In a food chemistry laboratory, an oven is an indispensable tool used for precise moisture content determination, sample preparation, dry-heat sterilization, and accelerated shelf-life testing. Its primary function is not just heating, but the controlled and uniform application of thermal energy to prepare samples and equipment for accurate analysis.
Beyond simple heating, a laboratory oven is a critical instrument for achieving sample stability and consistency. Its core purpose is to precisely control a sample's state—most often by removing water—which is a foundational step that underpins the accuracy of many essential food chemistry analyses.

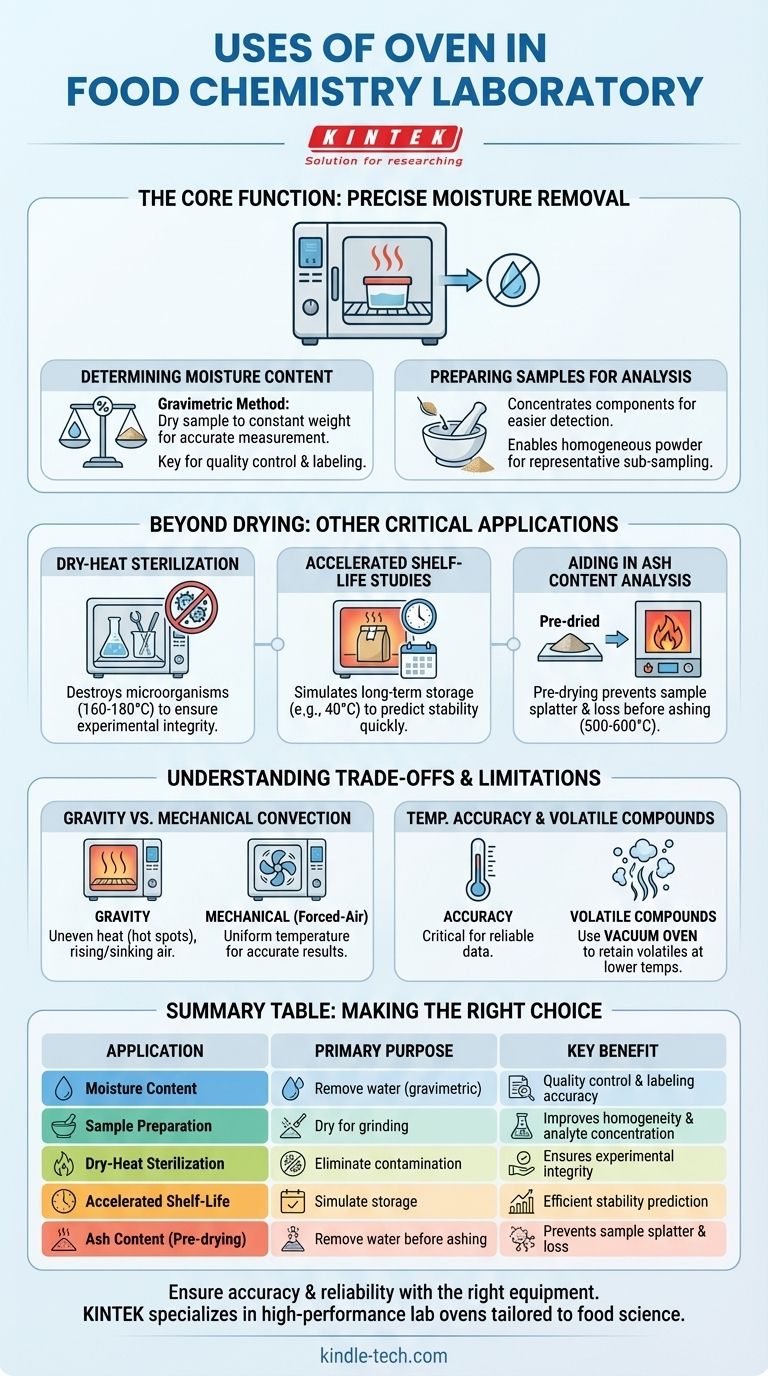
The Core Function: Precise Moisture Removal
The most frequent and critical application of a laboratory oven is the removal of water from a food sample. This process is fundamental to several analytical procedures.
Determining Moisture Content
Moisture content is a key metric for nutritional labeling, quality control, and determining a product's shelf stability. The oven is central to the standard "gravimetric" method.
A sample is weighed, placed in the oven at a specific temperature (typically 100-105°C), and dried until it reaches a constant weight. The difference between the initial and final weight is the amount of moisture that was removed.
