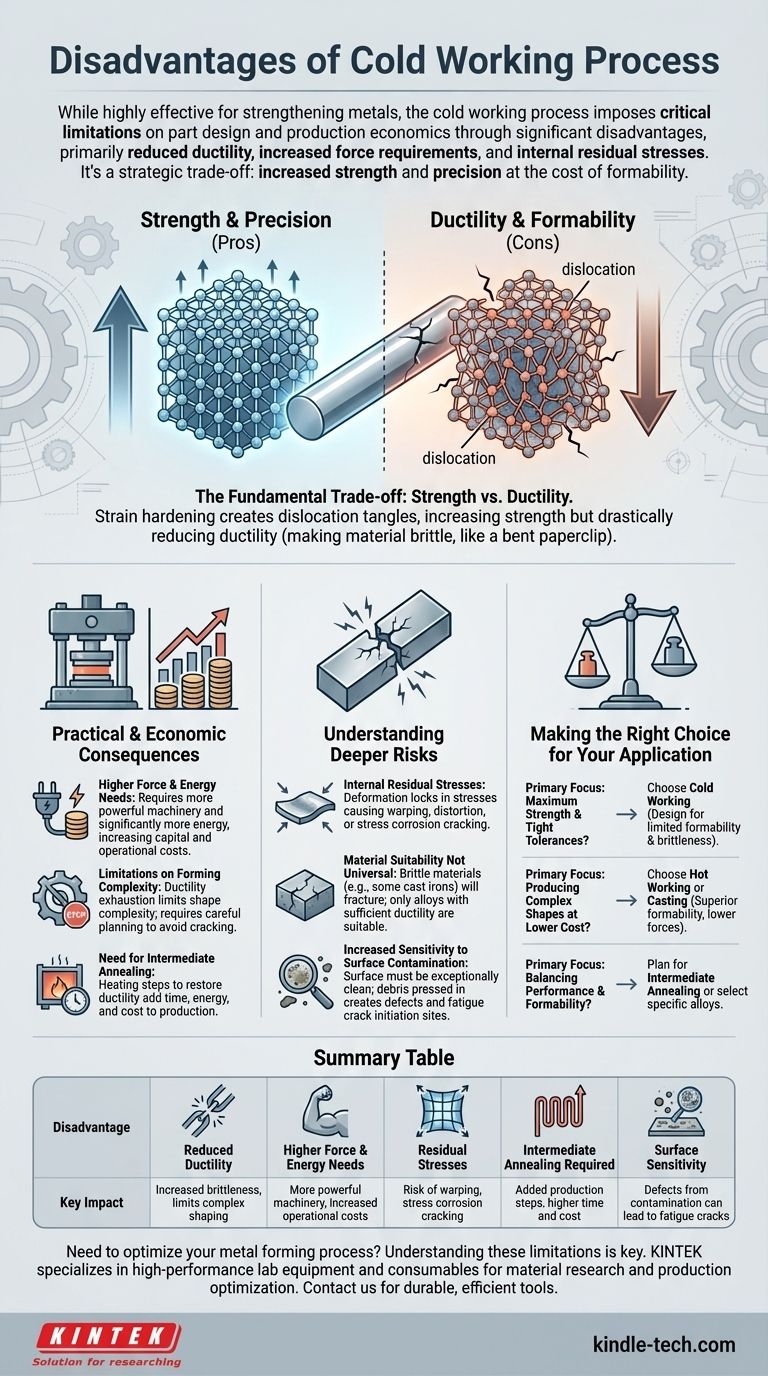
While highly effective for strengthening metals, the cold working process is not without significant disadvantages. The primary drawbacks are a severe reduction in the material's ductility, a substantial increase in the force and power required for forming, and the introduction of potentially harmful internal residual stresses. These factors impose critical limitations on both the design of the part and the economics of its production.
Cold working is a strategic trade-off. You are essentially exchanging a material's ductility and ease of forming for increased strength and dimensional precision. Understanding the costs of this exchange is critical for any engineering application.
