In practice, heating elements are most commonly fabricated from materials like nickel-chromium alloys, refractory metals such as molybdenum and tungsten, and non-metallic compounds like graphite and silicon carbide. The selection of a specific material is dictated almost entirely by the intended operating temperature and atmospheric environment of the application.
The core principle of heating element selection is not finding a single "best" material, but rather making a strategic trade-off. You must balance the required operating temperature, the chemical environment (air vs. vacuum), and overall cost to find the optimal solution for your specific goal.
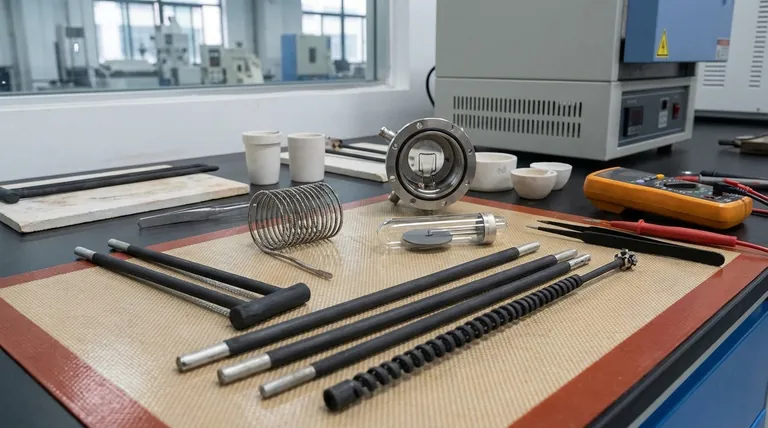

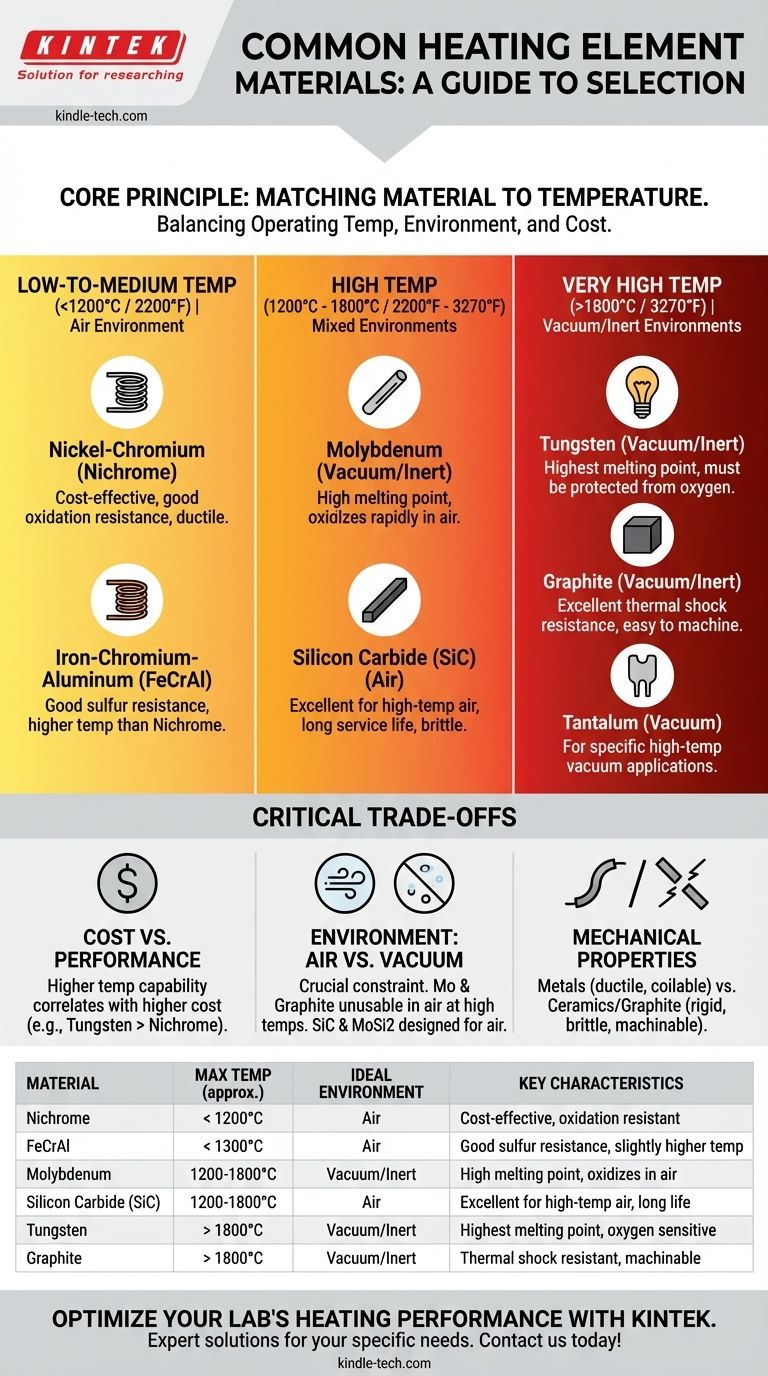
The Core Principle: Matching Material to Temperature
The single most important factor in choosing a heating element is its maximum service temperature. Materials are generally categorized by the heat range in which they can operate reliably without degrading.
