The central tube in a furnace is most commonly called a working tube, process tube, or reactor. This terminology is specific to a tube furnace, a specialized piece of equipment used in labs and industry for high-temperature material processing, not a standard residential heating unit. The tube's function is to hold the material being heated and isolate it from the heating elements themselves.
The tube in a tube furnace is not part of the heating system itself. Instead, it is the isolated chamber that contains the material or process. The furnace heats the outside of the tube, allowing for precise thermal control over the environment within it.

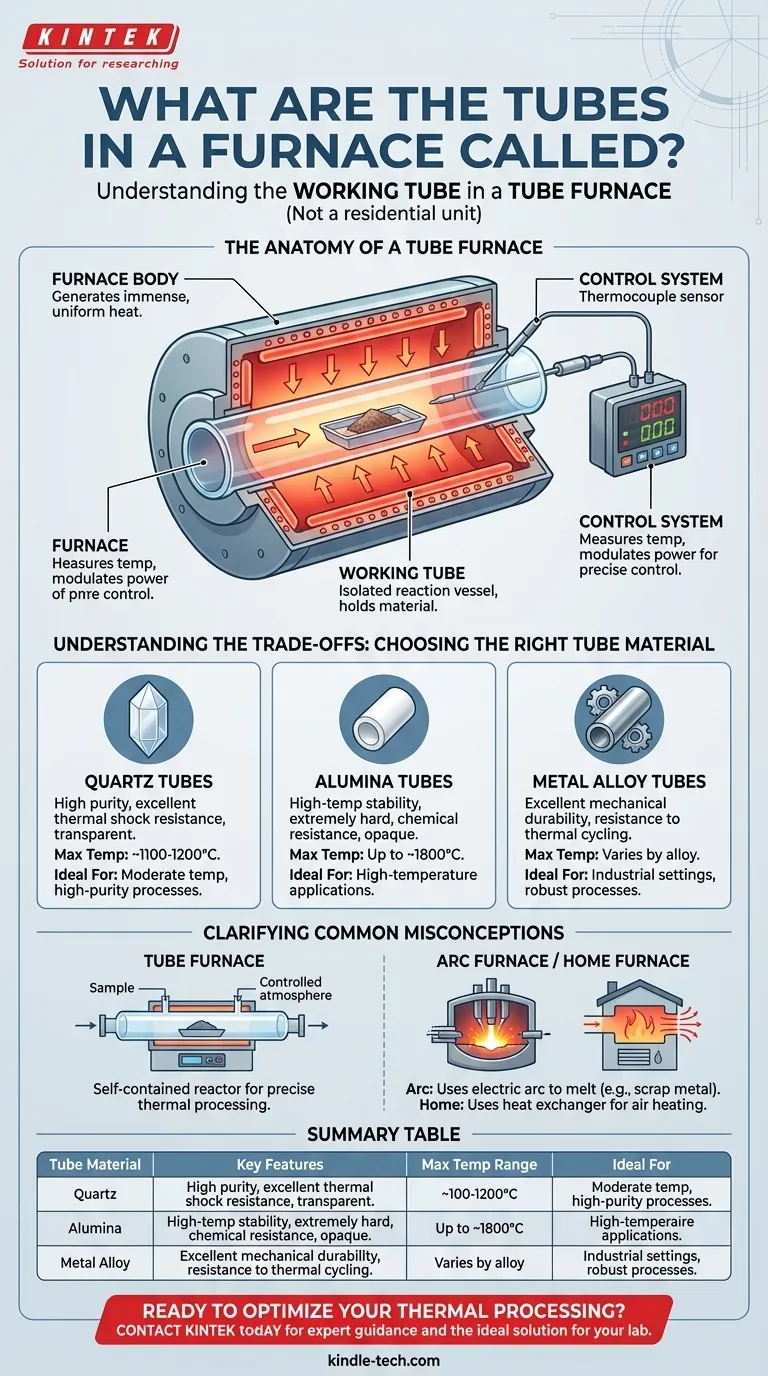
The Anatomy of a Tube Furnace
To understand the role of the working tube, it's essential to understand its place within the overall system. A tube furnace is a system of distinct components working together.