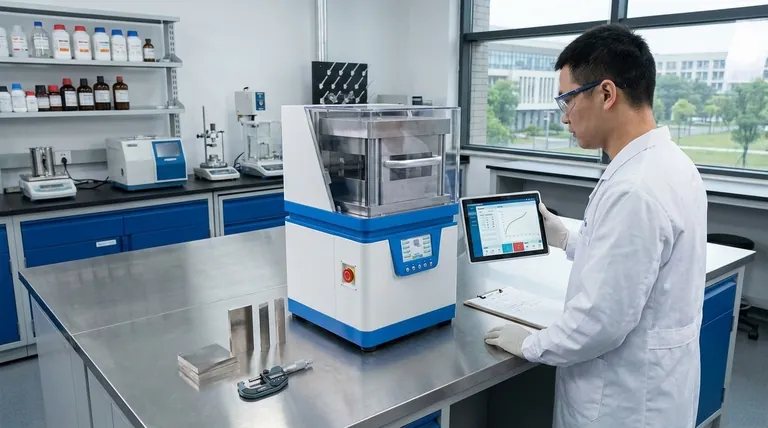

The Fundamental Trade-off: Strength vs. Ductility
Cold working strengthens a metal through a mechanism called strain hardening. While beneficial for final performance, this process fundamentally alters the material's ability to be formed.
How Cold Working Increases Strength
When a metal is deformed below its recrystallization temperature, microscopic defects called dislocations are generated and tangled within its crystal structure. Imagine trying to navigate a crowded room; the more people (dislocations) there are, the harder it is to move through. This interference makes the material significantly stronger and harder.
The Cost of Strength: Reduced Ductility
The same dislocation tangles that increase strength also eliminate the "free space" for crystals to slip past one another. This drastically reduces ductility, which is the material's ability to deform without fracturing. A cold-worked metal becomes more brittle, like a paperclip that has been bent back and forth—it becomes stiff, but one more bend will snap it.
Practical & Economic Consequences
The physical changes in a cold-worked material have direct and often costly consequences for the manufacturing process.
Higher Force and Energy Requirements
Deforming a stronger, harder material requires more powerful machinery and consumes significantly more energy. This translates directly to higher capital costs for equipment (stronger presses, rollers, etc.) and higher operational costs for every part produced.
Limitations on Forming Complexity
Because the material's ductility is quickly exhausted, there is a limit to how much you can shape a part in a single cold working operation. Complex geometries that require significant deformation may be impossible to achieve without the material cracking.
The Need for Intermediate Annealing
To overcome the loss of ductility during complex forming, a process called intermediate annealing is often required. The part is heated to soften it and restore its ductility, then allowed to cool before it can be worked again. This adds an entire step, increasing production time, energy consumption, and overall cost.
Understanding the Deeper Risks
Beyond the immediate forming challenges, cold working introduces less obvious risks that can impact the long-term integrity of the component.
Introduction of Internal Residual Stresses
The mechanical deformation of cold working locks internal stresses into the material. These residual stresses can be highly problematic, leading to unpredictable warping or distortion if a portion of the material is later machined away. More critically, they can make the component susceptible to premature failure from phenomena like stress corrosion cracking.
Material Suitability is Not Universal
Not all metals are good candidates for cold working. Inherently brittle materials, such as many cast irons, will simply fracture under the high strains of the process. The choice of alloy is critical, as only those with sufficient initial ductility can be effectively cold worked.
Increased Sensitivity to Surface Contamination
The surface of the workpiece must be exceptionally clean before cold working. Any scale, dirt, or lubricant residue can be pressed into the material's surface during the high-pressure operation. This creates surface defects that can compromise finish quality and act as initiation sites for fatigue cracks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a manufacturing process requires balancing the desired final properties with the realities of production.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and tight tolerances: Cold working is an excellent choice, but you must design for limited formability and manage the risk of brittleness in the final part.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes at a lower cost: Hot working or casting may be better alternatives, as they offer superior formability without requiring massive forces.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and formability: Plan for intermediate annealing steps in your process or select an alloy specifically designed for a good cold work response.
Understanding these limitations is the key to leveraging cold working effectively and avoiding costly production failures.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduced Ductility | Increased brittleness, limits complex shaping |
| Higher Force & Energy Needs | More powerful machinery, increased operational costs |
| Residual Stresses | Risk of warping, stress corrosion cracking |
| Intermediate Annealing Required | Added production steps, higher time and cost |
| Surface Sensitivity | Defects from contamination can lead to fatigue cracks |
Need to optimize your metal forming process? The limitations of cold working can be challenging, but choosing the right equipment and materials is key to success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's needs. Whether you're researching material properties or optimizing production parameters, our solutions help you achieve precise, reliable results. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your projects with durable, efficient tools designed for superior performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hot press improve the microscopic structure of polymer-ceramic composite cathodes? | KINTEK
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?



















