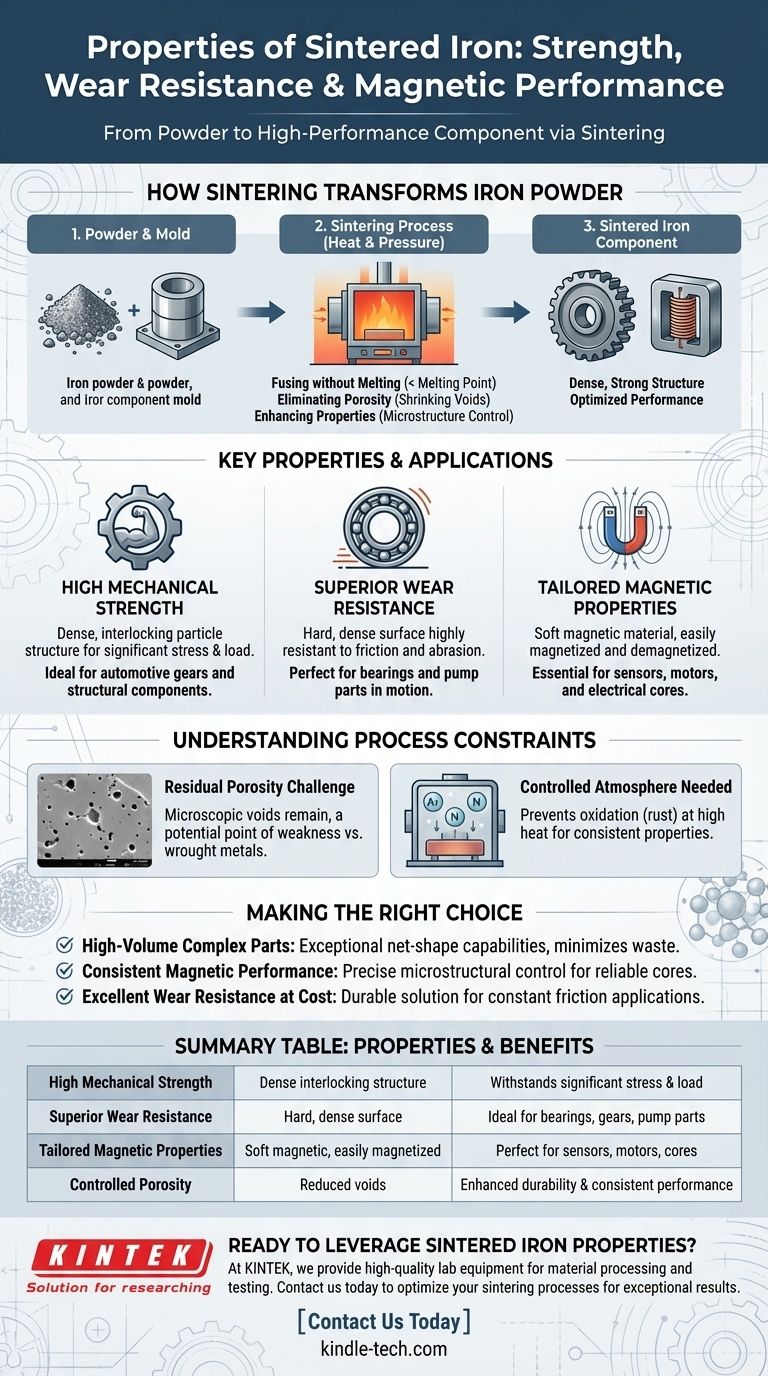
At its core, sintered iron is a material defined by high strength, excellent wear resistance, and valuable magnetic properties. This unique combination is achieved by taking iron powder and fusing it under heat and pressure—a process called sintering—which transforms the loose powder into a solid, high-performance component without ever melting it.
Sintering gives you the ability to engineer a final product with remarkable precision, turning simple iron powder into a dense, strong material optimized for demanding mechanical and electromagnetic applications.
