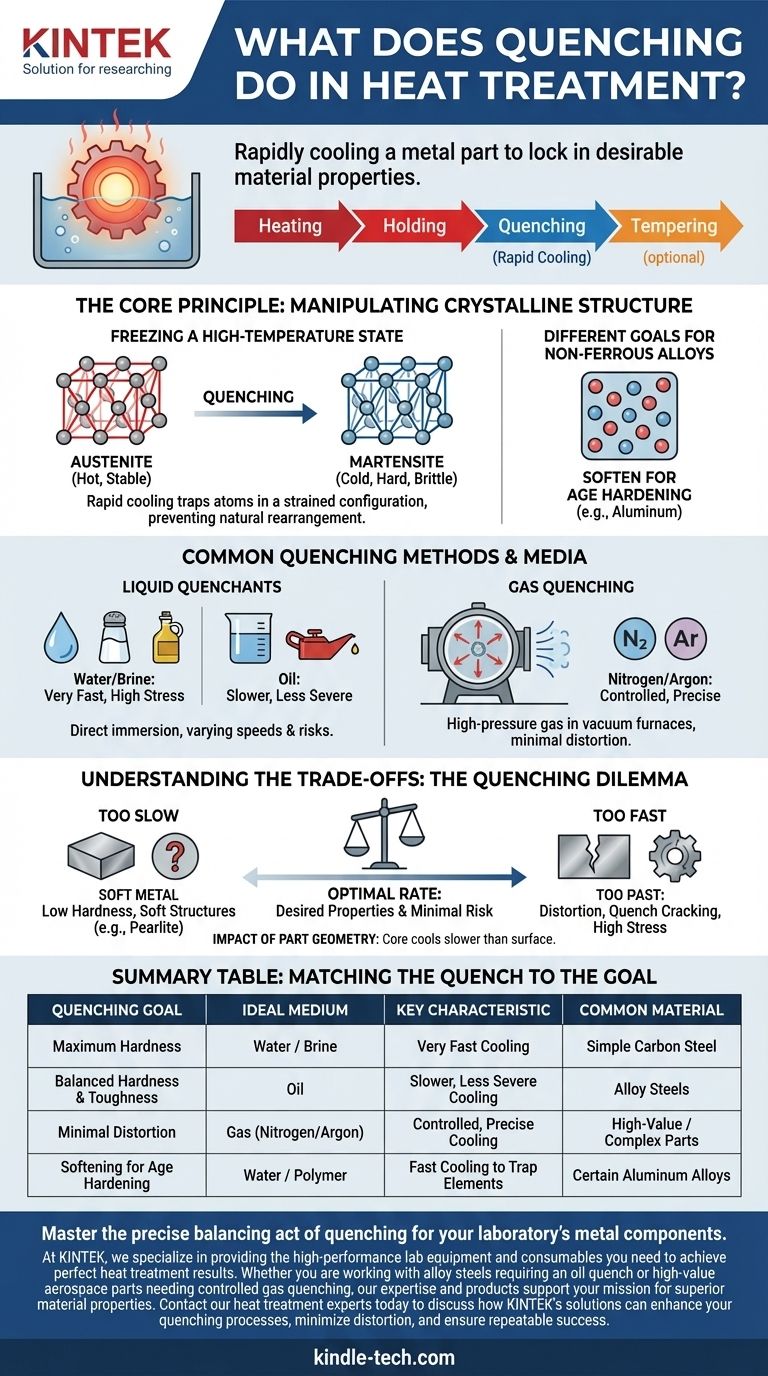
In heat treatment, quenching is the process of rapidly cooling a metal part to lock in specific, desirable material properties. By immersing a heated component in a medium like oil, water, or gas, the process intentionally "freezes" its high-temperature atomic structure. This controlled cooling is a fundamental tool for manipulating a metal's final hardness, strength, and durability.
Quenching is not merely about making a metal cold; it is about controlling the rate of cooling to dictate the metal's final internal crystalline structure. Achieving the correct cooling rate is the key to unlocking desired properties like hardness in steel, but getting it wrong introduces significant risks of distortion or failure.

