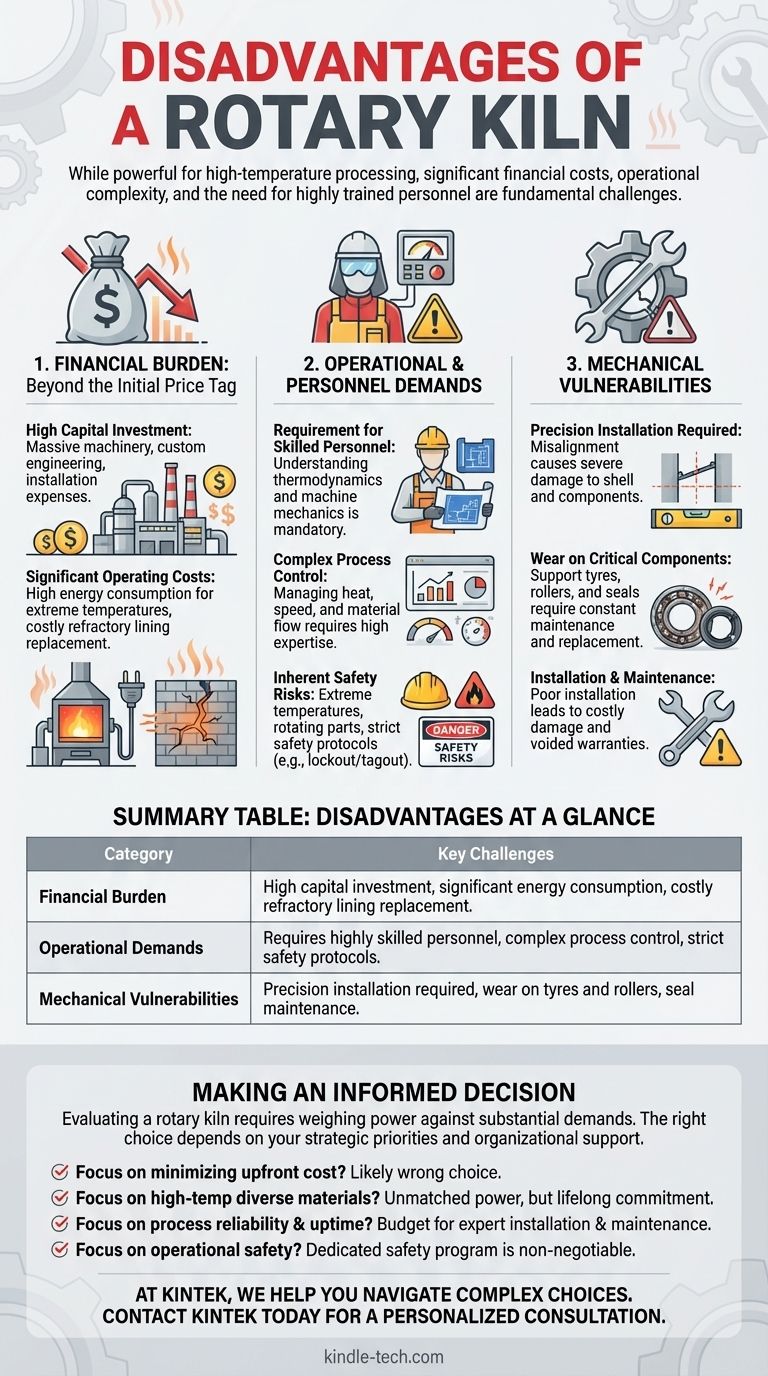
While powerful for high-temperature processing, the primary disadvantages of a rotary kiln are its significant financial costs, operational complexity, and the need for highly trained personnel. These are not minor considerations but fundamental challenges that demand careful evaluation before any investment is made.
The core issue with a rotary kiln is that its immense processing capability is directly tied to a high total cost of ownership. The disadvantages are interconnected: high capital costs are followed by demanding operational expenses, complex maintenance, and significant safety risks that require a permanent commitment of specialized expertise.

The Financial Burden: Beyond the Initial Price Tag
A rotary kiln is one of the most significant capital investments a facility can make. This cost is not a one-time event but extends throughout the equipment's entire lifecycle.
High Capital Investment
A rotary kiln is a massive piece of industrial machinery. Its core components—the shell, drive assembly, support tyres (riding rings), and rollers—are large, heavy, and must be engineered for extreme conditions.
