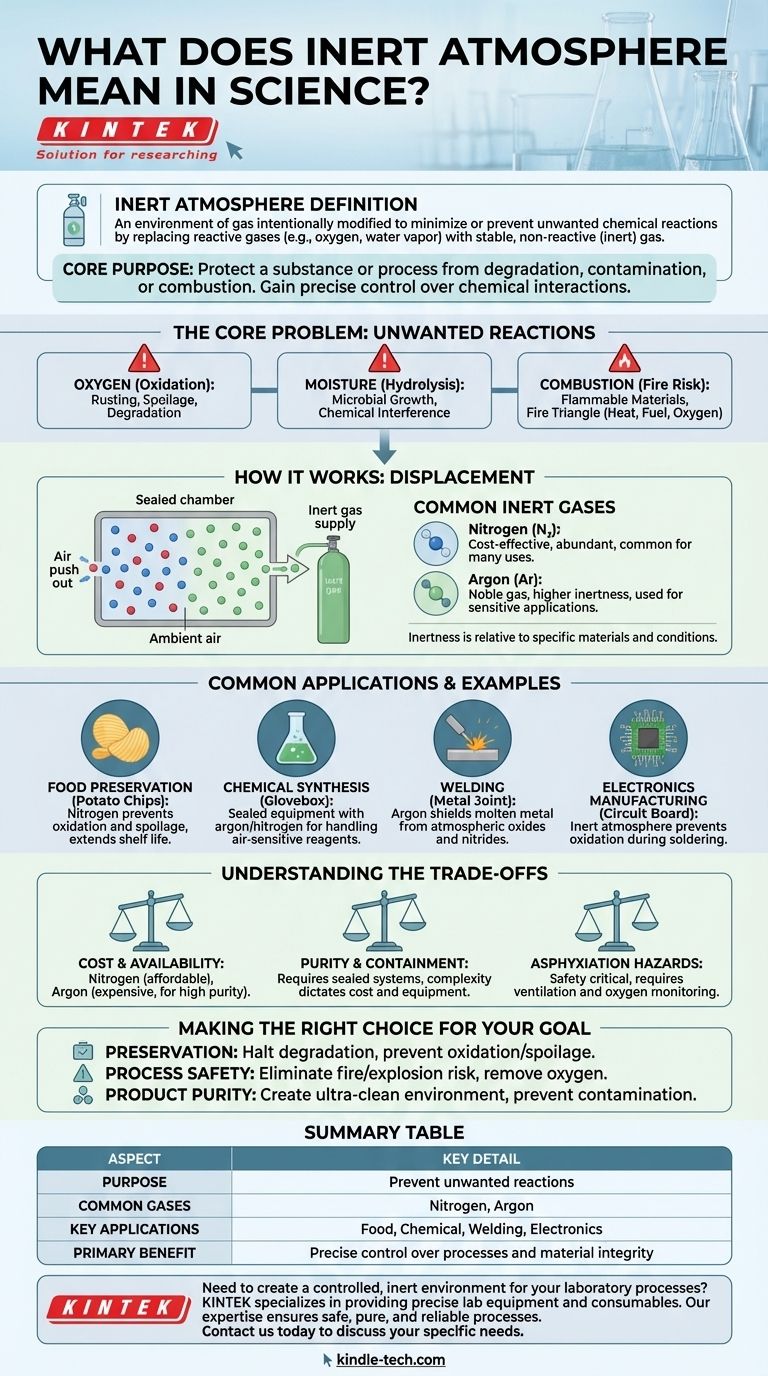
In a scientific context, an inert atmosphere refers to an environment of gas that has been intentionally modified to minimize or prevent unwanted chemical reactions. This is achieved by replacing reactive gases, most commonly oxygen and water vapor, with a stable, non-reactive (or "inert") gas like nitrogen or argon.
The core purpose of creating an inert atmosphere is to protect a substance or process from degradation, contamination, or combustion. By removing reactive elements from the environment, you gain precise control over the chemical interactions that can occur.

The Core Problem: Unwanted Reactions
To understand why inert atmospheres are necessary, we first must identify the problems they solve. Ambient air is a mixture of gases that is surprisingly reactive and often hostile to sensitive materials and processes.
