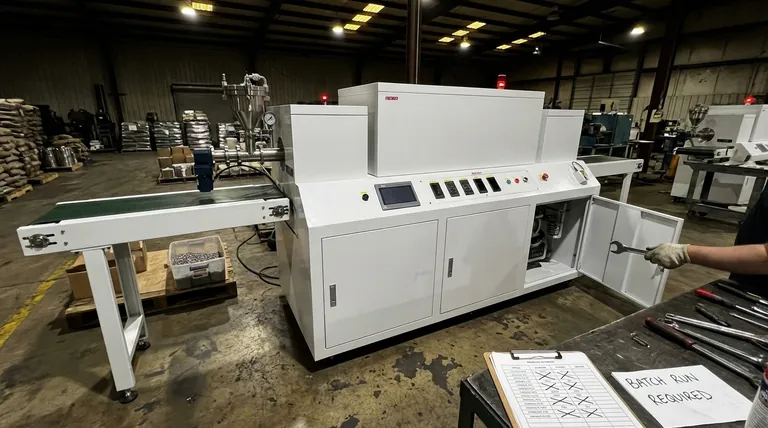
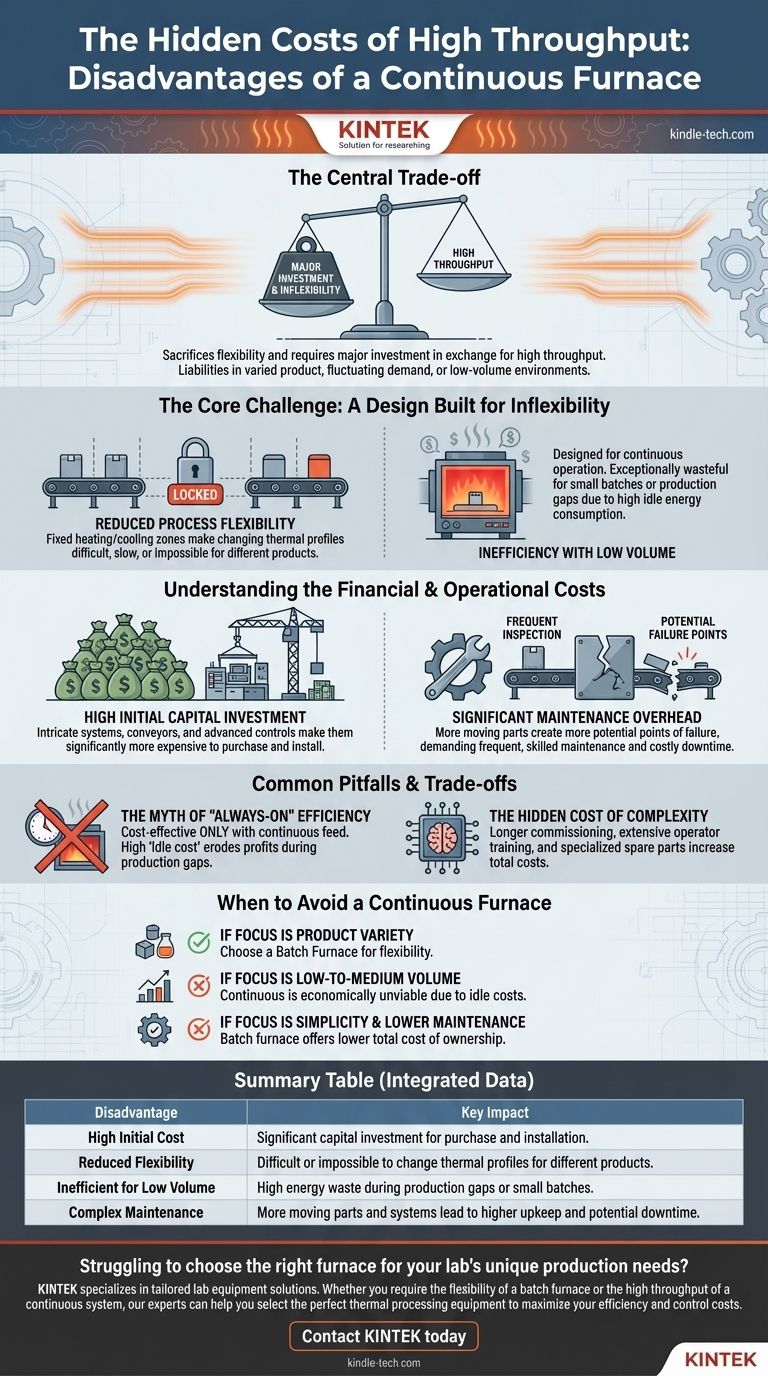
At its core, the primary disadvantages of a continuous furnace are its significant upfront cost, lack of process flexibility, and demanding maintenance requirements. These drawbacks stem directly from its complex design, which is optimized for high-volume, repetitive production of a single product type.
