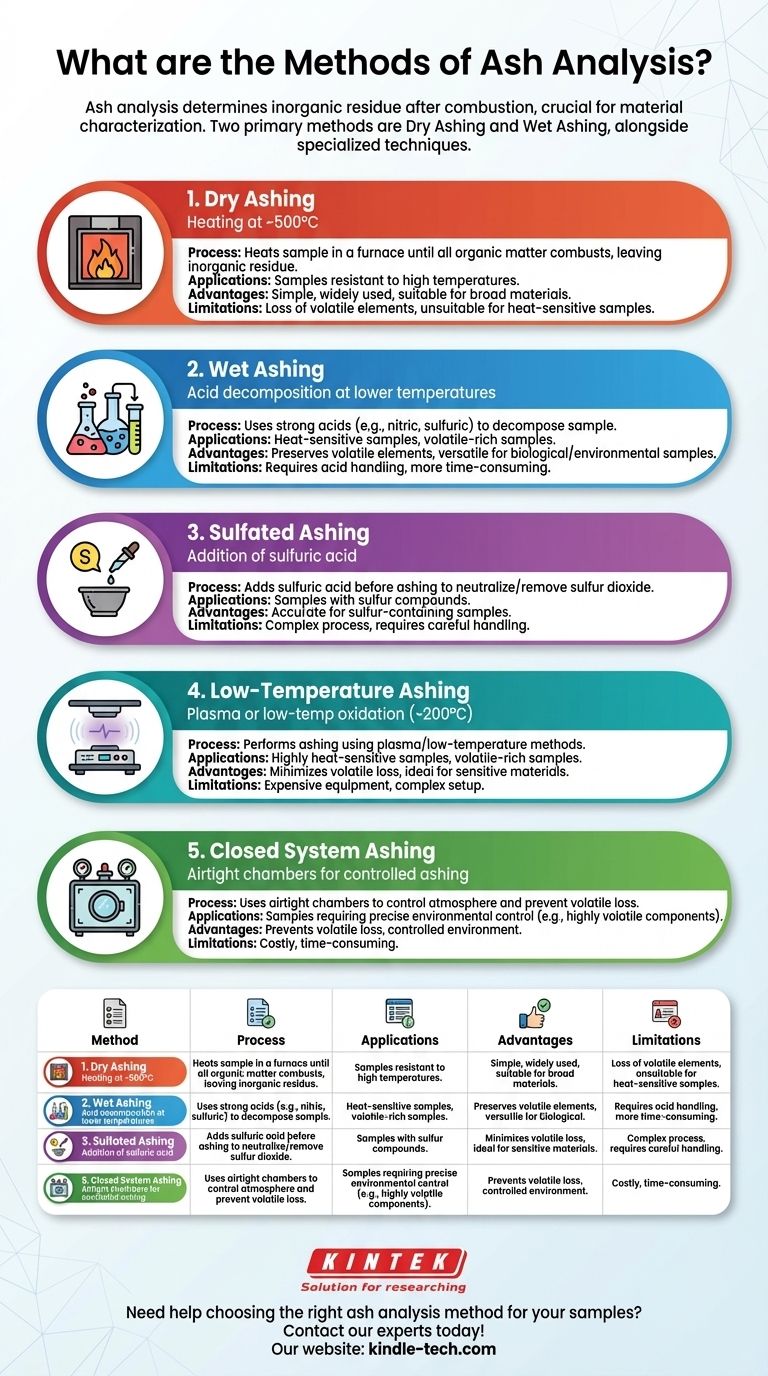
Ash analysis is a critical process in determining the inorganic residue left after the combustion of a material. The two primary methods for ash determination are dry ashing and wet ashing, each with specific applications and advantages. Dry ashing involves heating the sample at high temperatures (around 500°C) in a furnace, while wet ashing uses acids to decompose the sample at lower temperatures. Additionally, other techniques like sulfated ashing, low-temperature ashing, and closed system ashing are used depending on the sample type and analysis requirements. The choice of method depends on factors such as the nature of the sample, the desired accuracy, and the specific parameters like temperature, residence time, and sample preparation.