The Role of Oxygen
Oxygen is the most common culprit. It is highly reactive and readily participates in oxidation, a process that can fundamentally alter materials.
This includes the rusting of metals, the spoilage of food, and the degradation of sensitive chemical compounds.
The Impact of Moisture
Water vapor present in the air is another major source of unwanted reactions. It can hydrolyze sensitive materials, promote microbial growth, or interfere with chemical synthesis.
The Risk of Combustion
Many processes involve flammable materials or high temperatures. The presence of oxygen creates a significant risk of fire or explosion, as it is a key component of the fire triangle (heat, fuel, and oxygen).
How an Inert Atmosphere Works
The solution is conceptually simple: replace the reactive atmosphere with a non-reactive one. This is typically achieved through a process of purging or displacement.
The Principle of Displacement
The process involves flushing a sealed container or chamber (like a glovebox or reaction vessel) with an inert gas. This new gas physically pushes out the ambient air, effectively replacing the reactive oxygen and moisture with a stable gas.
Common Inert Gases
The choice of gas depends on the specific application, cost, and required level of inertness.
The most common is Nitrogen (N₂), which is effective for many applications and relatively inexpensive. For higher-purity or more demanding situations, noble gases like Argon (Ar) are used because they are even less reactive.
The Concept of "Inertness"
It's important to understand that "inert" is a relative term. A gas is considered inert if it does not react with the specific materials in a given system under specific conditions. Nitrogen, for instance, is inert for most purposes but can react under very high temperatures and pressures.
Common Applications and Examples
The practical use of inert atmospheres is widespread across science and industry, often in ways you encounter daily.
In Food Preservation
The air inside a bag of potato chips is not just "air"—it's typically nitrogen. This inert atmosphere prevents the oils in the chips from oxidizing and going rancid, dramatically extending their shelf life.
In Chemical Synthesis
Many chemical reagents are extremely sensitive to air or moisture. Chemists use sealed equipment flushed with argon or nitrogen to handle these materials, ensuring their reactions proceed as intended without contamination.
In Welding and Metallurgy
When welding high-strength alloys, an inert gas like argon is used to shield the molten metal from the atmosphere. This prevents the formation of oxides and nitrides that would otherwise weaken the weld.
In Electronics Manufacturing
During the soldering of microchips and circuit boards, components are vulnerable to oxidation. An inert atmosphere prevents this, ensuring strong, reliable electrical connections are formed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, implementing an inert atmosphere involves practical considerations that must be weighed.
Cost and Availability
Nitrogen is abundant and affordable, making it the workhorse for many industrial applications. High-purity argon and other noble gases are significantly more expensive and are reserved for when absolute non-reactivity is critical.
Purity and Containment
Maintaining a truly inert atmosphere requires well-sealed systems. The level of purity required dictates the complexity and cost of the equipment, from simple flushed containers to sophisticated gloveboxes with constant gas circulation and purification.
Asphyxiation Hazards
A critical safety consideration is that inert gases displace oxygen. In a poorly ventilated area, a leak can create an oxygen-deficient environment that can cause asphyxiation. Proper ventilation and oxygen monitoring are essential safety measures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an inert atmosphere is driven by the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is preservation: Your goal is to halt degradation by displacing oxygen and moisture, thereby preventing oxidation and spoilage.
- If your primary focus is process safety: Your goal is to eliminate the risk of fire or explosion by removing the oxygen required for combustion.
- If your primary focus is product purity: Your goal is to create an ultra-clean environment, ensuring no reactive contaminants can interfere with a sensitive process like chemical synthesis or electronics manufacturing.
Ultimately, an inert atmosphere is a powerful tool for taking control of a chemical environment to achieve a precise and reliable outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent unwanted reactions (oxidation, contamination, combustion) |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) |
| Key Applications | Food preservation, chemical synthesis, welding, electronics manufacturing |
| Primary Benefit | Precise control over chemical processes and material integrity |
Need to create a controlled, inert environment for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables required for your applications, from chemical synthesis to materials research. Our expertise ensures your processes are safe, pure, and reliable. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover the right solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















