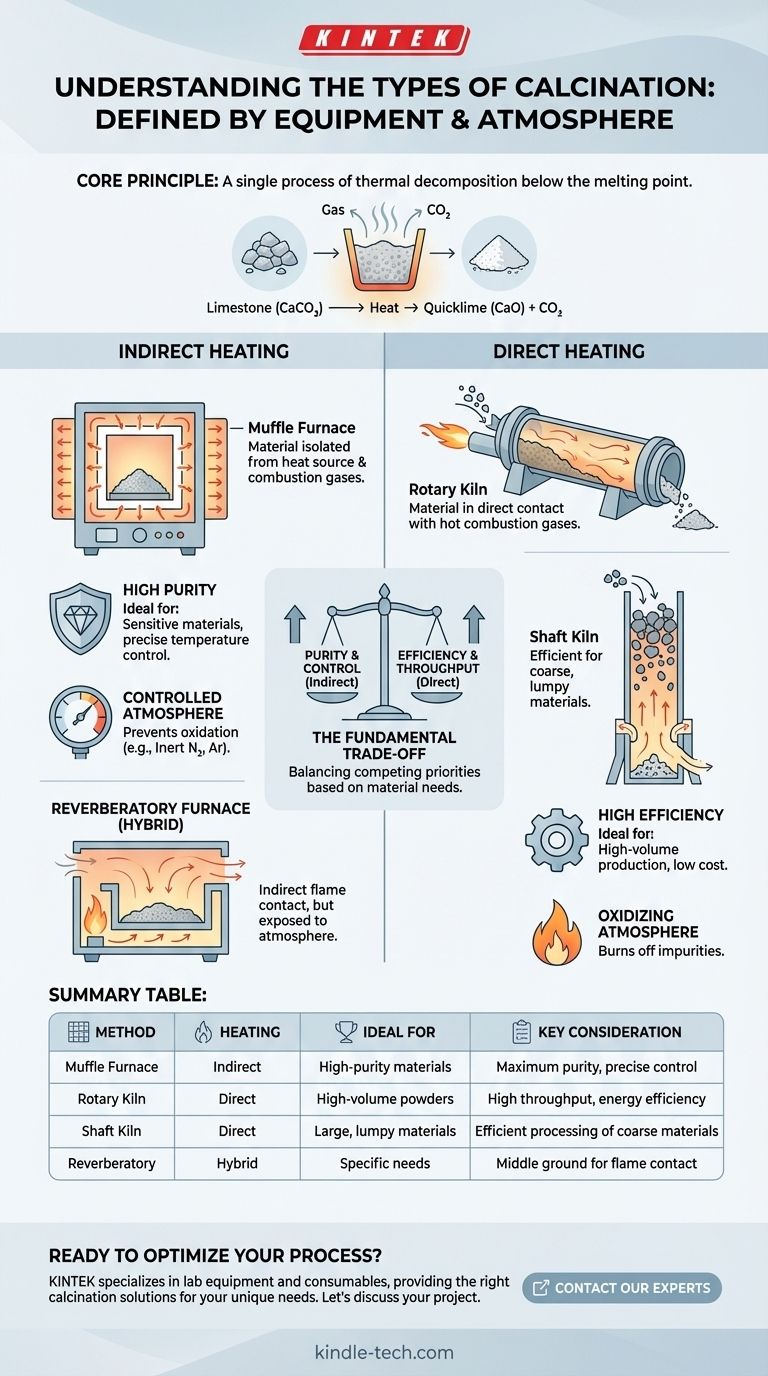
At its core, calcination is a single process of thermal decomposition. The different "types" are not distinct chemical reactions but are instead defined by the equipment and atmosphere used, which are chosen based on the material being processed and the desired final properties. The most fundamental distinction is between direct heating, where the material contacts combustion gases, and indirect heating, where it is isolated.
The choice of calcination method is a critical engineering decision. It hinges on a fundamental trade-off between the energy efficiency of direct heating and the material purity and process control offered by indirect heating.

What is Calcination? A Foundational Definition
Calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a thermal decomposition, phase transition, or removal of a volatile fraction. The process is always conducted at temperatures below the material's melting point.
The Classic Example: Limestone to Lime
The most common illustration of calcination is producing lime from limestone.
When limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is heated to a high temperature (around 825°C or 1517°F), it decomposes. It releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, leaving behind calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime. This resulting lime is often in an easily powdered condition.
Classifying Calcination: Equipment and Heating Method
The "type" of calcination is best understood by the furnace or kiln used. This choice is dictated by the material's sensitivity to contamination and the required scale of production.
