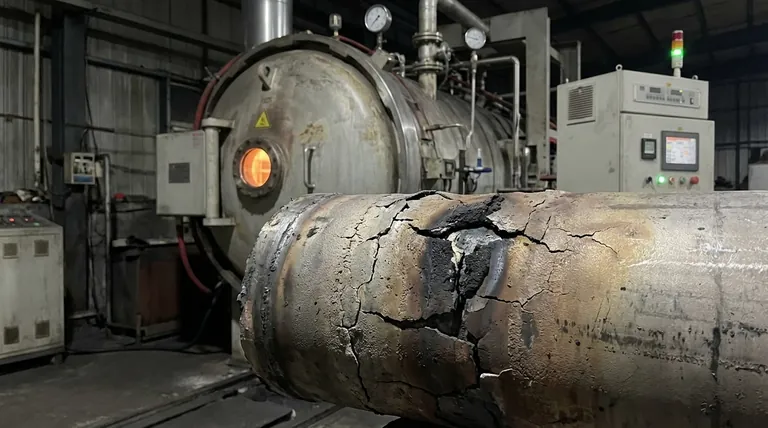
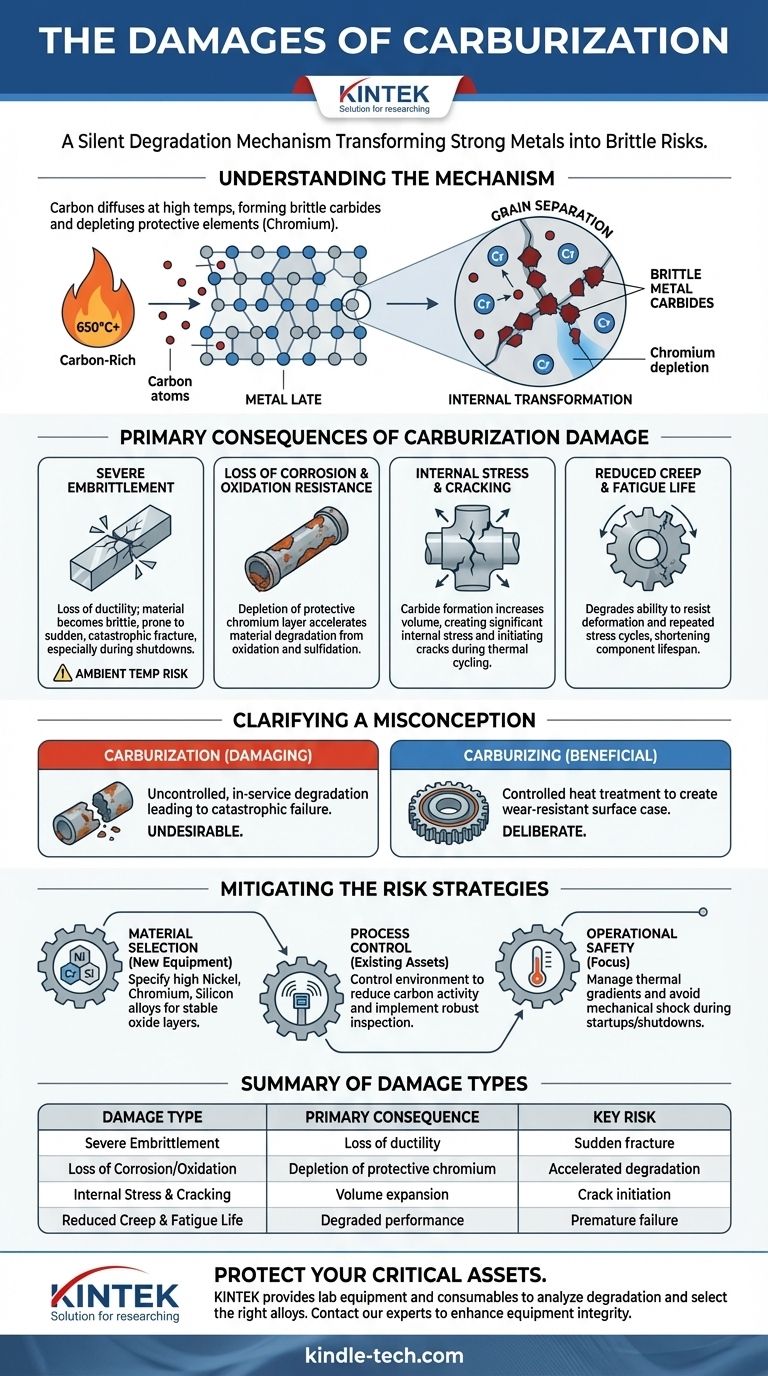
The primary damages of carburization are severe embrittlement, a catastrophic loss of corrosion and oxidation resistance, and a fundamental reduction in the material's overall structural integrity. This high-temperature degradation mechanism transforms strong, ductile metals into a brittle state, making them highly susceptible to sudden, unexpected fracture.
