At its core, brazing is a highly versatile and reliable method for joining materials. It serves the primary purpose of creating strong, permanent, and often leak-proof joints between two or more metal components. This process is uniquely suited for applications where you need to join dissimilar metals or where the high heat of traditional welding would warp or damage the parts.
The purpose of brazing is not just to join metals, but to do so with minimal thermal stress on the components. This creates strong, clean joints in complex, dissimilar, or delicate assemblies where traditional welding would be impractical or destructive.

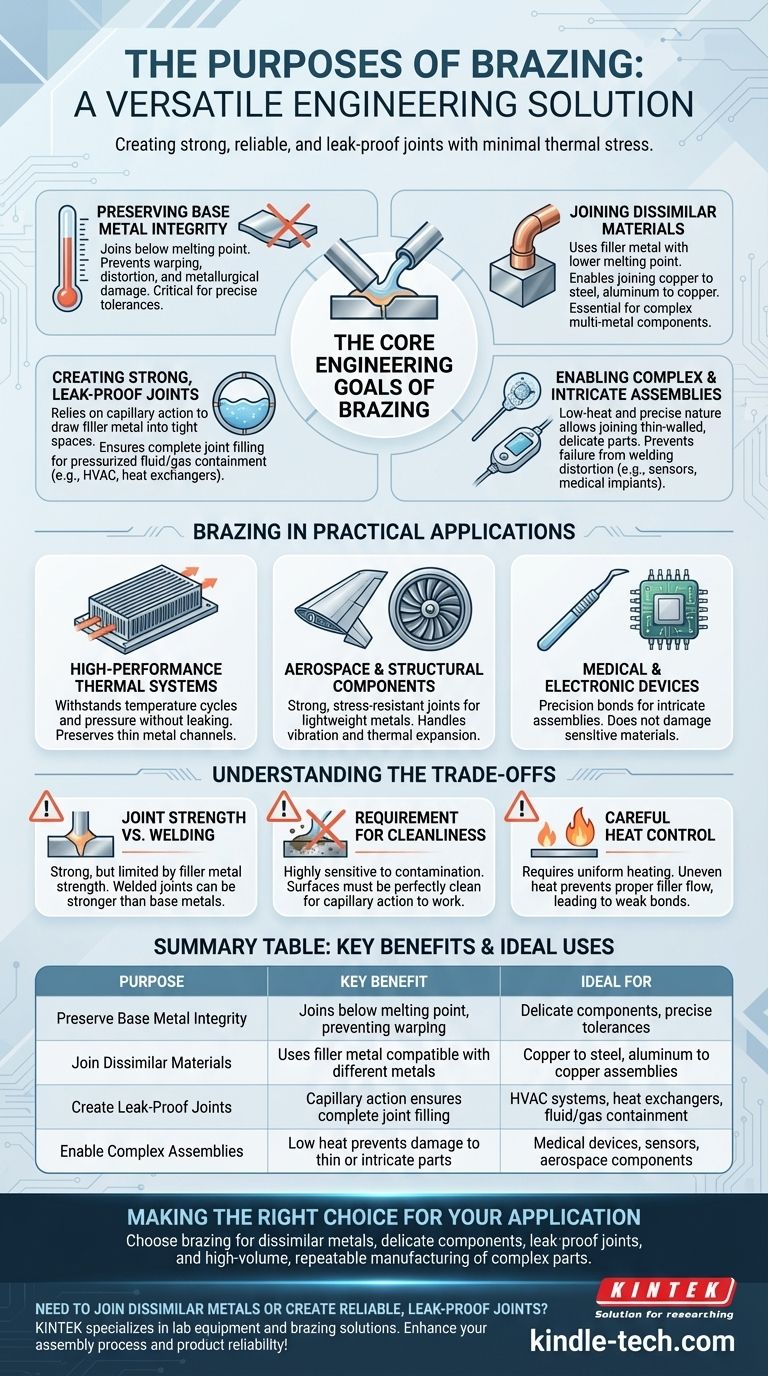
The Core Engineering Goals of Brazing
To understand brazing, it’s best to view it as a solution to specific engineering challenges. It is chosen over other methods to achieve distinct advantages in the final product.
