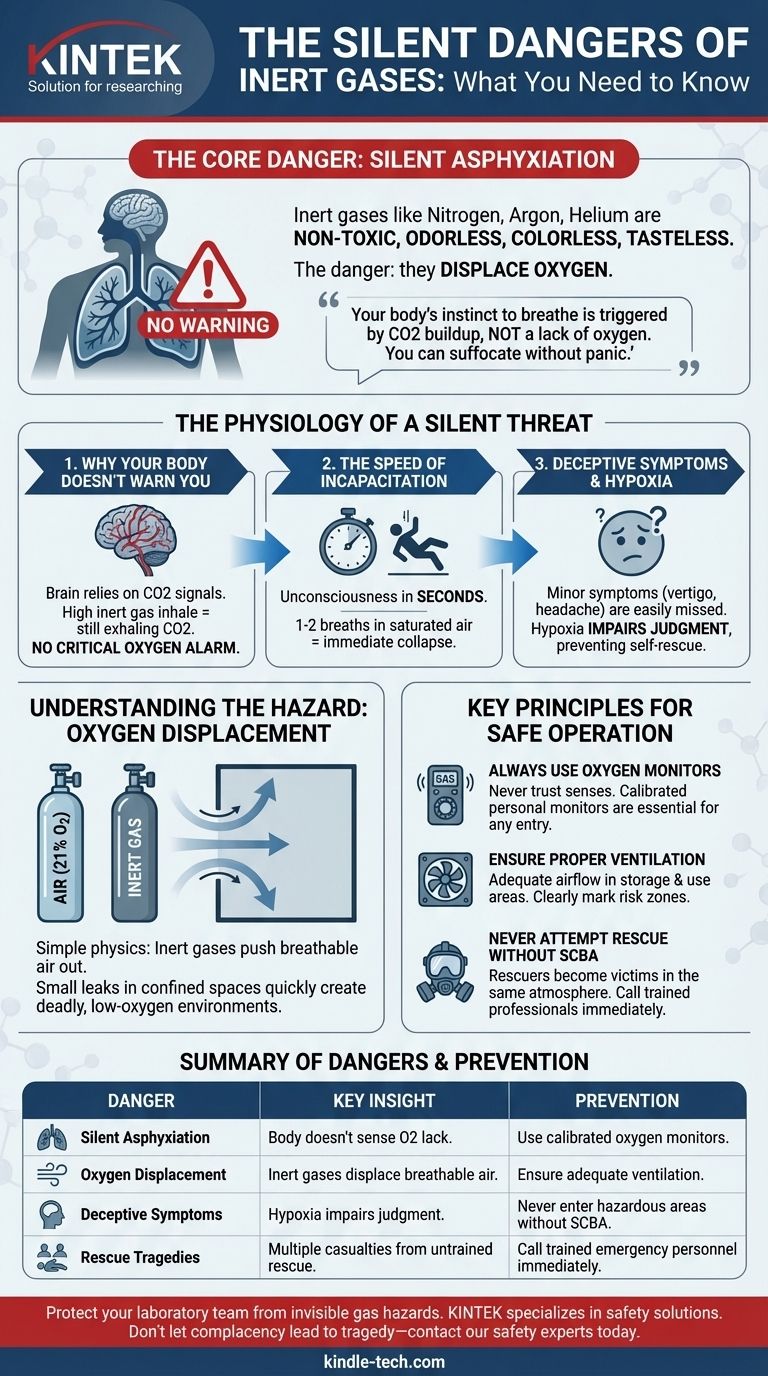
The primary danger of inert gases is silent asphyxiation. Unlike other hazardous materials, gases like nitrogen or argon are not toxic and have no smell, color, or taste. Their danger lies in their ability to displace oxygen from the air to a level where even one or two breaths can cause immediate unconsciousness and rapid death, all without the victim ever feeling the sensation of suffocation.
The core danger of inert gases isn't what they are, but what they are not: they are not oxygen. Your body's instinct to breathe is triggered by a buildup of carbon dioxide, not a lack of oxygen, meaning you can suffocate on an inert gas without any physical warning or panic.

The Physiology of a Silent Threat
The reason inert gas exposure is so uniquely dangerous is that it bypasses the body's natural defense mechanisms. It's a biological blind spot that can have fatal consequences.
Why Your Body Doesn't Warn You
Your overwhelming urge to take a breath is not driven by a lack of oxygen. It is a response to rising levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in your bloodstream.