Carburization is a silent degradation mechanism that works from the inside out. By infusing a metal with excess carbon at high temperatures, it depletes the elements that provide strength and protection, ultimately setting the stage for catastrophic equipment failure.

How Carburization Fundamentally Changes a Metal
Carburization is a metallurgical phenomenon, not just surface corrosion. It occurs when materials, typically stainless steels and other high-temperature alloys, are exposed to a carbon-rich environment at elevated temperatures (generally above 650°C / 1200°F).
The Diffusion of Carbon
At high temperatures, the atomic structure of the metal expands, allowing small carbon atoms from the surrounding environment to diffuse directly into the material's internal grain structure.
Formation of Brittle Carbides
Once inside, the carbon reacts with key alloying elements—most notably chromium—to form hard, brittle particles called metal carbides. These carbides precipitate along the grain boundaries of the metal.
Depletion of Protective Elements
This process effectively "steals" the chromium from the base metal. Since chromium is the primary element responsible for creating the protective passive oxide layer that gives stainless steel its corrosion resistance, its depletion leaves the material vulnerable.
The Consequences of Carburization Damage
The internal changes caused by carburization manifest as severe and often dangerous forms of damage to industrial components like furnace tubes, reactor components, and ethylene cracker coils.
Severe Embrittlement
The network of hard carbides created within the metal severely reduces its ductility, which is its ability to deform under stress. The material becomes brittle, much like glass, and can fracture without any warning.
This risk is especially high at ambient temperatures, such as during a plant shutdown. A component that operated reliably at high temperature may fracture from a minor mechanical shock or thermal stress once it has cooled down.
Loss of Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
With the chromium locked away in carbides, the metal can no longer form its self-healing protective layer. This makes it highly susceptible to subsequent high-temperature oxidation and sulfidation, rapidly accelerating overall material degradation.
Internal Stress and Cracking
The formation of carbides causes a localized increase in volume. This expansion creates significant internal stress within the material, which can lead to the initiation of cracks, especially during thermal cycling (heating and cooling).
Reduced Creep and Fatigue Life
While a mildly carburized surface can sometimes exhibit increased hardness, severe carburization significantly degrades the material's ability to resist deformation under long-term stress (creep) and repeated stress cycles (fatigue).
Clarifying a Critical Misconception
It is essential to distinguish between uncontrolled degradation and a controlled manufacturing process that sounds similar. This is a common point of confusion.
Carburization vs. Carburizing
Carburization is the uncontrolled, undesirable, and damaging degradation mechanism discussed here. It happens in-service and leads to failure.
Carburizing, on the other hand, is a deliberate heat treatment process. It is used to create a hard, wear-resistant surface "case" on a component (like a gear) while leaving the core tough and ductile. This is a highly controlled and beneficial process.
Making the Right Choice to Mitigate Risk
Preventing carburization damage requires a strategy focused on both material selection and controlling the operating environment. Your approach depends on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is material selection for new equipment: Specify alloys with high concentrations of nickel, chromium, and silicon. These elements form more stable, protective oxide layers that inhibit carbon ingress.
- If your primary focus is extending the life of existing assets: Prioritize controlling the process environment to reduce carbon activity and implement a robust inspection program to detect carburization early before it leads to failure.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Recognize that the greatest risk is brittle fracture during shutdowns or startups. Implement procedures to carefully manage thermal gradients and avoid mechanical shock to any components susceptible to carburization.
Ultimately, understanding carburization as an internal degradation mechanism is the key to preventing the sudden and costly failures it can cause.
Summary Table:
| Damage Type | Primary Consequence | Key Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Severe Embrittlement | Loss of ductility; material becomes brittle like glass | Sudden fracture, especially during shutdowns |
| Loss of Corrosion/Oxidation Resistance | Depletion of protective chromium | Accelerated degradation and material loss |
| Internal Stress & Cracking | Volume expansion from carbide formation | Crack initiation during thermal cycling |
| Reduced Creep & Fatigue Life | Degraded performance under long-term stress | Premature failure of critical components |
Protect your high-temperature equipment from the silent threat of carburization.
Carburization can lead to sudden, catastrophic failures that compromise safety and cause costly downtime. KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables that help you analyze material degradation and select the right alloys for your demanding applications.
Our expertise supports your efforts in material selection, process control, and preventive maintenance to mitigate carburization risks.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance the integrity and longevity of your critical assets.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of torch brazing? Discover the Superior Control of Modern Brazing
- What is the critical temperature of heat treatment? Unlock the Key to Steel's Hardness and Performance
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.



















