The primary methods for manufacturing Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) are arc discharge, laser ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While the first two are foundational techniques, CVD has become the dominant process for commercial-scale production due to its superior scalability and control.
While several methods exist to synthesize CNTs, the choice of manufacturing technique is a critical decision that dictates the material's cost, quality, and ultimate suitability for high-value applications, from batteries to advanced composites.

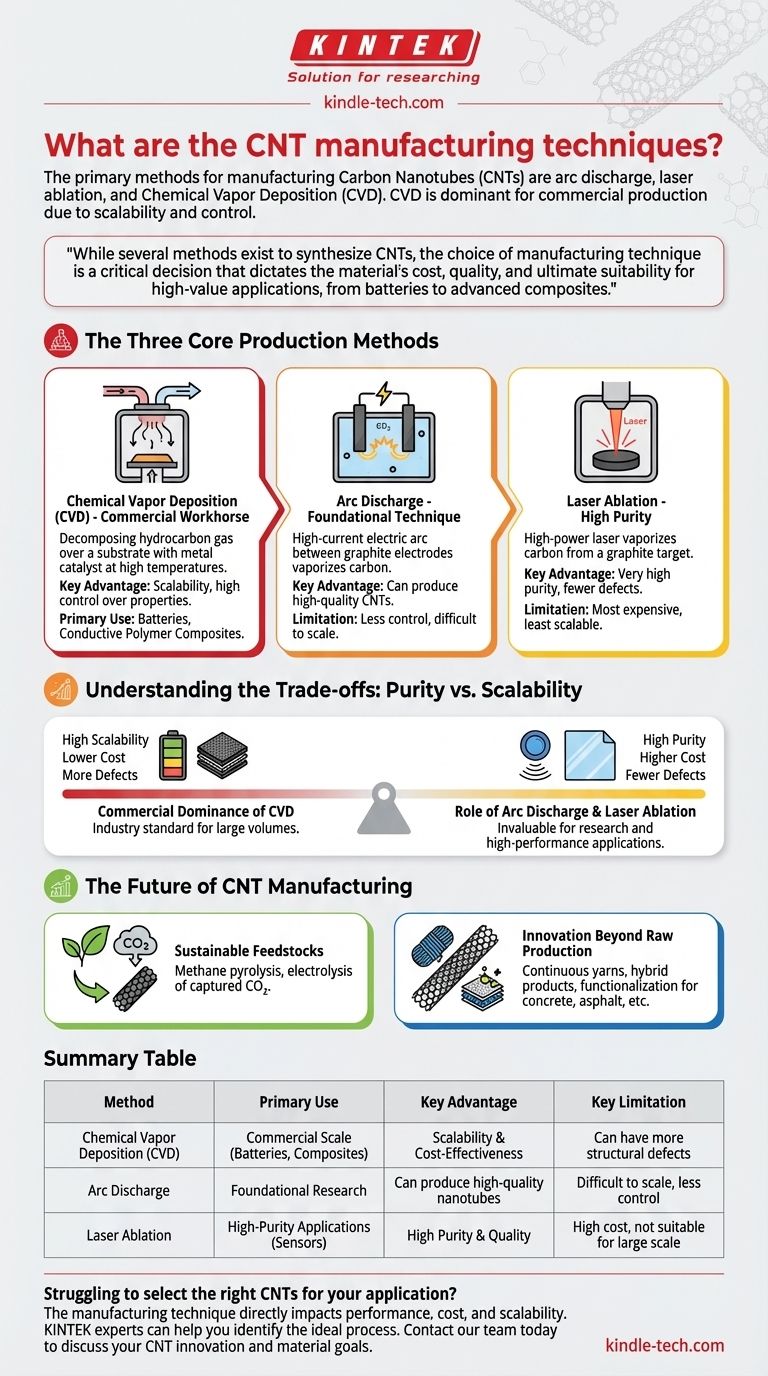
The Three Core Production Methods
Understanding the fundamental differences between the main synthesis techniques is the first step in evaluating CNTs for any project. Each method offers a distinct balance between production volume, purity, and cost.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the workhorse of the modern CNT industry. This process involves decomposing a hydrocarbon gas over a substrate coated with metal catalyst particles at high temperatures.