The central trade-off is clear: a continuous furnace sacrifices flexibility and requires a major investment in exchange for high throughput. Its disadvantages become critical liabilities in any environment that involves varied products, fluctuating demand, or low-volume production runs.

The Core Challenge: A Design Built for Inflexibility
A continuous furnace operates by moving items through different temperature zones at a constant speed. This principle is the source of its efficiency in mass production, but it is also the root of its most significant operational weaknesses.
Reduced Process Flexibility
Because the furnace has multiple, fixed heating and cooling zones, you cannot easily change the thermal profile. Adjusting the temperature or atmosphere for a different product is a slow, difficult, and sometimes impossible task.
In contrast, a batch furnace treats each load as a distinct job, allowing for complete control over the process parameters for every run.
Inefficiency with Low Volume
A continuous furnace is designed to be on and at temperature for extended periods. Running it for small or intermittent batches is exceptionally wasteful.
The energy required to keep the entire furnace at operational temperature is substantial. If the production line ahead of it stops, the furnace consumes vast amounts of energy while producing nothing.
Understanding the Financial and Operational Costs
The complexity of a continuous furnace introduces direct and indirect costs that are often much higher than those for simpler batch systems.
High Initial Capital Investment
The intricate systems of conveyors, multiple control zones, and advanced atmosphere management make continuous furnaces significantly more expensive to purchase and install than batch furnaces of a similar capacity.
Significant Maintenance Overhead
More moving parts and complex control systems inherently create more potential points of failure. The conveyor mechanism, in particular, requires frequent inspection and maintenance to prevent costly downtime.
This complexity demands a higher level of skill from maintenance staff and can lead to longer and more challenging troubleshooting when issues arise.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Choosing a continuous furnace based solely on its potential for high throughput can be a critical error if the full operational context isn't considered.
The Myth of "Always-On" Efficiency
A continuous furnace is only cost-effective when it is being continuously fed with product. Its efficiency plummets during production gaps, shift changes, or any upstream disruption.
This turns its greatest strength into a major liability, as the high "idle cost" can quickly erode the profits gained from its high throughput.
The Hidden Cost of Complexity
Beyond the purchase price, complexity adds costs in other areas. It requires longer commissioning times, more extensive training for operators, and a larger inventory of specialized spare parts.
When to Avoid a Continuous Furnace
Based on these disadvantages, you can make a clear decision based on your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is product variety: The ability to change process parameters for each job makes a batch furnace the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is low-to-medium volume production: The high capital and idle energy costs of a continuous furnace make it economically unviable.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and lower maintenance: The simpler, more robust design of a batch furnace results in a lower total cost of ownership and easier operation.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental trade-offs ensures you invest in a thermal processing solution that enhances your production, rather than constrains it.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Initial Cost | Significant capital investment for purchase and installation. |
| Reduced Flexibility | Difficult or impossible to change thermal profiles for different products. |
| Inefficient for Low Volume | High energy waste during production gaps or small batches. |
| Complex Maintenance | More moving parts and systems lead to higher upkeep and potential downtime. |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's unique production needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing tailored lab equipment solutions. Whether you require the flexibility of a batch furnace or the high throughput of a continuous system, our experts can help you select the perfect thermal processing equipment to maximize your efficiency and control costs.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our reliable lab furnaces and consumables can enhance your production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a suitable hot zone in a furnace? Boost Efficiency & Product Quality
- What is the working principle of vacuum brazing furnace? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Strength Metal Joining
- What is the source of electron beam welding? The High-Voltage Power Supply Explained
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability
- What are the different types of carburizing? Choose the Right Process for Your Steel Parts
- Why is a high-vacuum high-temperature furnace necessary for fusion experiments? Ensure Data Validity and Precision
- How is heat transfer in liquids different from that in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Management for Your Lab
- What role do high-precision melting furnaces play in stir casting? Master Precision in Zinc-Based Composites



