When you breathe in a high concentration of an inert gas, you are still exhaling CO2. Your brain, therefore, never receives the alarm signal that it is critically low on oxygen.
The Speed of Incapacitation
With no oxygen present, unconsciousness occurs within seconds. The brain is deprived of fuel and simply shuts down.
The reference to "1-2 breaths" is not an exaggeration. A person walking into an environment saturated with nitrogen can lose consciousness before they even have a chance to turn around and leave.
Deceptive and Unreliable Symptoms
In an atmosphere where oxygen is low but not completely absent, some minor symptoms may appear. These can include vertigo, headache, or difficulty speaking.
However, a critical effect of oxygen deprivation (hypoxia) is impaired judgment. The victim is incapable of recognizing these symptoms as a sign of imminent asphyxiation and will not be able to take corrective action or call for help.
Understanding the Hazard: Oxygen Displacement
The danger isn't a chemical reaction; it's a matter of simple physics. Inert gases are heavier or lighter than air and will physically push the breathable atmosphere out of a space.
The Nature of Inert Gas
Inert gases are elements that do not readily react with other substances. Common examples in industrial and laboratory settings include Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar), and Helium (He).
Because they are non-toxic and non-flammable, they are often perceived as "safe," which leads to complacency.
How an Environment Becomes Deadly
Normal air contains approximately 21% oxygen. When an inert gas is released into a poorly ventilated or confined space, it dilutes the percentage of available oxygen.
If a cylinder of compressed nitrogen were to leak in a small room, it would quickly lower the oxygen level to a point that cannot sustain consciousness or life.
Common Pitfalls and High-Risk Scenarios
Awareness of the danger is highest in obvious confined spaces, but fatal incidents often occur in seemingly innocuous situations.
Confined or Enclosed Spaces
This is the classic and most lethal scenario. Any work in tanks, vessels, pits, or even small, unventilated rooms where inert gases are used poses an extreme risk.
"Minor" Leaks
A slow, quiet leak from a gas line fitting or a valve in a storage closet can be enough to create a deadly atmosphere over several hours. The lack of smell or color makes it impossible to detect without proper equipment.
The Rescue Attempt Tragedy
A common and tragic scenario involves a would-be rescuer. Seeing a colleague collapse, their first instinct is to rush in to help. In doing so, they enter the same oxygen-deficient atmosphere and quickly become a second victim.
Key Principles for Safe Operation
Because you cannot rely on your senses to detect the presence of an inert gas hazard, you must rely on established procedures and technology.
- If your primary focus is entering any workspace with inert gases: Always use a calibrated, personal oxygen monitor. Never trust your senses, and treat every enclosed area as potentially hazardous until proven otherwise.
- If your primary focus is system design and storage: Ensure all areas where inert gases are used or stored have adequate ventilation, and clearly mark all potential risk areas with warning signs.
- If your primary focus is emergency response: Never enter an area to rescue a collapsed person without proper self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA). Immediately call for trained emergency responders.
Ultimately, safety with inert gases depends on recognizing that the danger is both invisible and neurologically deceptive.
Summary Table:
| Danger | Key Insight | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Silent Asphyxiation | Body doesn't sense oxygen lack; unconsciousness in seconds | Use calibrated oxygen monitors |
| Oxygen Displacement | Inert gases displace breathable air in confined spaces | Ensure adequate ventilation |
| Deceptive Symptoms | Hypoxia impairs judgment; victims can't self-rescue | Never enter hazardous areas without SCBA |
| Rescue Tragedies | Multiple casualties when untrained responders enter | Call trained emergency personnel immediately |
Protect your laboratory team from invisible gas hazards. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable safety solutions including gas monitoring systems and ventilation equipment. Don't let complacency lead to tragedy—contact our safety experts today to assess your inert gas risks and implement life-saving protocols.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- How do Teflon (PTFE) baskets facilitate glass thin-film leaching? Enhance Accuracy with Chemical Inertness
- What are the process advantages of using PTFE channels in electrode installation ports? Ensure Precise Data Integrity
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- What are the specific applications of PTFE in micro-batch slug flow systems? Enhance Your Microfluidic Reaction Purity
- Why is PTFE tape applied to ceramic crevice formers when assembling Alloy 22? Precision Tips for Corrosion Testing














