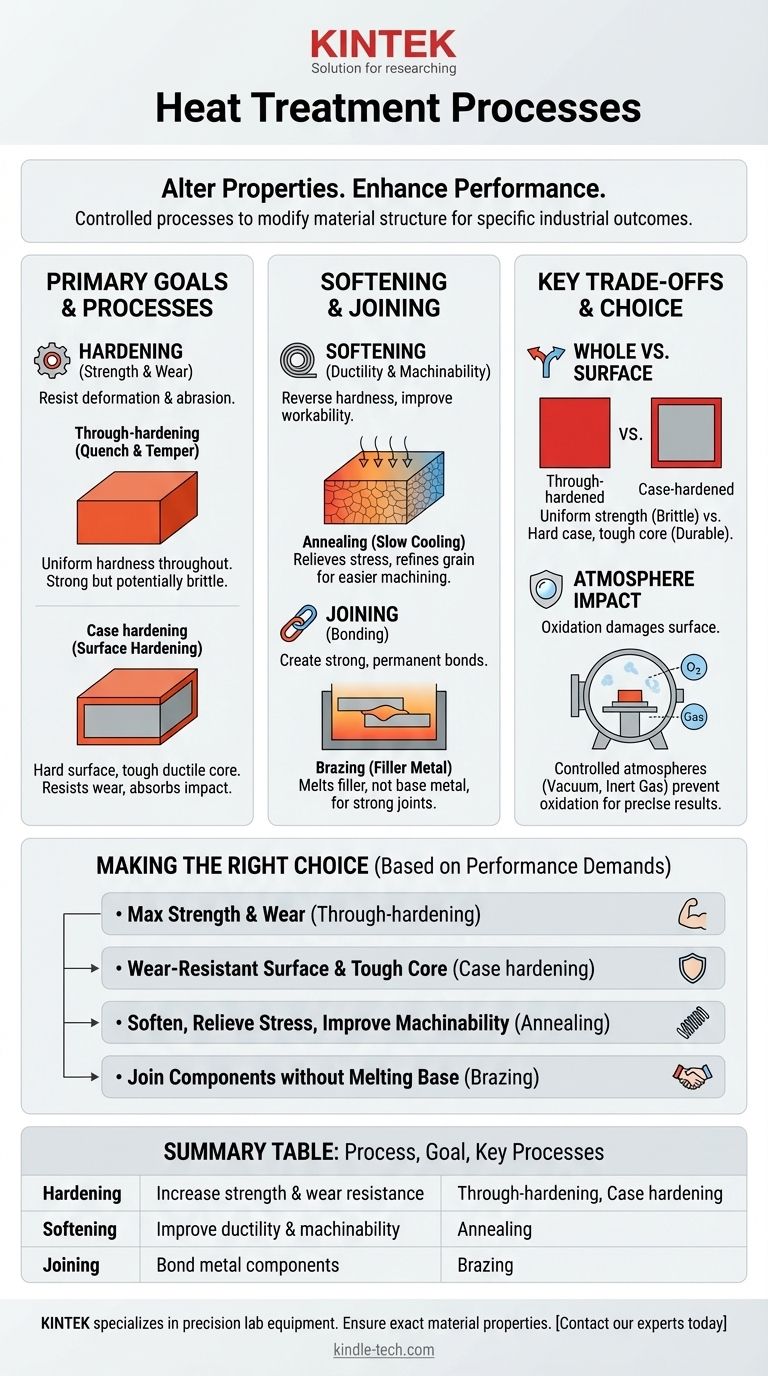
At its core, heat treatment is a family of controlled industrial processes used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. The most common types include hardening processes like through-hardening and case hardening, softening processes like annealing, and specialized techniques for joining materials, such as brazing. Each process involves carefully controlled heating and cooling to achieve a specific, desired outcome in the final part.
The specific heat treatment process chosen is never arbitrary. It is always dictated by the end-use requirements of the component—whether the goal is to create extreme surface durability, improve machinability, or increase overall strength.