Key Points Explained:
-
Dry Ashing:
- Process: Dry ashing involves heating the sample in a furnace at high temperatures, typically around 500°C, until all organic matter is combusted, leaving behind the inorganic residue (ash).
- Applications: This method is commonly used for samples that can withstand high temperatures without significant loss of volatile components.
- Advantages: It is a straightforward and widely used method, suitable for a broad range of materials.
- Limitations: High temperatures can lead to the loss of certain volatile elements, and the method may not be suitable for samples that decompose or react at high temperatures.
-
Wet Ashing:
- Process: Wet ashing involves the use of strong acids (such as nitric acid or sulfuric acid) to decompose the organic matter in the sample at relatively lower temperatures compared to dry ashing.
- Applications: This method is particularly useful for samples that are sensitive to high temperatures or contain volatile components that could be lost during dry ashing.
- Advantages: It allows for the preservation of volatile elements and is suitable for a wide range of sample types, including biological and environmental samples.
- Limitations: The use of strong acids requires careful handling and disposal, and the process can be more time-consuming than dry ashing.
-
Sulfated Ashing:
- Process: Sulfated ashing involves the addition of sulfuric acid to the sample before ashing, which helps neutralize and remove sulfur dioxide, a common byproduct of combustion.
- Applications: This method is particularly useful for samples that contain sulfur compounds, as it helps in obtaining a more accurate ash content by preventing the loss of sulfur as sulfur dioxide.
- Advantages: It improves the accuracy of ash determination in sulfur-containing samples.
- Limitations: The addition of sulfuric acid adds complexity to the process and requires careful handling.
-
Low-Temperature Ashing:
- Process: Low-temperature ashing is performed at much lower temperatures, typically around 200°C, using plasma or other low-temperature oxidation methods.
- Applications: This method is suitable for samples that are highly sensitive to heat or contain volatile components that would be lost at higher temperatures.
- Advantages: It minimizes the loss of volatile elements and is ideal for heat-sensitive materials.
- Limitations: The equipment required for low-temperature ashing can be more expensive and complex compared to traditional ashing methods.
-
Closed System Ashing:
- Process: Closed system ashing involves the use of airtight chambers to control the atmosphere during the ashing process, preventing the loss of volatile components and ensuring a more controlled environment.
- Applications: This method is used for samples that require precise control over the ashing environment, such as those containing highly volatile or reactive components.
- Advantages: It provides better control over the ashing process and minimizes the loss of volatile elements.
- Limitations: The equipment is more complex and costly, and the process may be more time-consuming.
-
Sample Preparation and Analysis:
- Preparation: Proper sample preparation is crucial for accurate ash determination. This may include drying, grinding, and homogenizing the sample to ensure uniformity.
- Analysis: After ashing, the resulting ash is often subjected to further analysis, such as proximity analysis (determining the moisture, volatile matter, fixed carbon, and ash content) and elementary analysis (determining the elemental composition of the ash).
By understanding the different methods of ash analysis and their respective advantages and limitations, one can choose the most appropriate technique based on the sample type and the specific requirements of the analysis.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process | Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Ashing | Heating at ~500°C in a furnace | Samples resistant to high temperatures | Simple, widely applicable | Loss of volatile elements, unsuitable for heat-sensitive samples |
| Wet Ashing | Acid decomposition at lower temperatures | Heat-sensitive or volatile-rich samples | Preserves volatile elements, versatile | Requires acid handling, time-consuming |
| Sulfated Ashing | Addition of sulfuric acid before ashing | Samples with sulfur compounds | Accurate for sulfur-containing samples | Complex process, requires careful handling |
| Low-Temperature Ashing | Plasma or low-temperature oxidation (~200°C) | Heat-sensitive or volatile-rich samples | Minimizes volatile loss, ideal for sensitive materials | Expensive equipment, complex setup |
| Closed System Ashing | Airtight chambers for controlled ashing | Samples requiring precise environmental control | Prevents volatile loss, controlled environment | Costly, time-consuming |
Need help choosing the right ash analysis method for your samples? Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What are the disadvantages of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Trade-offs for Your Lab
- What causes increase in ash content? Uncover the hidden culprits that harm your equipment.



