These systems are not off-the-shelf products. They are often customized for the specific material being processed, which adds to the initial engineering and manufacturing expense.
Significant Operating Costs
The very reason for a rotary kiln's existence—creating extremely high temperatures—is also a source of its high operating cost. Sustaining these temperatures requires a tremendous amount of energy, typically from fuel combustion.
Furthermore, the refractory lining inside the shell, which protects the steel from the heat, is a consumable component. It degrades over time and requires periodic, expensive replacement.
The Operational and Personnel Demands
A rotary kiln does not run itself. Its effective and safe operation is a complex task that relies entirely on human expertise and strict procedural adherence.
Requirement for Skilled Personnel
The reference to needing "trained personnel" is an understatement. Operators must understand the thermodynamics of the process and the mechanics of the machine.
They are responsible for managing the heat pattern, controlling the rotation speed, and ensuring the continuous, stable flow of material. This requires a level of skill far beyond that of a general equipment operator.
Inherent Safety Risks
Operating a massive, rotating piece of equipment at extreme temperatures presents substantial safety hazards. The references highlight strict prohibitions against performing any inspection or maintenance on moving parts.
Safety guards, lockout/tagout procedures, and specialized tools like fire mirrors for inspection are mandatory. An alarm must be sounded before startup to ensure no one is inside the kiln, underscoring the inherent danger of the equipment.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Mechanical Vulnerabilities
The mechanical nature of a rotary kiln makes it powerful but also susceptible to specific failures, often stemming from its installation and maintenance.
Precision Installation is Non-Negotiable
A rotary kiln is a dynamic system that must be perfectly aligned. As one reference notes, poor installation can lead directly to costly damage.
Misalignment of the support rollers and tyres can cause excessive wear and even damage the kiln's main shell. Missing critical inspection points during assembly can void warranties and necessitate expensive rework.
Wear on Critical Components
The constant rotation, massive weight, and thermal expansion place enormous stress on mechanical parts. The support tyres, trunnion wheels, and thrust rollers are all subject to continuous wear and require a rigorous maintenance and lubrication schedule.
Likewise, the seals at either end of the kiln are critical for maintaining temperature and preventing material from escaping, but they are wear items that require regular attention and eventual replacement.
Making an Informed Decision
Evaluating a rotary kiln requires weighing its immense processing power against its substantial demands. The right choice depends entirely on your strategic priorities and your organization's ability to support the equipment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost: A rotary kiln is almost certainly the wrong choice, as its capital expenditure is among the highest for processing equipment.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse materials at high temperatures: The kiln's power is unmatched, but you must be prepared for the lifelong financial and operational commitment this capability demands.
- If your primary focus is process reliability and uptime: You must budget for and invest in expert installation, rigorous preventive maintenance schedules, and highly trained, dedicated operators.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: A dedicated and strictly enforced safety program is non-negotiable, as the machine's fundamental nature presents significant inherent risks.
Ultimately, a successful rotary kiln implementation depends on recognizing it not as a simple purchase, but as a long-term strategic investment in specialized industrial capability.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Financial Burden | High capital investment, significant energy consumption, costly refractory lining replacement |
| Operational Demands | Requires highly skilled personnel, complex process control, strict safety protocols |
| Mechanical Vulnerabilities | Precision installation required, wear on tyres and rollers, seal maintenance |
Considering a rotary kiln for your high-temperature processing?
At KINTEK, we understand that selecting the right equipment is a critical strategic decision. Our experts specialize in helping laboratories and industrial facilities navigate these complex choices. We provide not only top-tier lab equipment but also the consultative support to ensure your investment is sound, safe, and efficient.
Let us help you evaluate your needs and find the best solution for your specific application. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis environmentally friendly? Unlocking Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Solutions
- What is the difference between pyrolysis and gasification? Unlocking the Right Thermal Conversion Process
- What is different between calcination? Unlocking Thermal Processing for Material Science
- Where does pyrolysis occur? Unlocking the Power of Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- What is the mechanism of pyrolysis decomposition? A Guide to Converting Waste into Valuable Products
- What is the purpose of calciner? Boost Cement Production Efficiency & Clinker Formation
- What is high temperature calcination? Mastering Material Transformation with Heat
- What is fast pyrolysis of plastic waste? Transform Waste Plastic into Valuable Oil



