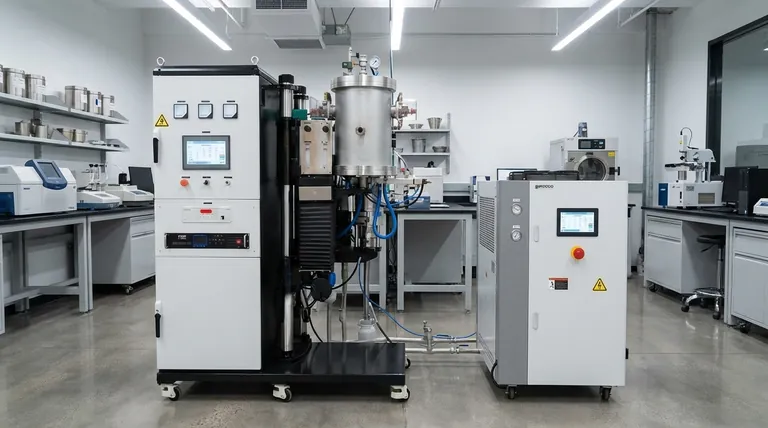

How Sintering Transforms Iron Powder
The unique properties of sintered iron are a direct result of the manufacturing process. Unlike casting, which involves molten metal, sintering works at a particle level to build a strong, cohesive structure.
The Core Principle: Fusing Without Melting
Sintering uses heat well below the melting point of iron. This heat, often combined with pressure, energizes the iron particles, causing them to bond and fuse at their contact points.
This process allows for the creation of complex shapes with tight tolerances directly from a mold, often eliminating the need for extensive secondary machining.
Eliminating Porosity for Strength
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce the empty space, or porosity, between the initial powder particles. As the particles fuse, these voids shrink, and the material's density increases significantly.
This reduction in porosity is directly responsible for the material's enhanced strength, structural integrity, and durability. A denser part is inherently stronger.
Enhancing Material Properties
The sintering process provides precise control over the final component's microstructure. This allows for the optimization of specific characteristics, such as electrical conductivity and, most notably for iron, its magnetic performance.
By controlling the density and grain structure, manufacturers can create components with highly consistent and reliable magnetic fields.
Key Properties and Their Applications
The transformation from powder to solid part imparts a set of highly desirable characteristics that make sintered iron a go-to material in several key industries.
High Mechanical Strength
By creating a dense, interlocking structure of iron particles, sintering produces components that can withstand significant mechanical stress. This makes them ideal for parts like automotive gears and structural components.
Superior Wear Resistance
The hard, dense surface created by sintering is highly resistant to friction and abrasion. This property is critical for components in constant motion, such as bearings and pump parts.
Tailored Magnetic Properties
Sintered iron is a soft magnetic material, meaning it can be easily magnetized and demagnetized. This, combined with the process's consistency, makes it perfect for applications in electronics and motors, including sensor rings and electrical cores.
Understanding the Process Constraints
While powerful, the sintering process has specific requirements and limitations that are important to understand when evaluating it for an application.
The Challenge of Residual Porosity
Although sintering dramatically reduces porosity, eliminating it completely is difficult. Any remaining microscopic voids can be a point of weakness compared to fully dense materials like wrought or forged metals.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Iron readily oxidizes (rusts) at the high temperatures used for sintering. To prevent this surface contamination, the process must be conducted in a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum or an inert shielding gas.
This requirement adds complexity and cost to the manufacturing setup but is essential for achieving the desired material properties and ensuring part-to-part consistency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting sintered iron depends entirely on balancing performance needs with manufacturing complexity and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex parts: Sintering offers exceptional net-shape capabilities, minimizing waste and secondary operations for components like gears and cams.
- If your primary focus is consistent magnetic performance: The precise microstructural control of sintering is ideal for creating reliable soft magnetic cores for sensors, inductors, and motors.
- If your primary focus is excellent wear resistance at a reasonable cost: Sintered iron provides a durable, high-performance solution for parts subjected to constant friction, such as bearings and pump components.
Ultimately, sintered iron delivers a powerful and precise balance of mechanical performance and manufacturability for a wide range of critical components.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High Mechanical Strength | Dense, interlocking particle structure | Withstands significant stress and load |
| Superior Wear Resistance | Hard, dense surface from sintering | Ideal for bearings, gears, and pump parts |
| Tailored Magnetic Properties | Soft magnetic material, easily magnetized | Perfect for sensors, motors, and electrical cores |
| Controlled Porosity | Reduced voids for structural integrity | Enhanced durability and consistent performance |
Ready to leverage the superior properties of sintered iron for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material processing and testing. Whether you are developing advanced sintered components for automotive, electronics, or industrial applications, our solutions help you achieve precise control over density, strength, and magnetic performance.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory needs and help you optimize your sintering processes for exceptional results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution

















