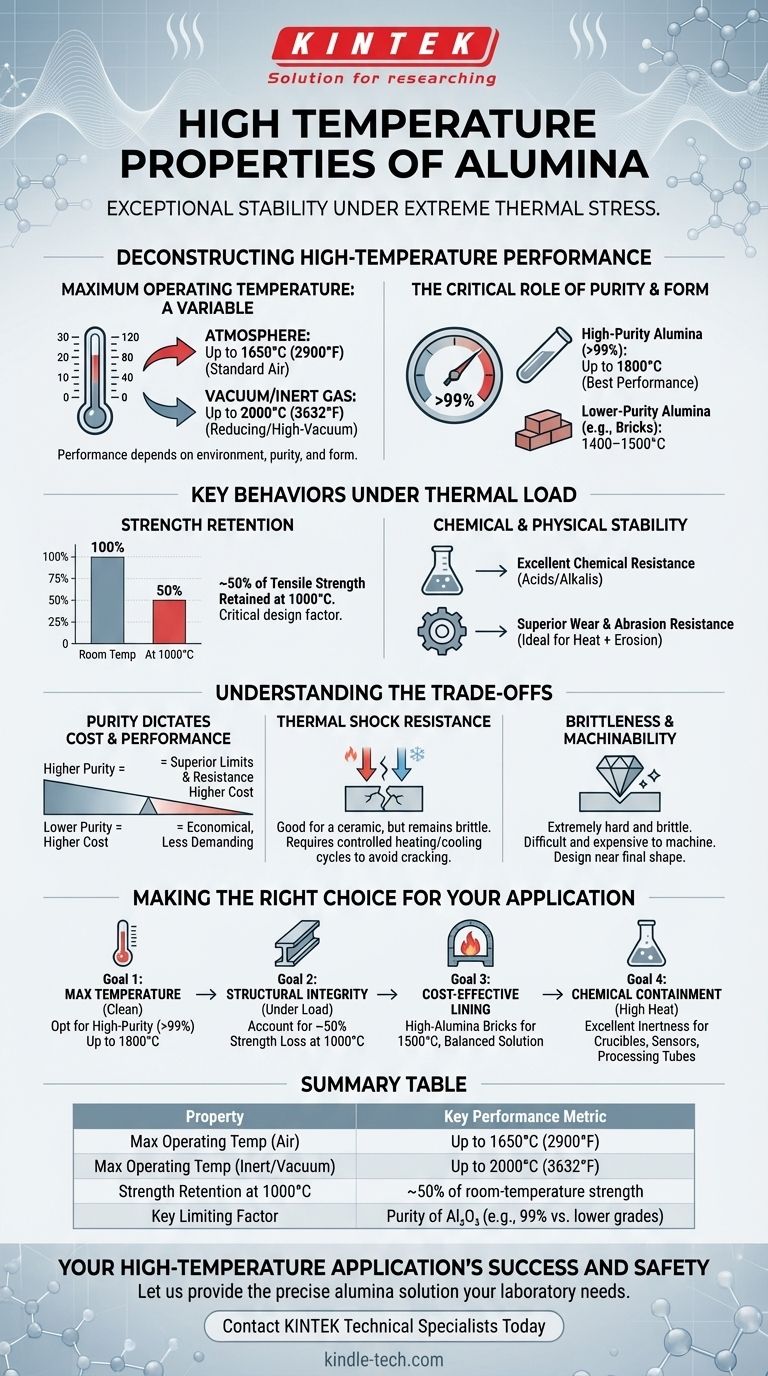
At its core, alumina is defined by its exceptional stability under extreme thermal stress. This advanced ceramic maintains its structural and chemical integrity at temperatures far beyond the limits of most metals and polymers. It can operate continuously in air at temperatures up to 1650°C (2900°F), retains half of its room-temperature strength at a blistering 1000°C, and exhibits outstanding resistance to chemical attack and physical wear.
Alumina's true value in high-temperature applications lies not just in its high melting point, but in its unique combination of thermal stability, mechanical strength retention, and chemical inertness. However, its ultimate performance is not a single value; it is directly dictated by the material's purity and manufactured form.

Deconstructing Alumina's High-Temperature Performance
To properly evaluate alumina, you must look beyond a single temperature rating and understand how its key properties behave under thermal load.
