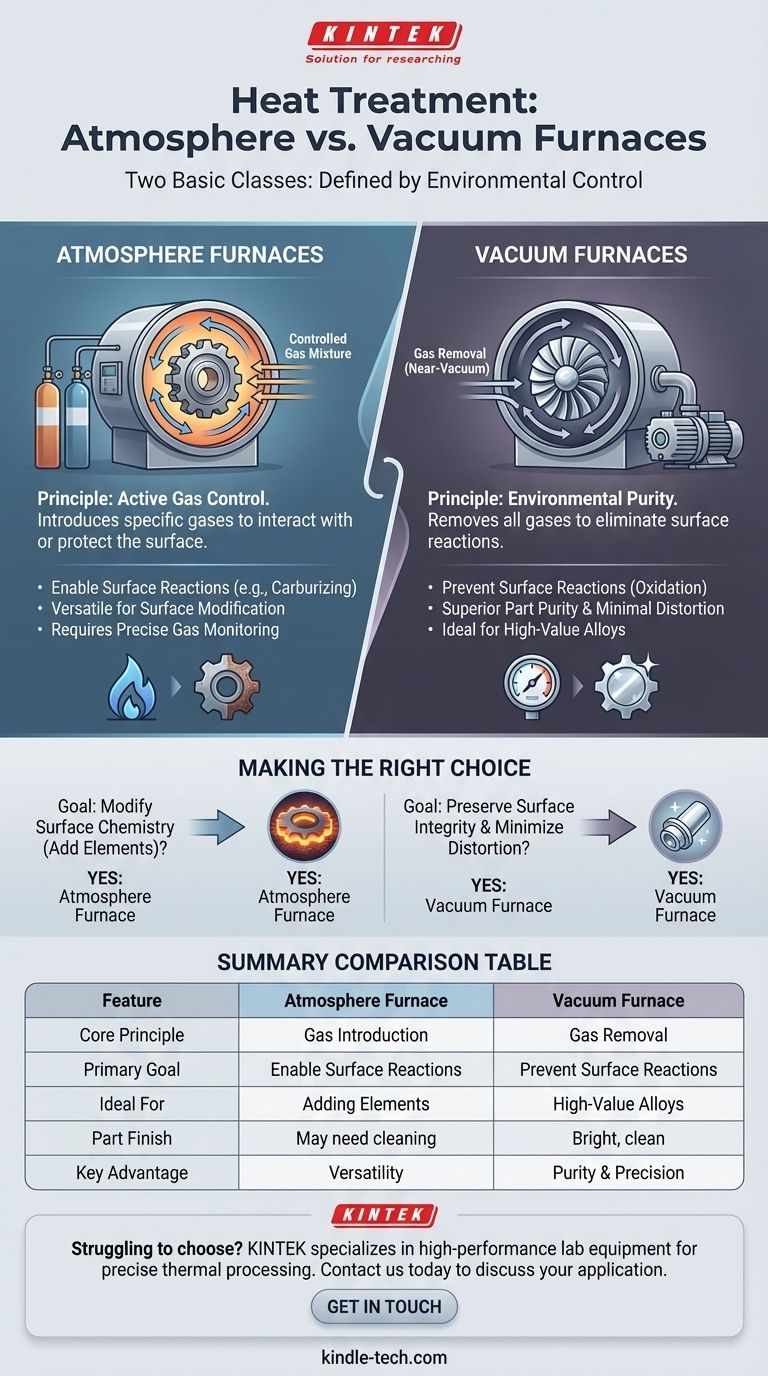
At a fundamental level, the two basic classes of furnaces used for industrial heat treatment are Atmosphere Furnaces and Vacuum Furnaces. The essential distinction between them lies not in how they generate heat, but in how they control the environment surrounding the metal component during the thermal cycle. This environmental control is the deciding factor for achieving the desired material properties.
The choice between these two furnace classes boils down to a single, critical question: Is it better to actively introduce a specific, controlled gas to achieve a desired surface reaction, or to remove all reactive gases to prevent any surface reaction whatsoever?

Understanding Atmosphere Furnaces
Atmosphere furnaces are designed to operate with a specific, carefully controlled gas mixture filling the heating chamber. This gas "atmosphere" displaces the ambient air to protect the workpiece.
