its True Heat Resistance & Avoid Thermal Shock



