Low-to-Medium Temperature Applications (<1200°C / 2200°F)
For common applications like household appliances, lab ovens, and small kilns, metallic alloys are the standard.
The most prevalent material in this range is nickel-chromium (Nichrome). It offers an excellent combination of relatively low cost, good ductility, and strong resistance to oxidation in air.
Another common choice is iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy, which can often reach slightly higher temperatures than Nichrome and has superior resistance to sulfurous atmospheres.
High-Temperature Applications (1200°C - 1800°C / 2200°F - 3270°F)
As temperatures climb, conventional alloys fail, and more specialized materials are required.
Molybdenum is a refractory metal widely used in vacuum or inert-atmosphere furnaces. It has a very high melting point but will rapidly oxidize and fail if operated in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a robust ceramic material that can be used at high temperatures in air. It is known for its structural integrity and long life, making it a workhorse for industrial furnaces and kilns.
Very High-Temperature Applications (>1800°C / 3270°F)
This realm is reserved for the most robust refractory metals and specialized non-metals, often used in vacuum environments.
Tungsten has one of the highest melting points of all metals, making it suitable for the most extreme temperature requirements, but it must be protected from oxygen.
Graphite is another excellent choice for very high-temperature vacuum or inert gas furnaces. It is easy to machine, has outstanding thermal shock resistance, and is relatively low-cost compared to refractory metals.
Tantalum is a refractory metal used for specific high-temperature vacuum applications where its unique properties are required, though it is less common than Molybdenum or Tungsten.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is never just about its temperature rating. You must consider critical trade-offs that impact cost, longevity, and furnace design.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost. Nichrome and FeCrAl alloys are inexpensive, while refractory metals like molybdenum, tungsten, and especially platinum are significantly more expensive.
Environment: Air vs. Vacuum
This is a critical design constraint. Materials like molybdenum and graphite are unusable in air at high temperatures and mandate a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere.
Conversely, materials like silicon carbide and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are designed specifically for use in air, as they form a protective glassy layer (silicon dioxide) that prevents further oxidation.
Mechanical Properties
Metallic elements like Nichrome are ductile and can be easily formed into coils. Ceramic elements like silicon carbide are much more rigid and brittle, which influences how they must be supported within a furnace. Graphite is easily machined but lacks the ductility of metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air (e.g., appliances, kilns <1200°C): Nickel-chromium (Nichrome) offers the best balance of cost, reliability, and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processing in air (e.g., ceramic firing, metal heat-treating): Silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are the superior choices for their ability to operate in oxygen-rich environments.
- If your primary focus is very high-temperature or vacuum processing (e.g., sintering, crystal growing): Molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite are the industry standards, with the specific choice depending on the precise temperature and chemical interactions involved.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element is a direct reflection of understanding your application's specific environmental and thermal demands.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Service Temp (approx.) | Ideal Environment | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) | < 1200°C | Air | Cost-effective, good oxidation resistance |
| Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) | < 1300°C | Air | Good sulfur resistance, slightly higher temp than Nichrome |
| Molybdenum | 1200°C - 1800°C | Vacuum/Inert | High melting point, oxidizes in air |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1200°C - 1800°C | Air | Excellent for high-temp air, long service life |
| Tungsten | > 1800°C | Vacuum/Inert | Highest melting point, must be protected from oxygen |
| Graphite | > 1800°C | Vacuum/Inert | Excellent thermal shock resistance, easy to machine |
Optimize Your Lab's Heating Performance with KINTEK
Selecting the right heating element is critical for the efficiency, safety, and success of your laboratory processes. Whether you need reliable heating for standard applications or extreme temperatures for specialized research, the correct material makes all the difference.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including heating elements tailored to your specific needs. We can help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, environment, and cost to ensure you get the optimal solution for your furnace or oven.
Let our experts help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact us today via our form to discuss your requirements and discover how our heating solutions can improve your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace












