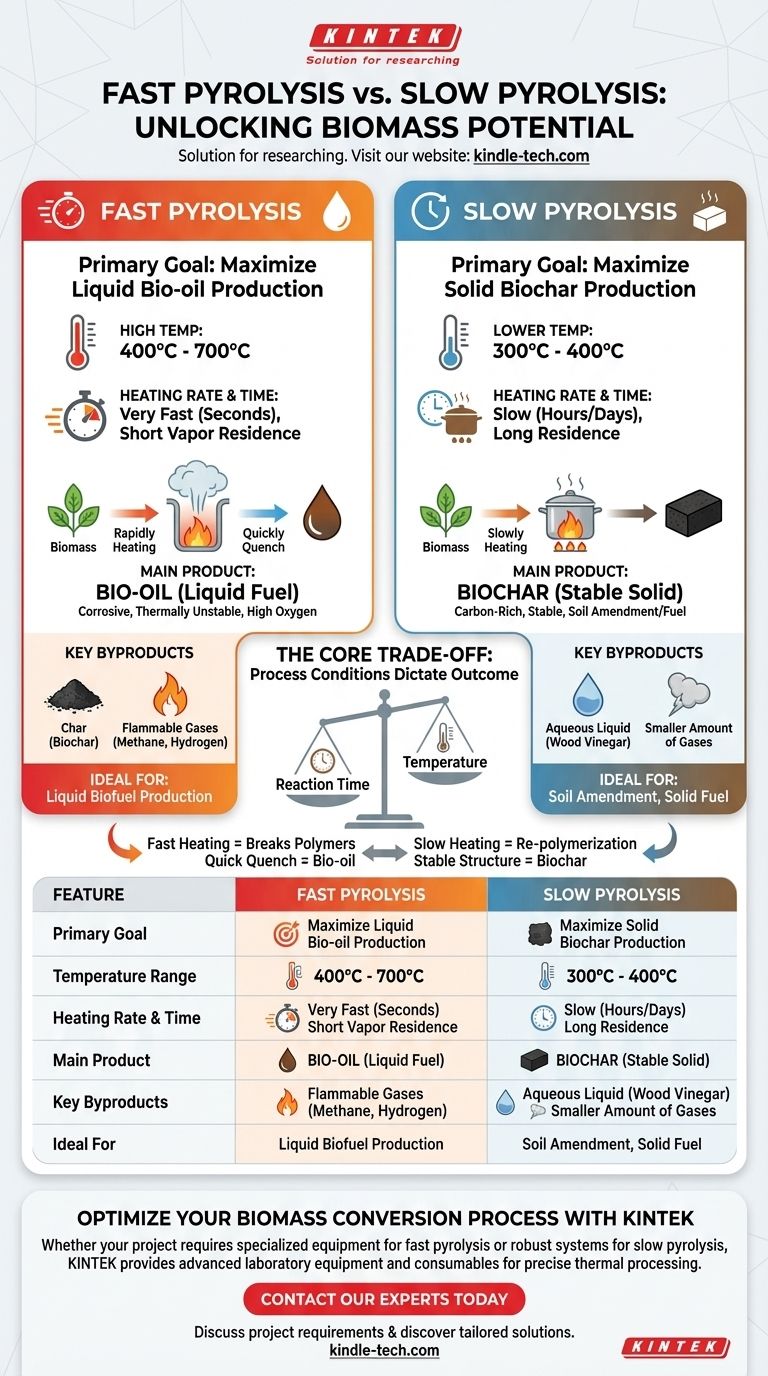
The fundamental difference between slow and fast pyrolysis lies in their primary goal, which dictates the process conditions. Fast pyrolysis uses rapid, high-temperature heating to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil. In contrast, slow pyrolysis uses a lower temperature over a much longer period to maximize the output of a stable, solid biochar.
The choice between fast and slow pyrolysis is not about which process is "better," but about which end product you intend to create. Fast pyrolysis is engineered to produce liquid fuel, while slow pyrolysis is optimized for solid charcoal.
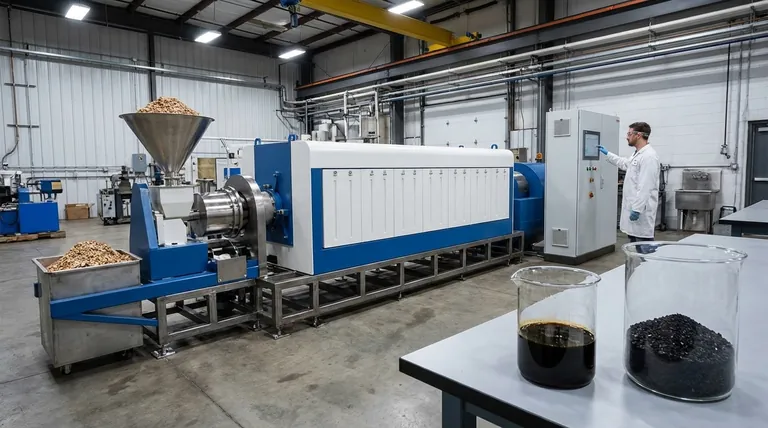

Unpacking Fast Pyrolysis: Speed for Liquid Fuel
Fast pyrolysis is a thermal conversion process designed to break down biomass into a vapor, which is then rapidly cooled and condensed into a liquid. The entire process is engineered for speed to prevent the formation of solid char.
