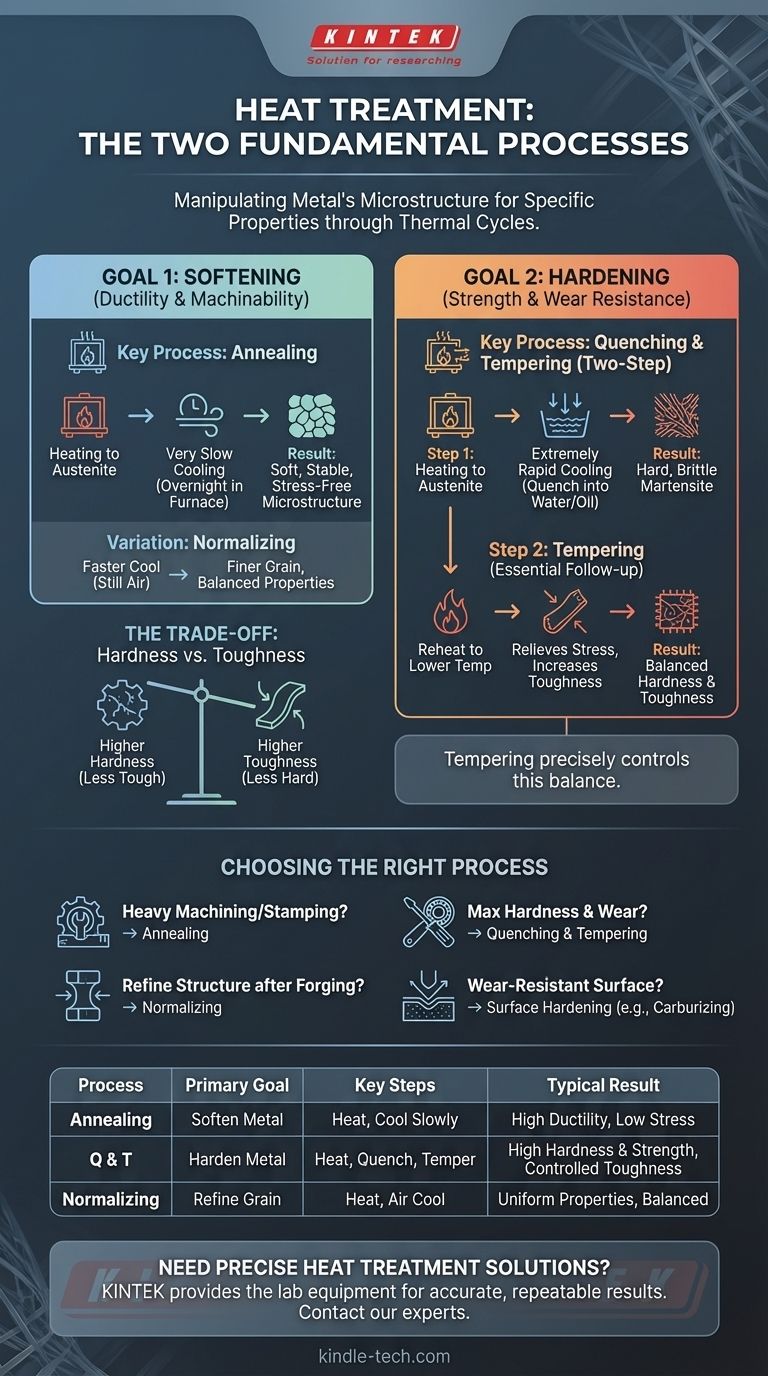
While the question is often simplified to two opposing processes, heat treatment is actually a broad field of metallurgy involving numerous techniques. The two most fundamental and contrasting goals are softening a metal, primarily through annealing, and hardening it, achieved through a two-step process of quenching and tempering. These procedures don't just change the metal; they fundamentally rearrange its internal microstructure to achieve specific mechanical properties.
Heat treatment is not about a handful of recipes; it is the deliberate control of a metal's thermal cycle—its heating, holding, and cooling phases—to precisely manipulate its internal crystal structure. Understanding this principle allows you to tailor a material's properties for almost any engineering application.
The Fundamental Goal: Manipulating a Metal's Microstructure
To understand heat treatment, you must look beyond the furnace and see what's happening at a microscopic level.
What is Heat Treatment?
