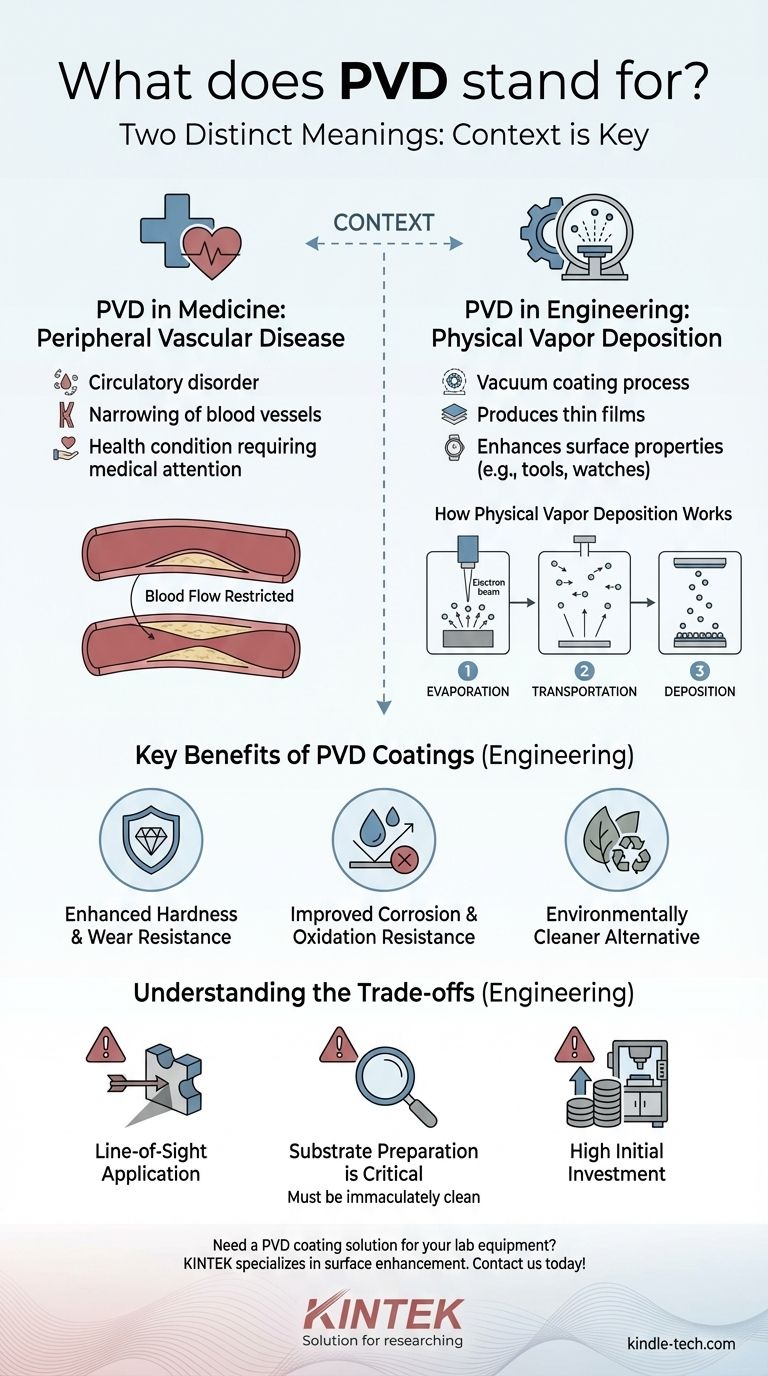
The acronym PVD has two common, yet completely distinct, meanings. In technical and manufacturing fields, PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition, a process for applying high-performance coatings. In a medical context, it stands for Peripheral Vascular Disease, a circulatory system disorder. The correct definition is entirely dependent on the context in which you encounter the term.
Your context is the key to the definition. In engineering, PVD is a sophisticated vacuum coating process that enhances a material's surface properties. In medicine, it's a serious health condition affecting blood vessels.

