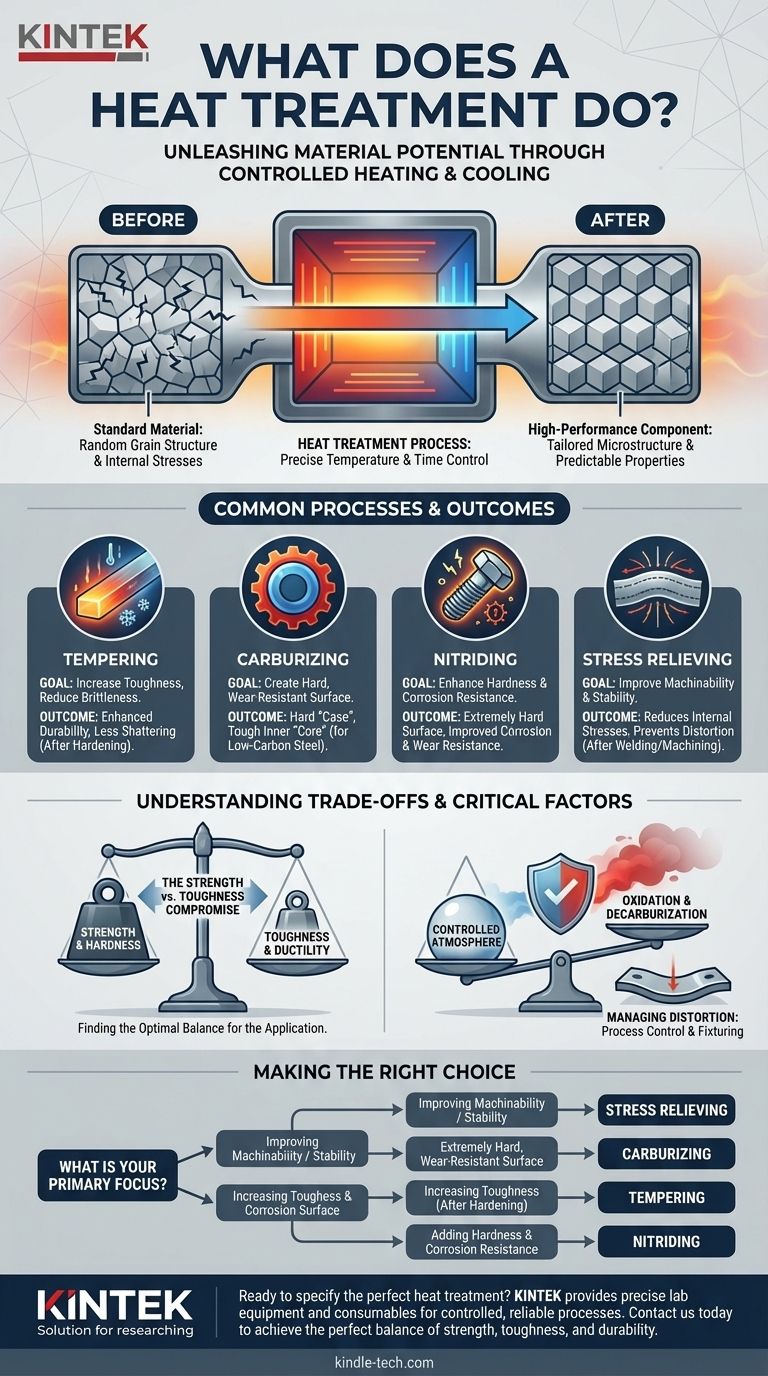
Fundamentally, heat treatment is a group of industrial processes that use controlled heating and cooling to alter a material's physical and mechanical properties. It is not a coating or an additive; instead, it changes the internal crystalline structure of the material itself. This allows engineers to achieve desirable characteristics such as increased strength, improved machinability, or enhanced wear resistance without changing the part's shape.
Heat treatment is not about making metal hot; it is about precisely manipulating a material’s internal structure to achieve specific, predictable engineering properties. It transforms a standard material into a high-performance component tailored for a specific task.