As the gas breaks down, carbon atoms deposit onto the catalyst particles and self-assemble into nanotube structures. The key advantage of CVD is its scalability and the relatively high degree of control it offers over the final CNT properties.
Arc Discharge
This was one of the original methods used to discover and produce CNTs. It involves creating a high-current electric arc between two graphite electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere.
The intense heat from the arc vaporizes the carbon from the positive electrode (anode), which then condenses on the cooler negative electrode (cathode), forming nanotubes. This method can produce high-quality CNTs but is often less controlled and harder to scale than CVD.
Laser Ablation
Similar to arc discharge, laser ablation uses a high-energy source to vaporize carbon. A high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target in a high-temperature reactor.
An inert gas flows through the chamber, carrying the vaporized carbon to a cooler surface where it condenses into CNTs. This technique is known for producing very high-purity nanotubes but is generally the most expensive and least scalable of the three.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Purity vs. Scalability
No single manufacturing method is universally superior; the "best" method depends entirely on the intended application. The core trade-off is almost always between the cost and scale of production versus the structural perfection of the final material.
The Commercial Dominance of CVD
For applications requiring large volumes of CNTs, such as in lithium-ion batteries and conductive polymer composites, CVD is the only viable option. Its ability to produce consistent material at an industrial scale makes it the standard for commercial products.
The Role of Arc Discharge and Laser Ablation
These methods excel in producing high-purity, often single-walled CNTs with fewer defects. This makes them invaluable for fundamental research and niche, high-performance applications like sensors or transparent conductive films, where material perfection is more critical than cost.
The Future of CNT Manufacturing
Innovation in CNT production is focused on improving both sustainability and functionality. The field is moving beyond simply making nanotubes to controlling their properties for specific, advanced applications.
Sustainable and Alternative Feedstocks
A significant area of research is the development of "green" production methods. These emerging techniques aim to use waste or renewable feedstocks, such as methane pyrolysis or the electrolysis of captured carbon dioxide in molten salts, to create CNTs more sustainably.
Innovation Beyond Raw Production
The next frontier lies in post-processing and integration. This includes developing methods for creating highly conductive continuous yarns from CNTs, forming hybrid products with other additives, and functionalizing the nanotubes to improve their integration into materials like concrete, asphalt, and fiber-reinforced composites.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct type of CNT begins with understanding how its manufacturing origin impacts its performance characteristics.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial use (e.g., batteries, composites, tires): CNTs produced via CVD are the industry standard, offering the best balance of cost-effectiveness and performance.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or high-purity electronics: CNTs from laser ablation or arc discharge may be necessary to achieve the required material quality, despite their higher cost.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and next-generation materials: Monitor emerging methods that utilize waste feedstocks like CO2, as these represent the future of environmentally conscious advanced materials.
Ultimately, understanding the manufacturing process is the key to selecting the right carbon nanotube to achieve your specific material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Commercial Scale (Batteries, Composites) | Scalability & Cost-Effectiveness | Can have more structural defects |
| Arc Discharge | Foundational Research | Can produce high-quality nanotubes | Difficult to scale, less control |
| Laser Ablation | High-Purity Applications (Sensors) | High Purity & Quality | High cost, not suitable for large scale |
Struggling to select the right CNTs for your application? The manufacturing technique directly impacts performance, cost, and scalability. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material research and development. Our experts can help you identify the ideal process for your specific needs, whether you're developing next-generation batteries, composites, or electronic devices.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your CNT innovation and material goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is CVD coating used for? Hardening Tools & Building Semiconductors for Industry
- How does a hollow-type dielectric window compare to a planar quartz window? Boost Plasma CVD Uniformity
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is chemical Vapour deposition in simple words? A Simple Guide to 'Painting' with Gas
- Is CVD a chemical process used to produce high-performance materials? Engineer Advanced Materials from the Atom Up
- How long does it take to grow a CVD diamond? A 2-4 Week Journey to a Flawless Gem
- Is temperature increasing or decreasing deposition? Mastering Rate vs. Quality for Your Application
- Why is high-speed wafer rotation necessary for vertical CVD? Master Flow Engineering for 4H-SiC Thin Films



