Understanding the Two Meanings of PVD
To ensure clarity, it's crucial to understand both definitions and the fields to which they apply.
PVD in Medicine: Peripheral Vascular Disease
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) is a slow, progressive disorder of the blood vessels. It refers to the narrowing, blockage, or spasms of any blood vessel outside of the heart, including arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels.
This condition restricts blood flow and is a serious medical diagnosis managed by healthcare professionals.
PVD in Engineering: Physical Vapor Deposition
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a family of vacuum deposition methods used to produce thin films and coatings. This process involves transferring material on an atomic level from a solid source to a substrate, creating a durable, bonded surface layer.
This is the definition used in manufacturing, materials science, and for creating high-performance finishes on products from tools to watches.
How Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Works
The PVD process is a highly controlled technique that takes place inside a vacuum chamber and fundamentally alters the surface of an object.
The Core Principle: Material in a Vacuum
All PVD processes occur under a vacuum to prevent the vaporized coating material from reacting with particles in the air, ensuring a pure and high-quality film.
Step 1: Evaporation
A solid source material, or "precursor," is bombarded with a high-energy source, such as a beam of electrons. This bombardment provides enough energy to vaporize the material, releasing individual atoms or molecules.
Step 2: Transportation
These newly freed atoms and molecules travel through the vacuum chamber from the source material toward the object being coated, which is called the substrate.
Step 3: Deposition
Upon reaching the substrate, the vaporized material condenses, forming a thin, tightly bonded film. Sometimes, a reactive gas like nitrogen is introduced, allowing the depositing atoms to react and form an even harder compound coating on the surface.
Key Benefits of PVD Coatings
Manufacturers choose PVD for its ability to dramatically improve a product's functional and aesthetic properties.
Enhanced Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are extremely hard and significantly reduce friction. This makes them ideal for cutting tools, engine components, and other parts subject to intense wear.
Improved Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
The thin film acts as a protective barrier, shielding the underlying material from moisture, chemicals, and air. This drastically improves resistance to rust and other forms of corrosion.
An Environmentally Cleaner Alternative
Compared to traditional coating methods like electroplating, which often use hazardous chemicals, PVD is a much cleaner process with minimal waste products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PVD process has specific requirements and limitations that are important to recognize.
Line-of-Sight Application
PVD is primarily a "line-of-sight" process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line, which can make it challenging to evenly coat complex shapes with deep recesses or internal channels.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The substrate surface must be immaculately clean for the PVD coating to adhere properly. Any contaminants like oils or dust will cause the coating to fail, requiring extensive pre-treatment.
High Initial Investment
PVD coating equipment is complex, precise, and operates under a vacuum, making it expensive. This cost often means it is best suited for high-value or high-volume industrial applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, identifying which "PVD" is relevant to you depends entirely on the field of discussion.
- If your primary focus is on a medical chart or health article: PVD almost certainly refers to Peripheral Vascular Disease, a circulatory condition requiring medical attention.
- If your primary focus is on manufacturing, watches, tools, or material finishes: PVD refers to Physical Vapor Deposition, the high-performance coating process.
- If your goal is to enhance a product's durability and appearance: Investigating Physical Vapor Deposition coatings is the correct path for improving surface performance.
Understanding the context is the first and most critical step in deciphering any technical acronym.
Summary Table:
| PVD Meaning | Field | Definition | Key Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peripheral Vascular Disease | Medicine | A circulatory disorder causing narrowed blood vessels. | Health articles, medical charts, patient discussions. |
| Physical Vapor Deposition | Engineering | A vacuum coating process for durable, high-performance surfaces. | Manufacturing, tools, watches, material science. |
Need a PVD coating solution for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering expertise in surface enhancement technologies like PVD to improve durability, corrosion resistance, and efficiency. Enhance your laboratory's capabilities—contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