Preparing Samples for Analysis
Many analytical techniques require a dry sample. Removing water concentrates the other components (like protein, fat, or minerals), making them easier to detect and quantify.
Furthermore, a dry, brittle sample is much easier to grind into a fine, homogenous powder. This homogeneity is essential for ensuring that a small sub-sample taken for analysis is truly representative of the entire batch.
Beyond Drying: Other Critical Applications
While moisture removal is its primary job, the lab oven's utility extends to several other key tasks that ensure experimental integrity and efficiency.
Dry-Heat Sterilization
For experiments where microbial contamination must be avoided, an oven provides a way to sterilize certain types of equipment. Clean glassware and some heat-resistant metal tools can be placed in the oven at high temperatures (e.g., 160-180°C) for a set period.
This dry-heat process destroys microorganisms, ensuring that analytical results are not skewed by microbial activity.
Accelerated Shelf-Life Studies
Manufacturers need to know how their products will hold up over time. An oven can be used to simulate long-term storage in a much shorter period.
By storing a product at a controlled, elevated temperature (e.g., 40°C), chemists can accelerate the chemical degradation reactions that affect flavor, color, texture, and nutritional value, allowing them to predict a product's shelf life.
Aiding in Ash Content Analysis
Determining the total mineral (ash) content of a food involves burning off all organic matter in a very high-temperature muffle furnace (500-600°C).
Placing a wet sample directly into a muffle furnace can cause it to splatter, resulting in sample loss. To prevent this, the sample is often pre-dried in a standard laboratory oven to gently remove the water first.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Not all ovens are created equal, and understanding their limitations is critical for generating reliable data. The wrong choice or improper use can directly compromise your results.
Gravity vs. Mechanical Convection
Gravity convection ovens are simpler and rely on the natural circulation of hot air rising and cool air sinking. This can lead to uneven heating and "hot spots" within the chamber.
Mechanical (or forced-air) convection ovens use a fan to actively circulate air, ensuring a much more uniform temperature throughout the chamber. For most analytical work, especially moisture determination, a mechanical convection oven is required for accurate and repeatable results.
Temperature Accuracy and Uniformity
The reliability of your data depends on the oven's ability to hold a precise temperature. A high-quality lab oven has a sensitive thermostat and is well-insulated to maintain temperature uniformity. An inaccurate oven can lead to incomplete drying or degradation of heat-sensitive compounds, skewing results.
Not for Volatile Compounds
A standard oven removes mass by evaporation. However, it cannot distinguish between water and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like aromas or certain oils. If a food is rich in these compounds, heating it in a conventional oven will cause them to evaporate along with the water, leading to an overestimation of the moisture content.
For such samples, a vacuum oven is necessary. By reducing the pressure, it allows water to boil at a much lower temperature, preserving the volatile compounds you want to retain.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The oven's application must be matched to the analytical objective. Your choice of method and equipment will determine the validity of your conclusions.
- If your primary focus is nutritional labeling: You will use a calibrated, mechanical convection oven for precise moisture content determination by drying samples to a constant weight.
- If your primary focus is preparing samples for extraction: The main goal is complete drying to improve grinding efficiency and concentrate non-volatile analytes for subsequent analysis.
- If your primary focus is microbiological integrity: You will use a high-temperature setting for the dry-heat sterilization of glassware and tools to prevent cross-contamination.
- If your primary focus is analyzing heat-sensitive or aromatic foods: You must use a vacuum oven to determine moisture content without driving off valuable volatile compounds.
Mastering the proper use of a laboratory oven is a foundational skill for generating reliable and reproducible data in food science.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content Determination | Remove water for gravimetric analysis | Essential for quality control and labeling |
| Sample Preparation | Dry samples for grinding and analysis | Improves homogeneity and analyte concentration |
| Dry-Heat Sterilization | Eliminate microbial contamination on equipment | Ensures experimental integrity |
| Accelerated Shelf-Life Testing | Simulate long-term storage at elevated temperatures | Predicts product stability efficiently |
| Ash Content Analysis (Pre-drying) | Gently remove water before high-temperature ashing | Prevents sample splatter and loss |
Ensure the accuracy and reliability of your food chemistry analyses with the right laboratory equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab ovens and consumables tailored to the precise needs of food science laboratories. Whether you require mechanical convection for uniform drying or vacuum ovens for heat-sensitive samples, our solutions are designed to enhance your lab's efficiency and data quality. Contact our experts today to find the perfect oven for your specific applications and take the first step toward superior sample preparation and analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the processing and chemical analysis of aluminum dross?
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in W18Cr4V steel sample preparation? Expert Microstructural Drying Guide
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?



