Core Process Parameters
This method involves heating biomass very quickly to high temperatures, typically between 400°C and 700°C. The key is the rapid heating rate and the short residence time for the resulting vapors, ensuring they are quickly removed and cooled.
The Primary Product: Bio-oil
The main output, representing the majority of the product yield, is bio-oil. This is a dark, dense liquid fuel.
However, this bio-oil is chemically distinct from petroleum. It has a high oxygen content, which makes it corrosive, thermally unstable, and immiscible with traditional fossil fuels.
Byproducts and Advantages
Fast pyrolysis also produces char (biochar) and non-condensable flammable gases like methane and hydrogen. A key advantage is that these gases can be recycled and burned to provide the heat needed to run the reactor, making the process more self-sustaining.
The reactors are relatively simple, and facilities can be built on a small, mobile scale. This allows bio-oil to be produced near the biomass source before being transported to a central facility for upgrading.
Understanding Slow Pyrolysis: Time for Solid Biochar
Slow pyrolysis is a much older and simpler technology, historically used for making charcoal. The process conditions are deliberately managed to encourage the formation of a carbon-rich solid.
Core Process Parameters
This process uses significantly lower temperatures (300°C to 400°C) and much slower heating rates. The biomass is allowed to "cook" for an extended period, sometimes for hours or even days.
The Primary Product: Biochar
The main product of slow pyrolysis is biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid material also known as biocoal or charcoal. This product is often used as a soil amendment to improve fertility or as a solid fuel.
The Byproducts
Slow pyrolysis also produces an aqueous liquid byproduct, sometimes referred to as wood vinegar, along with a smaller amount of gases compared to fast pyrolysis.
The Core Trade-off: Process Conditions Dictate the Outcome
The dramatic difference in products between these two methods comes down to chemistry and reaction time. The specific heating rate and temperature directly control which chemical reactions dominate.
Why Heating Rate Matters
Fast heating at high temperatures rapidly breaks down the complex polymers in biomass (like cellulose and lignin) into smaller, volatile molecules. Quenching these vapors quickly captures them as a liquid (bio-oil) before they can react further to form solids.
Slow heating at lower temperatures provides the time and conditions for these molecules to re-polymerize and arrange themselves into stable, carbon-rich aromatic structures, forming solid char.
Product Quality and Application
The bio-oil from fast pyrolysis is a potential liquid fuel, but its corrosive and unstable nature often requires significant and costly upgrading before it can be used.
The biochar from slow pyrolysis is a stable and valuable product with immediate applications in agriculture (improving soil) and metallurgy (as a fuel or carbon source) without needing further refinement.
Reactor Technology
The choice of method influences the equipment used. While many reactor types exist, such as fluidized-bed, auger, and ablative reactors, they are typically optimized for the specific conditions required by either fast or slow pyrolysis to maximize the desired product yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use fast or slow pyrolysis depends entirely on the desired final product and its intended application.
- If your primary focus is liquid biofuel production: Fast pyrolysis is the correct pathway, as it is specifically designed to maximize the yield of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid soil amendment or a stable solid fuel: Slow pyrolysis is the superior choice, as it is optimized to produce high-quality biochar.
By understanding that each process is a tool for a different objective, you can select the right approach for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Fast Pyrolysis | Slow Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize liquid bio-oil production | Maximize solid biochar production |
| Temperature Range | 400°C - 700°C | 300°C - 400°C |
| Heating Rate & Time | Very fast (seconds), short vapor residence | Slow (hours/days), long residence |
| Main Product | Bio-oil (liquid fuel) | Biochar (stable solid) |
| Key Byproducts | Char, flammable gases | Aqueous liquid (wood vinegar), gases |
| Ideal For | Liquid biofuel production | Soil amendment, solid fuel |
Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Process with KINTEK
Whether your project requires specialized equipment for fast pyrolysis to maximize bio-oil yield or robust systems for slow pyrolysis to produce high-quality biochar, KINTEK has the solution. We specialize in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing, helping researchers and engineers achieve their specific biomass conversion goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and development efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