The Primary Goals of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes are best understood by grouping them based on their intended outcome. The fundamental goal is to manipulate the microscopic structure of a material, primarily metals, to enhance its performance characteristics.
Hardening Processes: For Strength and Wear Resistance
Hardening is used when a component needs to resist deformation, abrasion, and wear. This is achieved by heating the material to a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly, a process known as quenching.
Through-hardening, also known as quench and tempering, imparts hardness uniformly throughout the entire cross-section of the part. This creates a component that is strong and hard from the surface to the core.
Case hardening (or surface hardening) is a targeted process. It hardens only the outer surface layer of a part while leaving the interior core soft and tough, creating a component with a wear-resistant exterior and a damage-tolerant core.
Softening Processes: For Ductility and Machinability
Sometimes, a material is too hard or brittle to be effectively machined, formed, or worked. Softening processes reverse this state, making the material more ductile and easier to handle in subsequent manufacturing steps.
Annealing is the most common softening process. It involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then cooling it very slowly, which relieves internal stresses and refines the material's grain structure to make it softer and more workable.
Joining and Other Modifications
Heat treatment isn't limited to just making materials harder or softer. It also includes specialized processes for joining or fundamentally altering material properties for specific applications.
Brazing is a metal-joining process where a filler metal is heated above its melting point and distributed between two or more close-fitting parts. The heat of the furnace melts the filler metal, which then flows into the joint, creating a strong bond upon cooling.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Selecting the right heat treatment involves balancing performance requirements with material limitations and cost. Each choice has direct consequences for the final part.
Whole Part vs. Surface Treatment
The decision between through-hardening and case hardening is a classic engineering trade-off. A through-hardened part is uniformly strong but can be brittle and susceptible to cracking under sharp impacts.
A case-hardened part, by contrast, offers an excellent combination of properties. The hard case resists wear, while the tough, ductile core absorbs impact energy, preventing catastrophic failure.
The Impact of Atmosphere
Nearly all heat treatment occurs at elevated temperatures where oxygen can react with the metal's surface. This reaction, known as oxidation, can damage the part's finish and compromise its integrity.
To prevent this, critical processes are performed in controlled atmospheres, such as a vacuum or an environment filled with inert gases. This adds complexity and cost but is essential for achieving the precise surface properties required in industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the specific performance demands of your component. By defining your primary goal, you can narrow down the most suitable process.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and wear resistance throughout the part: Through-hardening is the most direct approach.
- If you need a wear-resistant surface but a tough, impact-resistant core: Case hardening provides the ideal combination of properties.
- If your goal is to soften a material to relieve stress or improve machinability: Annealing is the standard process to increase ductility.
- If you are joining multiple metal components with a strong, permanent bond: Brazing is an effective method that avoids melting the base materials.
Understanding these fundamental processes empowers you to specify material characteristics that directly contribute to superior performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Process Category | Primary Goal | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Increase strength & wear resistance | Through-hardening, Case hardening |
| Softening | Improve ductility & machinability | Annealing |
| Joining | Bond metal components | Brazing |
Need the right heat treatment for your components? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for material testing and processing. Our expertise ensures you achieve the exact material properties—whether hardness, ductility, or strong bonds—that your application demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main source of biochar? Unlock the Power of Sustainable Feedstocks
- What role does an ultrasonic cleaner play in the cleaning stage prior to the electroless nickel plating of ductile iron?
- What is the most common method used for synthesis of nanomaterials? A Guide to Dominant Techniques
- How does concentration affect IR? Master Quantitative Analysis and Spectral Interpretation
- Why is my vacuum pump so loud? Diagnose Gurgling, Grinding & Rattling Noises
- How is temperature controlled in an experiment? Master Precision, Stability, and Uniformity
- What is the difference between CBD isolate and distillate? Purity vs. Entourage Effect Explained
- What are the two types of hot air ovens? Choose the Right Air Circulation for Your Lab



