Heat treatment is a group of controlled processes used to alter the physical and, at times, chemical properties of a material. The process involves heating the metal to a specific temperature, holding it at that temperature for a set duration (soaking), and then cooling it at a prescribed rate.
The goal is to change properties like hardness, strength, toughness, ductility, and wear resistance without altering the part's shape.
How Heat Transforms Metal
Heating a metal rearranges its internal crystal lattice, known as its microstructure. For steel, heating it above a critical temperature transforms its structure into a state called austenite, where the atomic arrangement is uniform and capable of dissolving carbon.
The final properties of the metal are determined entirely by what happens to this austenitic structure as it cools. The rate of cooling is the most critical variable.
The Two Primary Objectives: Softening vs. Hardening
Nearly all heat treatment processes can be categorized by their primary objective: to make a metal softer and more formable, or to make it harder and more durable.
Category 1: Softening for Ductility and Machinability
Sometimes, the goal is to make a metal as soft as possible. This relieves internal stresses, improves ductility (the ability to be drawn or formed), and makes the material easier to machine.
-
Key Process: Annealing Annealing involves heating the steel to its austenitic range and then cooling it very slowly, often by leaving it inside the furnace to cool overnight. This slow cooling allows the microstructure to form into its softest, most stable, and stress-free state.
-
A Variation: Normalizing Normalizing is similar to annealing, but the cooling is done faster, typically in still air. This results in a finer, more uniform grain structure. A normalized part is slightly harder and stronger than an annealed one but is much tougher and less brittle than a fully hardened part.
Category 2: Hardening for Strength and Wear Resistance
This is the more commonly known objective, used to create tools, bearings, and gears that can withstand high stress and wear. This is always a multi-step process.
-
Key Process: Quenching To achieve maximum hardness, the steel is heated to form austenite and then cooled extremely rapidly. This is done by plunging it into a quenching medium like water, oil, or even forced air.
This rapid cooling, or quenching, traps the atomic structure in a very hard, brittle, and highly stressed state known as martensite. A quenched-only part is often too brittle for practical use.
-
The Essential Follow-up: Tempering A quenched part is almost always tempered. This involves reheating the hardened part to a much lower temperature (e.g., 200-650°C or 400-1200°F) and holding it for a period.
Tempering reduces the extreme hardness and brittleness of the martensite, relieving internal stresses and significantly increasing the material's toughness. The final balance of hardness and toughness is precisely controlled by the tempering temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process is an exercise in managing engineering trade-offs. You can't maximize every property simultaneously.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
This is the most critical trade-off in heat treatment. Hardness is the resistance to scratching and indentation, while toughness is the ability to absorb energy and resist fracture.
As you increase a metal's hardness, you almost always decrease its toughness, making it more brittle. Tempering is the act of deliberately sacrificing some hardness to regain essential toughness.
The Role of Cooling Rate
The rate of cooling dictates the final microstructure. A very slow cool (annealing) produces a soft structure. A very fast cool (quenching) produces a hard structure. Intermediate cooling rates (normalizing) produce properties somewhere in between.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
Rapid cooling is a violent process that induces massive internal stress. If not managed correctly, this stress can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack during the quench. The choice of quenchant (water is more severe than oil) and part geometry are critical factors.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Goal
Your selection must be driven by the final application of the component.
- If your primary focus is preparing a material for heavy machining or stamping: Annealing is the correct choice to maximize softness and relieve internal stress.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness and wear resistance for a tool or bearing: Quenching followed by tempering is the required two-step process.
- If your primary focus is refining the grain structure and ensuring uniform properties after forging: Normalizing provides a good balance of strength and ductility.
- If your primary focus is creating a wear-resistant surface on a tough, impact-resistant component: A surface hardening process like carburizing or induction hardening is ideal.
By understanding these core principles, you can move beyond simple definitions and begin to specify material properties with intention and precision.

Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Steps | Typical Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften Metal | Heat to austenite, cool slowly | Increased ductility, reduced stress, improved machinability |
| Quenching & Tempering | Harden Metal | Heat to austenite, quench rapidly, then temper | High hardness and strength, with controlled toughness |
| Normalizing | Refine Grain Structure | Heat to austenite, cool in air | Uniform properties, balanced strength and ductility |
Need to specify the perfect heat treatment for your lab materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve accurate and repeatable heat treatment results. Whether you're annealing for softness or quenching for hardness, our solutions ensure you can control the thermal cycle with confidence.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's material science and metallurgy needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















