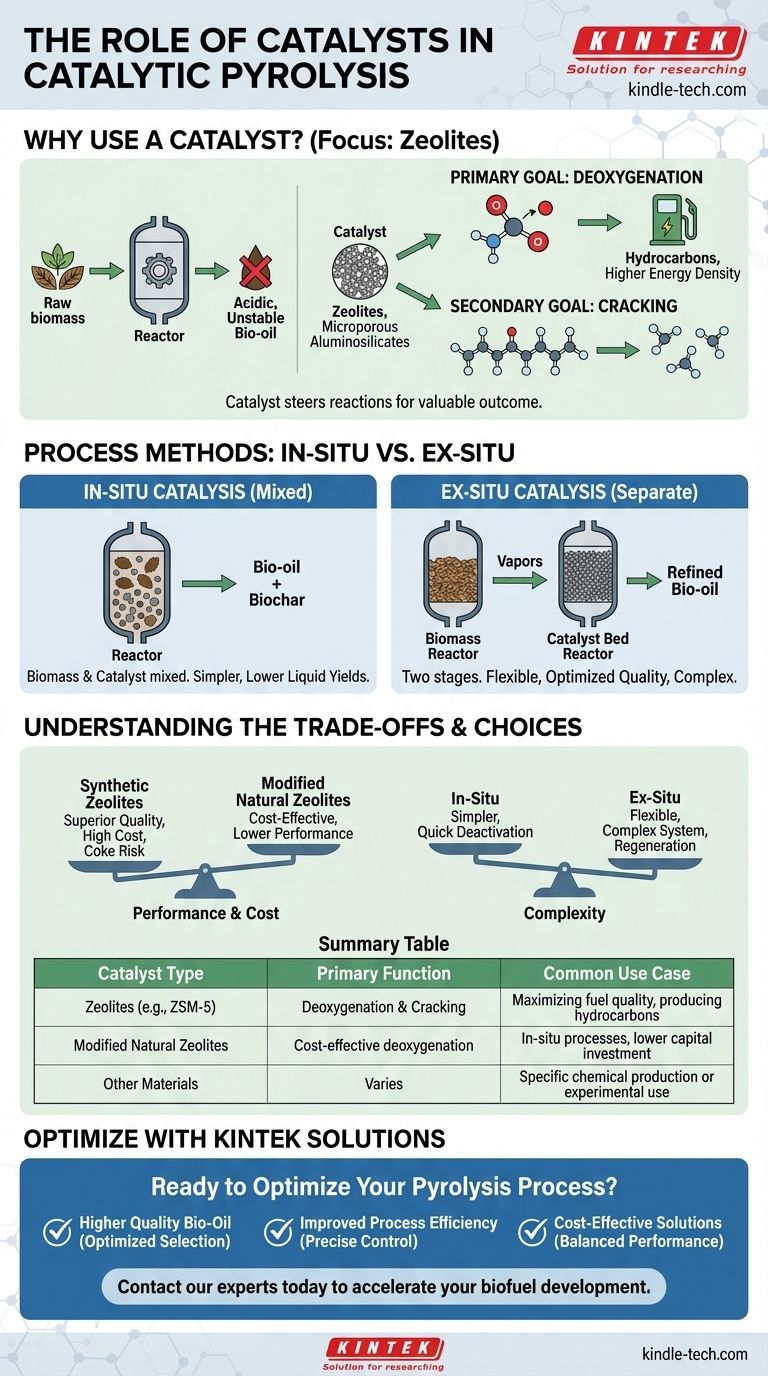
In catalytic pyrolysis, the most common and widely studied catalysts are zeolites, which are microporous aluminosilicate minerals. While many materials can be used, zeolites are favored for their unique structural and chemical properties that are highly effective for upgrading biomass vapors into higher-quality fuels and chemicals.
The core function of a catalyst in pyrolysis is to steer the chemical reactions toward a more valuable outcome. It actively removes oxygen and breaks down large, unstable molecules from raw biomass into a more refined, stable, and useful product like bio-oil.

The Fundamental Role of Catalysts in Pyrolysis
Why Use a Catalyst at All?