Indirectly Heated Calciners (Muffle Furnaces)
In an indirectly heated system, the material being processed is physically separated from the heat source and its combustion gases. Think of this like baking something in a covered dish placed inside a larger oven.
The material sits inside a chamber, or muffle, which is then heated from the outside. This method prevents contamination from fuel or combustion byproducts, making it ideal for high-purity applications.
Directly Heated Calciners (Rotary & Shaft Kilns)
In a directly heated system, the material comes into direct contact with the hot gases from the combustion flame. This is more thermally efficient but risks contaminating the material.
Rotary kilns are large, rotating cylinders used for continuous processing of powders and granular materials. Shaft furnaces are vertical chambers where lump-form material is fed in the top and heated by rising hot gases as it descends.
Reverberatory Furnaces: A Hybrid Approach
A reverberatory furnace is a type of direct heating system where fuel is burned in a separate area. The flame and hot gases are passed over the material and radiated down from the furnace roof.
While the material is exposed to the combustion atmosphere, it does not come into direct contact with the flame itself. This offers a middle ground in some applications.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Beyond the heating method, the gaseous atmosphere inside the calciner is a critical variable that can define the outcome of the process.
Oxidizing Atmospheres
An oxygen-rich (or air) atmosphere is used to burn off organic impurities or to promote oxidation reactions in the material.
Inert Atmospheres
Using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon prevents unwanted oxidation. This is crucial when calcining sensitive metals or compounds that would be damaged by reacting with oxygen at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a calcination method is not about finding a single "best" type, but about balancing competing priorities.
Purity vs. Efficiency
This is the primary trade-off. Indirect heating (muffle furnaces) delivers high purity but is less energy-efficient because the heat must transfer through the chamber walls. Direct heating (rotary/shaft kilns) is highly energy-efficient but can introduce impurities from the fuel and combustion gases.
Temperature Control vs. Throughput
Indirectly heated systems generally offer more precise temperature control, which is vital for materials with a narrow processing window. However, they are often batch or low-throughput processes. Direct-fired rotary and shaft kilns are built for massive, continuous throughput, making them the workhorses of industries like cement and lime production.
Material Handling Challenges
The physical form of the raw material dictates the equipment. Lumpy, coarse materials like limestone ore are perfectly suited for shaft kilns. Fine powders or granular materials would fall through a shaft kiln and are therefore processed in rotary kilns.
Choosing the Right Calcination Method
Your choice of calcination method must align directly with your material requirements and production goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity: You must use an indirectly heated system, like a muffle furnace, to isolate your material from contaminants.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: A directly heated system, such as a rotary or shaft kiln, will provide the necessary energy efficiency and throughput.
- If your primary focus is processing large, lumpy raw materials: A vertical shaft furnace is the most effective and efficient design for the job.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of a sensitive material: You must ensure the furnace can operate with a controlled inert atmosphere, regardless of the heating method.
Ultimately, effective calcination depends on matching the process technology to the specific chemical and physical needs of your material.
Summary Table:
| Method | Heating Type | Ideal For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Indirect | High-purity materials, sensitive compounds | Maximum purity, precise temperature control |
| Rotary Kiln | Direct | High-volume powders & granules | High throughput, energy efficiency |
| Shaft Kiln | Direct | Large, lumpy raw materials (e.g., limestone ore) | Efficient processing of coarse materials |
| Reverberatory Furnace | Direct (Hybrid) | Applications needing indirect flame contact | Middle ground for specific material needs |
Ready to Optimize Your Calcination Process?
Choosing the right calcination equipment is critical to achieving your desired material properties, whether your priority is ultimate purity, maximum production volume, or precise atmosphere control.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the right calcination solutions for your laboratory's unique needs. We can help you navigate the trade-offs between efficiency and purity to select the perfect furnace for your application.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today to find the calcination system that will drive your research and development forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy, Fuel, and More
- What type of energy is required to break down material during pyrolysis? Harnessing Thermal Energy for Efficient Conversion
- How does pyrolysis plant work? Turning Waste into Valuable Resources
- What are the different types of pyrolysis plants? Choose the Right Process for Your Output Goal
- What are the components of a pyrolysis machine? A Complete Breakdown of the Waste-to-Energy System
- What are the advantages of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Homogeneity & Efficiency for Powders & Granules
- What is the use of a rotary furnace? Achieve Unmatched Process Uniformity for Your Materials
- What are the disadvantages of a rotary kiln? High Costs and Operational Challenges



















