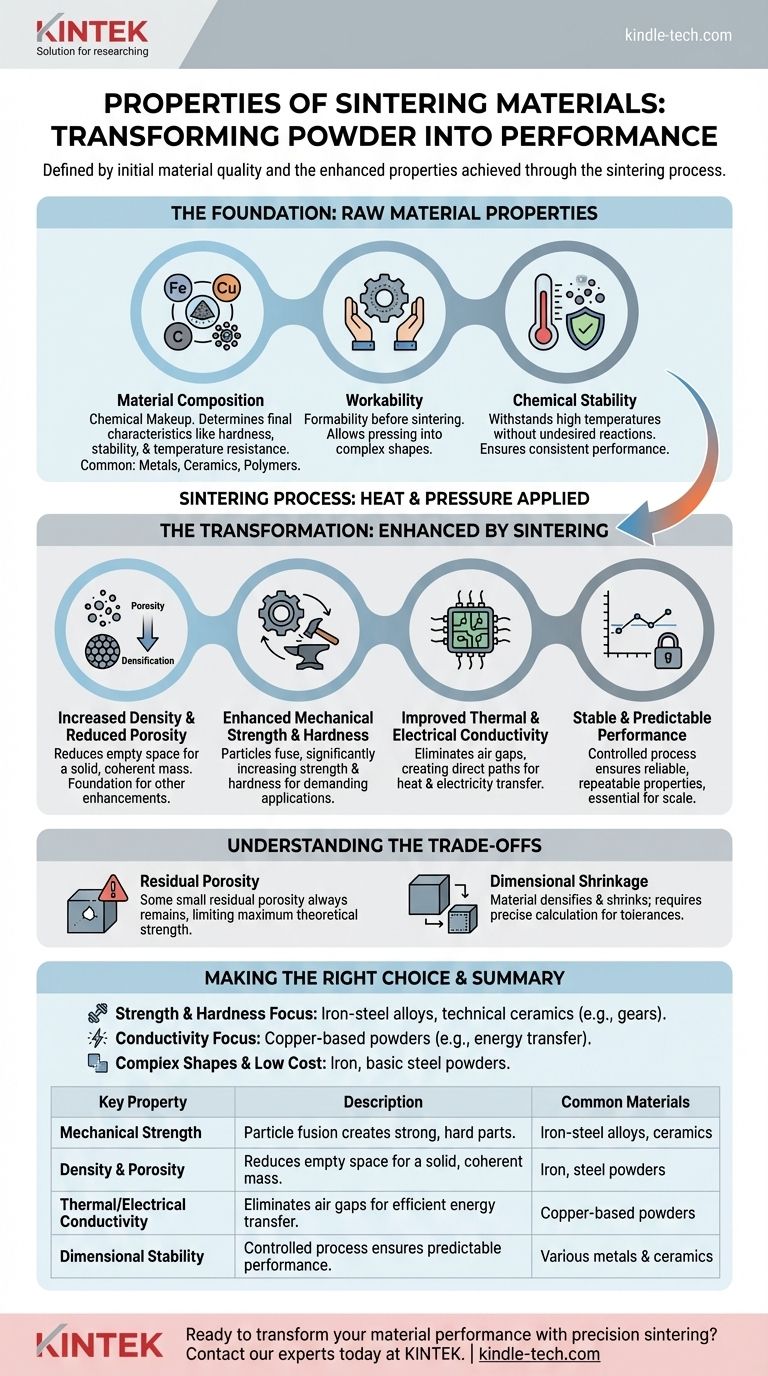
The properties of sintering materials are defined by two key factors: the inherent qualities of the initial powdered material—such as its composition and particle characteristics—and the enhanced physical properties achieved through the sintering process itself. Successful sintering fundamentally transforms loose powder into a solid object by reducing porosity while significantly improving strength, hardness, conductivity, and overall performance.
Sintering is a transformative process, not a simple molding technique. The goal is to take a base powder and fundamentally alter its structure to create a solid, dense component with superior and highly predictable physical properties.

The Foundation: Properties of the Raw Material
Before the process even begins, the choice of raw powder dictates the potential of the final product. The initial characteristics of the material are the building blocks for all subsequent enhancements.
Material Composition
The chemical makeup of the powder is the most critical factor. This determines the part's final characteristics, such as its hardness, chemical stability, and temperature resistance.
Common materials include metals like iron, steel, and copper alloys; ceramics for high-temperature applications; and even polymers for specific uses like filters.
Workability
Workability refers to the ability of the powdered material to be formed and handled before sintering. This property is determined by the mix of powders and additives used.
A material with good workability can be pressed into complex shapes, like gears and pulleys, holding its form until it is heated.
Chemical Stability
The material must be stable enough to withstand the high temperatures of the sintering furnace without undesired chemical reactions or degradation. This is especially critical for producing parts with consistent, reliable performance.
The Transformation: Properties Enhanced by Sintering
Sintering is an engineering process designed to impart specific, desirable properties that the loose powder does not possess. The heat and pressure applied create atomic bonds between particles, leading to a monolithic part.
Increased Density and Reduced Porosity
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce the empty space, or porosity, between the powder particles. This process, known as densification, creates a solid, coherent mass.
This reduction in porosity is the foundation for almost all other property enhancements.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Hardness
As particles fuse together, the resulting part becomes significantly stronger and harder than the initial compressed powder. This allows sintered components to be used in demanding applications like gears and bearings.
Materials like iron-nickel and carbon steels are specifically chosen for their ability to achieve high strength through this process.
Improved Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
By eliminating the air gaps between particles, sintering creates a more direct path for heat and electricity to travel. This greatly enhances the thermal and electrical conductivity of the material.
This property is crucial for components used in electronics or heat management systems.
Stable and Predictable Performance
A key outcome of a controlled sintering process, especially in a vacuum environment, is the creation of parts with highly stable and repeatable properties. This consistency and reliability are essential for manufacturing high-performance components at scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that engineers must manage to achieve the desired outcome.
Residual Porosity
It is nearly impossible to achieve 100% density through sintering alone. There will almost always be some small amount of residual porosity in the final part.
This can be a limiting factor for applications requiring the absolute maximum theoretical strength of a material, which might be better served by forging or machining from a solid billet.
Dimensional Shrinkage
As the material densifies and porosity is reduced, the component will shrink. This change in dimension must be precisely calculated and controlled to ensure the final part meets its required tolerances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The material and process parameters you select should be directly aligned with the primary requirement of your component.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and hardness: Use iron-steel alloys or technical ceramics, as these are engineered for high-performance structural components like gears.
- If your primary focus is thermal or electrical conductivity: Choose copper-based powders or other materials known for high intrinsic conductivity to create effective pathways for energy transfer.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes at a lower cost: Iron and basic steel powders offer excellent workability and are cost-effective for producing large volumes of intricate parts.
Ultimately, the properties of a sintered material are a direct result of intentional engineering, turning simple powders into high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Description | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Particle fusion creates strong, hard parts. | Iron-steel alloys, ceramics |
| Density & Porosity | Reduces empty space for a solid, coherent mass. | Iron, steel powders |
| Thermal/Electrical Conductivity | Eliminates air gaps for efficient energy transfer. | Copper-based powders |
| Dimensional Stability | Controlled process ensures predictable, reliable performance. | Various metals & ceramics |
Ready to transform your material performance with precision sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve superior results in your sintering projects. Whether you are developing high-strength components, conductive parts, or complex shapes, our expertise and reliable products ensure your materials meet their full potential.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sintering solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations



