Standard pyrolysis breaks down biomass with heat in the absence of oxygen, but the resulting liquid (bio-oil) is often acidic, unstable, and has a high oxygen content.
This high oxygen content makes the bio-oil incompatible with conventional fuels and difficult to upgrade. A catalyst is introduced to solve this problem directly at the source.
The Primary Goal: Deoxygenation
The most critical job of the catalyst is deoxygenation, or the removal of oxygen atoms from the pyrolysis vapors.
By removing oxygen, the catalyst converts the vapors into hydrocarbons, which are chemically much closer to conventional fossil fuels. This dramatically increases the energy density and stability of the final product.
The Secondary Goal: Cracking
Catalysts also perform cracking, where they break down large, heavy organic molecules into smaller, lighter, and more valuable ones. This results in a product with a molecular composition more suitable for transportation fuels.
How Catalysts Are Used in the Process
The method of introducing the catalyst into the process has significant implications for the outcome. The references point to two primary configurations.
In-Situ Catalysis (Mixed)
In this approach, the biomass and catalyst are physically mixed together inside the main pyrolysis reactor.
This ensures immediate contact between the fresh pyrolysis vapors and the catalyst, promoting rapid deoxygenation and cracking. It is simpler from an equipment standpoint but can lead to lower liquid yields.
Ex-Situ Catalysis (Separate)
In the ex-situ method, the process is separated into two stages. First, biomass is pyrolyzed in one reactor, and then the resulting hot vapors are passed over a separate, dedicated bed of catalyst.
This two-step process allows for independent control over the pyrolysis and the catalytic upgrading steps, offering more flexibility to optimize the final product quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a catalyst and a method involves balancing performance, cost, and complexity. There is no single "best" solution for every application.
Catalyst Performance vs. Lifespan
Highly active catalysts like synthetic zeolites produce superior quality bio-oil but can be expensive and prone to deactivation by coke (a form of carbon) buildup.
Less expensive options, like the modified natural zeolites mentioned in the references, offer a cost-effective alternative, though their performance may be lower. Activation methods, such as acid or thermal treatments, are used to enhance their effectiveness.
In-Situ vs. Ex-Situ Complexity
The in-situ method is mechanically simpler but makes it difficult to separate the spent catalyst from the solid biochar byproduct. The catalyst also deactivates more quickly.
The ex-situ method allows for easier catalyst regeneration and more precise control over the upgrading reaction, but it requires a more complex and expensive dual-reactor system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates the optimal catalytic strategy.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible fuel quality: An ex-situ process using a highly active, shape-selective zeolite catalyst is the superior choice for maximizing deoxygenation and producing drop-in hydrocarbons.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity and lower capital investment: An in-situ method using an abundant, cost-effective catalyst like a modified natural zeolite provides a more direct and economical pathway.
Ultimately, the catalyst is the critical lever that transforms the basic pyrolysis of biomass into a sophisticated process for producing tailored, high-value fuels and chemicals.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst Type | Primary Function | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Zeolites (e.g., ZSM-5) | Deoxygenation & Cracking | Maximizing fuel quality, producing hydrocarbons |
| Modified Natural Zeolites | Cost-effective deoxygenation | In-situ processes, lower capital investment |
| Other Materials | Varies | Specific chemical production or experimental use |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
The right catalyst is key to transforming biomass into high-value fuels and chemicals. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and expert support for catalytic pyrolysis research and development.
We help our customers in the bioenergy and chemical sectors achieve:
- Higher Quality Bio-Oil: Through optimized catalyst selection and process configuration (in-situ or ex-situ).
- Improved Process Efficiency: With equipment designed for precise temperature control and catalyst handling.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: By identifying the right balance between catalyst performance and operational expenses.
Let's discuss your specific pyrolysis goals. Contact our experts today to explore how our solutions can accelerate your biofuel development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Three-Necked Round Bottom Flask
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What are the advantages of using PTFE molds for epoxy resin flame retardant samples? Ensure High-Purity Material Testing
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- Why are PTFE laboratory consumables required when testing stainless steel against organic acids? Ensure Data Integrity



