Preserving Base Metal Integrity
Brazing is performed at a temperature below the melting point of the materials being joined.
This lower-heat approach is its most significant advantage. It prevents the warping, distortion, and metallurgical damage that high-heat welding can cause, which is critical for parts that must maintain precise tolerances.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
Brazing uses a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base metals.
This allows it to join materials that cannot be easily welded together, such as copper to steel or aluminum to copper. This capability is essential for creating complex multi-metal components.
Creating Strong, Leak-Proof Joints
The process relies on capillary action, where the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting space between the base components.
This action ensures the entire joint is filled completely, creating a strong, continuous, and leak-proof bond. This is why brazing is a standard in manufacturing HVAC assemblies and heat exchangers that must contain pressurized fluids or gases.
Enabling Complex and Intricate Assemblies
The low-heat and precise nature of brazing makes it ideal for joining delicate or thin-walled components.
It allows for the construction of complex parts, such as sensors or medical devices, where even slight distortion from welding would lead to product failure.
Brazing in Practical Applications
The engineering goals of brazing translate directly into its use across several demanding industries.
High-Performance Thermal Systems
Applications like micro-channel heat exchangers and heating/cooling assemblies depend on brazing. The joints must withstand constant temperature cycles and pressure without leaking, and the process preserves the integrity of the thin metal channels.
Aerospace and Structural Components
In aerospace, joining lightweight metals without compromising their structural strength is critical. Brazing provides strong, stress-resistant joints for various components that must handle vibration and thermal expansion.
Medical and Electronic Devices
Precision is paramount for medical implants, surgical tools, and electronic sensors. Brazing allows for the creation of clean, strong bonds in intricate assemblies without damaging sensitive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing is not the solution for every problem. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Joint Strength vs. Welding
A properly brazed joint is very strong, but its ultimate strength is limited by the filler metal. A welded joint, by contrast, can be as strong or stronger than the base metals themselves.
Requirement for Cleanliness
Brazing is highly sensitive to surface contamination. The base metals must be perfectly clean for capillary action to work correctly. Oxides, oils, or dirt will prevent the filler metal from flowing and result in a failed joint.
Careful Heat Control
Although it uses lower temperatures than welding, the heat must be applied uniformly to the entire joint. Uneven heating will prevent proper filler flow and create a weak bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct joining method depends entirely on your project's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or delicate components: Brazing is often the superior choice due to its lower process temperature, which prevents damage to the base materials.
- If your primary focus is creating leak-proof joints for fluid or gas systems: Brazing excels at creating complete, sealed joints through capillary action, making it ideal for HVAC and thermal applications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable manufacturing of complex parts: Automated brazing provides exceptional precision and consistency, making it a highly effective production method.
Ultimately, understanding the purpose of brazing is about recognizing it as a precise engineering tool for creating strong, reliable joints where heat control and material integrity are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Preserve Base Metal Integrity | Joins below melting point, preventing warping | Delicate components, precise tolerances |
| Join Dissimilar Materials | Uses filler metal compatible with different metals | Copper to steel, aluminum to copper assemblies |
| Create Leak-Proof Joints | Capillary action ensures complete joint filling | HVAC systems, heat exchangers, fluid/gas containment |
| Enable Complex Assemblies | Low heat prevents damage to thin or intricate parts | Medical devices, sensors, aerospace components |
Need to join dissimilar metals or create reliable, leak-proof joints? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including brazing solutions for laboratory and manufacturing needs. Our expertise helps you achieve strong, precise bonds while preserving the integrity of your materials. Contact us today to discuss how our brazing solutions can enhance your assembly process and product reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining



















