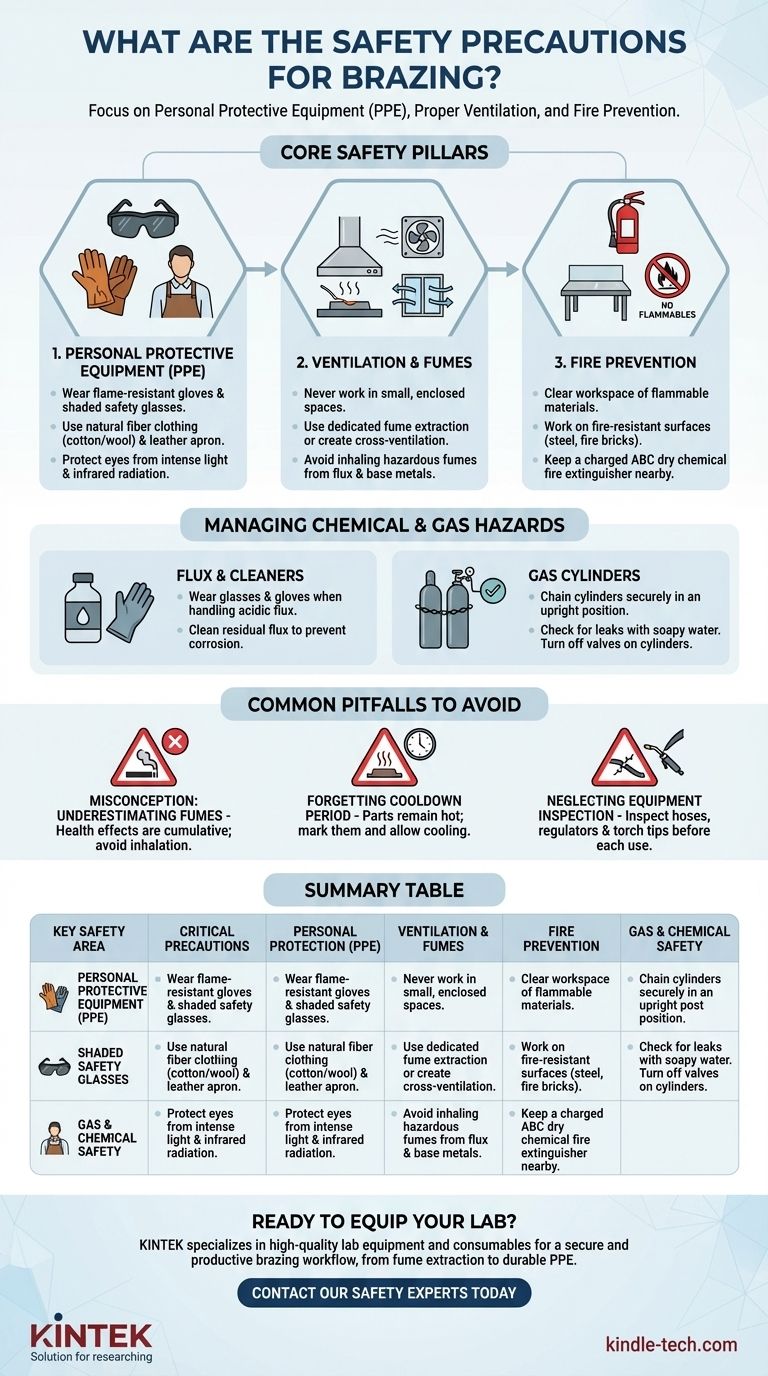
To braze safely, you must focus on three critical areas: personal protective equipment (PPE) to guard against heat and radiation, proper ventilation to remove hazardous fumes, and fire prevention within your workspace. These precautions address the primary risks of high heat, chemical exposure from flux, and the toxic fumes generated when heating metals.
Brazing safety is not just about avoiding burns. A truly safe process requires a systematic approach that manages the invisible dangers of chemical fumes and pressurized gases just as diligently as the visible threat of the torch flame.
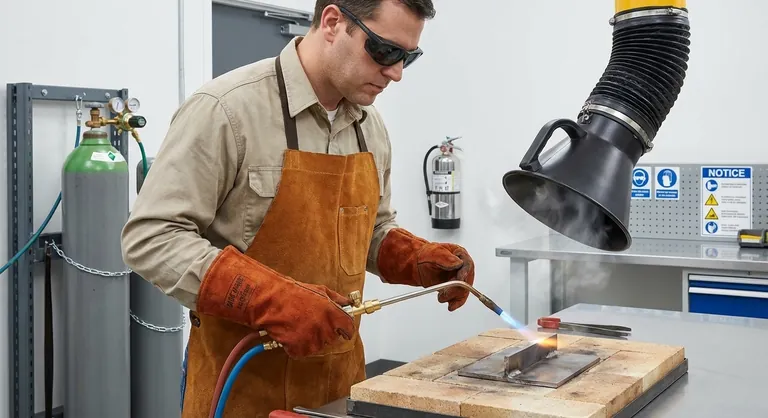

The Primary Hazard: Extreme Heat and Fire Risk
The most obvious danger in brazing is the high temperature required to melt the filler metal. Protecting yourself and your environment from this heat is the first step.