The Principle of Active Gas Control
The core principle is to use a specific gas or mixture of gases to create a predictable and beneficial environment. This environment actively interacts with or protects the surface of the metal part being treated.
Key factors like the furnace atmosphere, temperature, and airflow are precisely monitored to ensure the process is repeatable and the final product meets specification.
Why Use a Controlled Atmosphere?
While a primary goal is often to prevent oxidation and scaling, controlled atmospheres can also be used to intentionally change the surface chemistry of a part. Different gas mixtures are used for different metallurgical outcomes.
Common controllable atmospheres include endothermic gas, exothermic gas, and ammonia-based atmospheres, each designed for processes like carbonitriding, annealing, or sintering.
Understanding Vacuum Furnaces
Vacuum furnaces operate on the opposite principle. Instead of introducing a specific gas, they are designed to remove virtually all gases and vapors from the heating chamber, creating a near-vacuum.
The Principle of Environmental Purity
The primary goal of a vacuum furnace is to create the purest possible environment for heat treatment. By pumping out air and other potential contaminants, reactions between the hot metal surface and environmental gases are eliminated.
This ensures a complete lack of oxidation and contamination, resulting in bright, clean parts directly out of the furnace with no need for subsequent cleaning.
Ideal Applications for Vacuum
Vacuum treatment is the preferred method for high-value materials where surface integrity is paramount. It is highly recommended for heat-treating tool steels, martensitic stainless steels, and other advanced alloys.
The precise temperature control and lack of atmosphere provide superior quality with minimal deformation, which is a significant economic advantage for complex or high-precision components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace class is universally superior; the correct choice is dictated entirely by the process requirements and the material being treated.
Atmosphere Furnaces: Versatility vs. Complexity
These furnaces are highly versatile and are required for any process that involves adding elements to a material's surface, such as carburizing (adding carbon).
However, they require complex external systems for gas generation and precise monitoring. An improperly controlled atmosphere can ruin parts by causing unintended decarburization or sooting.
Vacuum Furnaces: Purity vs. Limitation
Vacuum furnaces offer the ultimate in part protection, repeatability, and cleanliness. They are unmatched for processes like hardening and annealing sensitive alloys.
Their primary limitation is that they can only be used for processes that do not require a reactive gas. Furthermore, they often represent a higher initial capital investment and may have lower throughput than large, continuous atmosphere furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of furnace technology must be driven by the end goal for your material's properties.
- If your primary focus is modifying the surface chemistry (e.g., adding carbon or nitrogen): An atmosphere furnace is the necessary choice, as it provides the required reactive gases for the process.
- If your primary focus is preserving surface integrity and minimizing distortion on high-value alloys: A vacuum furnace is the superior option due to its inert environment and precise thermal control.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace means choosing the environment that best serves the material's final intended properties and performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Atmosphere Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Introduces controlled gas mixture | Removes all gases (near-vacuum) |
| Primary Goal | Enable surface reactions (e.g., carburizing) | Prevent surface reactions (oxidation) |
| Ideal For | Adding elements to surface (carbon, nitrogen) | High-value alloys, sensitive materials |
| Part Finish | May require post-treatment cleaning | Bright, clean parts out of furnace |
| Key Advantage | Process versatility for surface modification | Superior part purity and minimal distortion |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your heat treatment process? The choice between an atmosphere and vacuum furnace is critical for achieving your desired material properties and surface integrity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces tailored for precise thermal processing. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your laboratory's specific needs, whether you're working with tool steels, stainless steels, or advanced alloys. Contact us today to discuss your application and ensure optimal results for your materials. Get in touch with our specialists to find the perfect furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum high-temperature furnace necessary for fusion experiments? Ensure Data Validity and Precision
- How does heat treating make metal stronger? Optimize Your Metal's Strength and Durability
- What industry is annealing used in? From Automotive to Medical Devices
- What is the process of a mesh belt furnace? Achieve Consistent, High-Volume Heat Treatment
- What role does a high-temperature sintering furnace play in NZSP fabrication? Key to Optimal Ionic Conductivity
- Is brazing better than soldering? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Strength Joining Method
- Why do superdry reforming processes require high-temperature furnaces? Unlock Higher Conversion with Precision Control
- What are the benefits of using a suitable hot zone in a furnace? Boost Efficiency & Product Quality



