Maximum Operating Temperature: A Variable, Not a Constant
The maximum temperature alumina can withstand is highly dependent on its environment, purity, and form.
- Atmosphere: In a standard air atmosphere, alumina components are stable up to approximately 1650°C (2900°F).
- Vacuum/Inert Gas: In a reducing, inert, or high-vacuum environment, the lack of oxygen allows for even higher operating temperatures, reaching up to 2000°C (3632°F) for high-purity grades.
The Critical Role of Purity and Form
Not all alumina is created equal. The percentage of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) directly impacts its thermal limits.
- High-Purity Alumina (>99%): Components like tubes made from 99.6% alumina can withstand temperatures up to 1800°C. This grade offers the best performance.
- Lower-Purity Alumina: Forms like "high alumina bricks" used in furnace linings typically have a lower maximum operating temperature, generally in the range of 1400–1500°C.
Strength Retention Under Thermal Load
A material's strength at its operating temperature is a critical design factor. Alumina performs admirably but is not immune to thermal weakening.
At 1000°C, components made from alumina retain approximately 50% of their room-temperature tensile strength. Engineers must account for this strength reduction when designing structural or load-bearing parts for high-heat applications.
Chemical and Physical Stability
Alumina’s utility is cemented by its ability to resist degradation from sources other than just heat.
It maintains excellent chemical resistance to acids and alkalis even at high temperatures. Furthermore, its inherent hardness gives it superior wear and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for components that face both heat and physical erosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting alumina requires an objective look at its limitations and the relationship between cost and performance.
Purity Dictates Performance and Cost
There is a direct and unavoidable correlation between alumina's purity, its performance capabilities, and its price. Higher purity grades (99% and above) deliver superior temperature limits and chemical resistance but come at a significantly higher cost. Lower purity grades offer a more economical solution for less demanding applications.
Thermal Shock Resistance
While alumina has good thermal shock resistance for a ceramic, it remains a brittle material. Rapid and uneven temperature changes can induce internal stresses, leading to cracks and catastrophic failure. Any design using alumina must incorporate controlled heating and cooling cycles to mitigate this risk.
Brittleness and Machinability
Alumina is an extremely hard and brittle material. This makes it difficult and expensive to machine into complex shapes after it has been fired. Parts should be designed to be manufactured as close to their final shape as possible to avoid costly post-processing like diamond grinding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine which grade and form of alumina is the correct choice for your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature in a clean environment: Opt for high-purity (>99%) alumina components, which can operate reliably up to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under load: Design your system knowing that alumina loses about half of its tensile strength by the time it reaches 1000°C.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective furnace lining: High-alumina bricks provide a balanced solution, offering good thermal resistance up to 1500°C without the expense of ultra-high-purity forms.
- If your primary focus is chemical containment at high heat: Alumina's excellent chemical inertness makes it a superior choice for crucibles, sensors, and processing tubes in reactive atmospheres.
By understanding the direct relationship between alumina's purity, form, and performance, you can confidently select the precise grade for your high-temperature challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Performance Metric |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Temp (Air) | Up to 1650°C (2900°F) |
| Max Operating Temp (Inert/Vacuum) | Up to 2000°C (3632°F) |
| Strength Retention at 1000°C | ~50% of room-temperature strength |
| Key Limiting Factor | Purity of Al₂O₃ (e.g., 99% vs. lower grades) |
Selecting the right alumina grade is critical for your high-temperature application's success and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including alumina components like tubes, crucibles, and furnace linings. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between purity, performance, and cost to ensure you get a material that delivers reliability under extreme thermal stress.
Let us provide the precise alumina solution your laboratory needs.
Contact our technical specialists today to discuss your requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- High Purity Alumina Granulated Powder for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and handling precautions for alumina powder as a polishing material? Achieve a Flawless Finish with Precision
- Which materials are used as high temperature resistance materials? A Guide to Superalloys, Ceramics & Composites
- Which of the following is used in furnace to withstand high temperature? Key Materials for Extreme Heat
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What is the most common industrial ceramic? Discover Why Alumina Dominates Countless Applications



