The Furnace Body: The Heat Source
The main body of the furnace is a thermally insulated shell containing heating elements. These elements, often high-resistance coils or rods made of materials like silicon carbide, are embedded in a ceramic fiber matrix.
This part of the furnace does one job: it generates immense, uniform heat within its central cavity. It is the "oven" that surrounds the tube.
The Working Tube: The Controlled Environment
The working tube is a separate, removable cylinder that slides into the central cavity of the furnace body. It does not generate heat. Its purpose is to act as the reaction vessel.
This is where you place your samples or run your chemical processes. Because it is a distinct component, it can be sealed with flanges to create a vacuum or introduce specific gases, creating a highly controlled atmosphere that is isolated from the heating elements.
The Control System: The Brain
A thermocouple is used to measure the temperature, typically near the outside of the working tube. This sensor sends feedback to a controller, which modulates the power to the heating elements.
This feedback loop allows for extremely precise and stable temperature control for the process happening inside the tube.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Choosing the Right Tube Material
The material of the working tube is not a minor detail; it is a critical choice that dictates the furnace's capabilities and limitations.
Quartz Tubes
Quartz is a very common material due to its high purity and excellent thermal shock resistance at moderate temperatures. It is transparent to some forms of radiation and is chemically inert in many situations.
However, quartz typically has a maximum operating temperature of around 1100-1200°C, above which it will soften and devitrify.
Alumina Tubes
Alumina is a high-purity ceramic capable of withstanding much higher temperatures, often up to 1800°C. It is extremely hard and resistant to chemical attack.
The trade-off is that alumina is opaque and more susceptible to cracking from severe thermal shock compared to quartz.
Metal Alloy Tubes
Tubes made from nickel alloys or other refractory metals offer excellent mechanical durability and resistance to thermal cycling. They are often used in industrial settings where robustness is key.
The primary drawback is the potential for metal ions to contaminate the sample or process, making them unsuitable for high-purity applications.
Clarifying Common Misconceptions
The term "furnace" can cause confusion. It's important to distinguish between different types of equipment.
Tube Furnace vs. Arc Furnace
An arc furnace operates on a completely different principle. It uses a high-power electric arc to directly melt material, like scrap metal. It has an "electrode" or "stinger" to create the arc, not a working tube to contain a process.
Lab Furnace vs. Home Furnace
A residential furnace for heating a home uses a heat exchanger. Air is blown across a heated metal surface and then distributed through ductwork. It shares no design principles with a laboratory tube furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal tube material is dictated entirely by your application's temperature, chemical environment, and purity requirements.
- If your primary focus is high purity at moderate temperatures (below 1100°C): Quartz is the standard choice for its inertness and optical clarity.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability (up to 1800°C): High-purity Alumina offers excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is durability and resistance to thermal shock: A specific metal or refractory alloy tube may be necessary, especially in industrial environments.
- If your primary focus is creating a controlled atmosphere: Your choice of tube must be paired with appropriate vacuum flanges and seals to ensure the integrity of your process.
Understanding that the tube functions as the self-contained reactor, separate from the heater, is the key to mastering your thermal processing applications.
Summary Table:
| Tube Material | Key Features | Max Temp Range | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | High purity, thermal shock resistance, transparent | ~1100-1200°C | Moderate temp, high-purity processes |
| Alumina | High-temp stability, chemical resistance, opaque | Up to ~1800°C | High-temperature applications |
| Metal Alloy | Mechanical durability, thermal cycling resistance | Varies by alloy | Industrial settings, robust processes |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing?
Choosing the right working tube is critical for your application's success. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, helping you select the ideal tube furnace and components for your specific temperature, atmosphere, and purity requirements.
We provide the guidance and equipment to ensure precise, reliable results for your laboratory needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Purity
- What factors influence the general design of a tube furnace? Match Your Process with the Perfect System
- How does an alumina tube furnace with a controlled atmosphere simulate conditions in CSP environments? Master Accuracy.



