The Fundamental Goal: Manipulating a Material's Microstructure
The purpose of heat treatment is to intentionally modify a material's internal grain structure to produce a desired outcome. This is a critical step in manufacturing for components that must withstand stress, wear, or extreme environments.
Beyond Simple Heating and Cooling
The effectiveness of heat treatment lies in the precision of the process. Key variables include the rate of heating, the maximum temperature reached, the duration at that temperature, and the rate and method of cooling. Each variable influences the final microstructure and, therefore, the material's properties.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding, casting, and heavy machining introduce internal stresses into a metal part. These stresses can cause distortion or cracking over time. A stress-relieving heat treatment gently heats the part and allows it to cool slowly, relaxing these internal forces and making the component more stable.
Increasing Strength and Toughness
By controlling the cooling rate, technicians can refine a metal's grain structure. A faster cooling process (quenching) can significantly increase hardness and strength, while a slower process can increase ductility and toughness, which is a material's ability to absorb energy and resist fracture.
Common Processes and Their Specific Outcomes
Different heat treatments are used to achieve different goals. They can be broadly categorized by whether they affect the entire part (through-hardening) or just its surface (case-hardening).
Tempering: Increasing Toughness and Reducing Brittleness
After a part is hardened through a process like quenching, it is often extremely strong but also very brittle. Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature heat treatment that reduces this brittleness and increases the material's overall toughness, making it more durable and less likely to shatter under impact.
Carburizing: Creating a Hard, Wear-Resistant Surface
Carburizing is a case-hardening process used on low-carbon steel. The part is heated in a carbon-rich atmosphere, which allows carbon to diffuse into the surface layer. This creates a component with an exceptionally hard, wear-resistant "case" while retaining a softer, tougher inner "core."
Nitriding: Enhancing Hardness and Corrosion Resistance
Nitriding is another case-hardening technique that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal, typically steel. This process creates a very hard surface with the added benefit of significantly improving the material's resistance to corrosion and wear. It is often performed at lower temperatures than carburizing, reducing the risk of part distortion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Specifying a heat treatment requires understanding the inherent compromises and critical environmental factors involved in the process.
The Strength vs. Toughness Compromise
A fundamental trade-off in metallurgy is that of strength versus toughness. As you increase a material's hardness and strength, you almost always decrease its ductility and toughness, making it more brittle. The goal of a well-designed heat treatment plan is to find the optimal balance for the component's application.
The Critical Role of a Controlled Atmosphere
High-temperature treatments must be performed in a controlled atmosphere. The purpose is to protect the workpiece from reacting with the air. An uncontrolled atmosphere can lead to oxidation (scaling or rust) or decarburization (the loss of carbon from the steel's surface), both of which compromise the part's integrity and intended properties.
The Risk of Distortion
The rapid heating and cooling cycles inherent to many heat treatments can cause parts to warp or distort. This risk is managed through careful process control, proper fixturing of the parts in the furnace, and selecting treatments (like nitriding) that operate at lower temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct heat treatment is entirely dependent on the final application of the component. Use these guidelines to inform your decision.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or stability after welding: A stress-relieving cycle is the most effective approach to prevent distortion.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely hard, wear-resistant surface on a steel part: Case-hardening processes like carburizing are the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is increasing the toughness and impact resistance of an already-hardened part: Tempering is the necessary subsequent step to reduce brittleness.
- If your primary focus is adding surface hardness and corrosion resistance simultaneously: Nitriding offers a unique and highly effective combination of these benefits.
By understanding these core principles, you can specify the precise treatment needed to unlock the full engineering potential of your chosen material.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Recommended Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Improve Machinability / Stability | Stress Relieving | Reduces internal stresses |
| Create a Hard, Wear-Resistant Surface | Carburizing | Hard outer case, tough inner core |
| Increase Toughness & Reduce Brittleness | Tempering | Enhances durability after hardening |
| Add Hardness & Corrosion Resistance | Nitriding | Hard surface with improved corrosion resistance |
Ready to specify the perfect heat treatment for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve controlled, reliable heat treatment processes. Whether you are developing new materials or ensuring the quality of high-performance parts, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of strength, toughness, and durability.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