Protecting Yourself from Burns
Always wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). This is not optional. Your minimum gear should include flame-resistant gloves (often leather), and safety glasses with a shade rating (e.g., shade 3-5) to protect your eyes from the intense light and infrared radiation.
Wear clothing made of natural fibers like cotton or wool, as synthetic materials like polyester can melt and stick to your skin if exposed to high heat or sparks. A leather apron provides an excellent additional layer of protection.
Securing Your Workspace
Your brazing area must be completely free of flammable materials. Clear a wide radius around your work of any paper, rags, wood, or flammable liquids.
Work on a fire-resistant surface, such as a steel table, fire bricks, or a welding blanket. Always keep a charged, appropriate class of fire extinguisher (e.g., ABC dry chemical) within arm's reach.
The Invisible Danger: Fumes and Ventilation
What you can't see can be more dangerous than the flame itself. Heating metals and flux releases fumes that can be toxic.
Why Ventilation is Non-Negotiable
When heated, the base metals, filler metal, and especially the flux release fumes into the air. Inhaling these can cause short-term illness, like metal fume fever, or long-term respiratory damage.
Some filler metals historically contained cadmium, a highly toxic substance. While less common now, you should always assume fumes are hazardous and protect yourself accordingly. Read the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for your specific filler metal and flux.
Establishing Proper Airflow
Never braze in a small, enclosed, or poorly ventilated space. At a minimum, work in an area with open doors and windows to create cross-ventilation.
For frequent work, a dedicated fume extraction system that captures fumes at the source is the best practice. A fan blowing air away from your breathing zone is a good secondary measure, but it does not remove the contaminants from the room.
Managing Chemical and Gas Hazards
Beyond heat and fumes, you are working with corrosive chemicals and high-pressure gas cylinders that demand respect.
Handling Flux and Cleaners
Brazing flux is often acidic or corrosive to facilitate cleaning the metal. Always wear safety glasses and gloves when handling flux to prevent skin irritation and eye damage. Ensure you clean any residual flux off the part after brazing, as it can cause corrosion over time.
Safe Use of Gas Cylinders
Gas cylinders for your torch (e.g., acetylene, propane, oxygen) are under immense pressure. Always chain cylinders securely to a wall or cart in an upright position to prevent them from falling and breaking the valve.
Check for leaks at all connections using a soapy water solution before you light the torch; if you see bubbles, there is a leak that must be fixed. When finished, always turn off the valves on the cylinders themselves, not just at the torch handle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Trusting your senses is not enough. Many hazards are not immediately obvious, leading to dangerous complacency.
The Misconception: "It's Just a Little Smoke"
The most common mistake is underestimating the danger of fumes. The health effects of inhaling metal and flux fumes are cumulative. What seems like minor irritation today can contribute to serious chronic health problems years later.
Forgetting the Cooldown Period
The danger does not end when you extinguish the torch. The workpiece will remain hot enough to cause severe burns for several minutes. Clearly mark hot parts and allow them to cool completely before handling without gloves.
Neglecting Equipment Inspection
Hoses, regulators, and torch tips are not permanent. They degrade over time. Before each use, perform a quick visual inspection for cracks, cuts, or worn spots in your hoses. A failing hose or regulator is a significant fire and explosion risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to safety should be a consistent, disciplined workflow, not a series of afterthoughts.
- If your primary focus is a quick, one-off repair: Prioritize workspace safety by clearing all combustibles and ensuring you have a fire extinguisher and basic PPE. Open every available door and window for maximum ventilation.
- If your primary focus is setting up a permanent workstation: Invest in a proper fume extraction system and a dedicated fire-resistant work surface. Create a permanent, secure storage solution for your gas cylinders.
- If your primary focus is training others or establishing professional procedure: Write a formal safety checklist covering pre-work (PPE, ventilation, equipment check), in-process (situational awareness), and post-work (cooldown, gas shutoff, cleanup).
A safe brazing operation is the direct result of a prepared and disciplined operator.
Summary Table:
| Key Safety Area | Critical Precautions |
|---|---|
| Personal Protection (PPE) | Flame-resistant gloves, shaded safety glasses, natural fiber clothing, leather apron. |
| Ventilation & Fumes | Source fume extraction or cross-ventilation; never work in enclosed spaces. |
| Fire Prevention | Clear workspace of flammables; use fire-resistant surfaces; keep a fire extinguisher nearby. |
| Gas & Chemical Safety | Securely chain gas cylinders; check for leaks; wear gloves/glasses when handling flux. |
Ready to Equip Your Lab for Safe and Efficient Brazing?
Brazing safety is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support a secure and productive workflow. From fume extraction systems to durable PPE, we have the solutions your laboratory needs.
Contact our safety experts today to discuss how we can help you build a safer brazing operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