The Core Principle: Manipulating Crystalline Structure
Quenching's primary function is to prevent the natural, slower transformation that would occur if a metal were allowed to cool in ambient air. This rapid intervention forces the formation of specific microstructures.
Freezing a High-Temperature State
When a ferrous alloy like steel is heated to a critical temperature, its atoms arrange into a structure called austenite. If allowed to cool slowly, these atoms will rearrange into softer, more stable structures.
Quenching short-circuits this natural process. The extremely fast temperature drop denies the atoms the time needed to rearrange, trapping them in a less stable, highly stressed configuration.
The Goal for Steels: Creating Martensite
For most steels, the goal of quenching is to form martensite. This is a very hard, brittle, needle-like crystalline structure that forms when austenite is cooled so rapidly that the carbon atoms are trapped within the iron crystal lattice.
This trapped-atom structure is what gives a quenched steel its characteristic high strength and wear resistance. However, it is also very brittle, which is why a post-quenching process called tempering is almost always required to restore some toughness.
Different Goals for Non-Ferrous Alloys
It's important to note that quenching doesn't always increase hardness. For some non-ferrous alloys, such as certain aluminum grades, quenching actually makes the metal softer.
In this context, the rapid cool traps alloying elements in a "solid solution," creating a soft, workable condition. The material is then hardened later through a separate process called age hardening.
Common Quenching Methods and Media
The choice of quenching medium is critical, as it directly controls the cooling rate. Different media extract heat at vastly different speeds.
Liquid Quenchants: Water, Brine, and Oil
The most common method involves immersing the hot part in a liquid bath. Water and brine (salt water) offer extremely fast cooling but create immense thermal shock, increasing the risk of cracking.
Oil provides a slower, less severe quench. This reduces the risk of distortion and cracking, making it a suitable choice for many alloy steels and parts with complex geometries.
Gas Quenching: Nitrogen and Argon
In vacuum furnaces, parts are often quenched using high-pressure streams of inert gas like nitrogen or argon. This method offers a high degree of control over the cooling rate.
While typically slower than an oil quench, gas quenching minimizes part distortion and produces a clean, bright surface, making it ideal for high-value components used in industries like aerospace.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Quenching Dilemma
The success or failure of heat treatment often hinges on finding the perfect cooling rate—fast enough to achieve the desired properties, but not so fast that it destroys the part.
The Risk of Cooling Too Slowly
If the cooling rate is insufficient, the desired martensitic transformation will not occur. Instead, softer structures (like troostite or pearlite) will form, resulting in low core hardness and a failure to meet mechanical specifications.
The Risk of Cooling Too Quickly
An excessively rapid quench generates massive internal stresses as the part's surface cools and contracts much faster than its core. This can cause distortion (warping), significant dimensional changes, or even quench cracking, rendering the part unusable.
The Impact of Part Geometry
The thickness and complexity of a part heavily influence the quenching outcome. The core of a thick section will always cool more slowly than its surface, potentially leading to a hard outer shell but a soft, weak interior.
Matching the Quench to the Goal
The right quenching strategy is dictated entirely by the material and the desired final properties. There is no single "best" method.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness in a simple carbon steel: A rapid quench in water or brine is often used, but it carries the highest risk of cracking and distortion.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness and toughness in an alloy steel: An oil quench provides a slower, less severe cooling rate that reduces internal stresses.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion in a complex or high-value part: Controlled gas quenching in a vacuum furnace offers the highest level of precision and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is preparing a non-ferrous alloy for age hardening: A quench is used to create a soft, supersaturated solid solution, which is a fundamentally different metallurgical goal.
Ultimately, successful quenching is a precise balancing act between achieving the target microstructure and managing the internal stresses created by rapid cooling.
Summary Table:
| Quenching Goal | Ideal Medium | Key Characteristic | Common Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Hardness | Water / Brine | Very Fast Cooling | Simple Carbon Steel |
| Balanced Hardness & Toughness | Oil | Slower, Less Severe Cooling | Alloy Steels |
| Minimal Distortion | Gas (Nitrogen/Argon) | Controlled, Precise Cooling | High-Value / Complex Parts |
| Softening for Age Hardening | Water / Polymer | Fast Cooling to Trap Elements | Certain Aluminum Alloys |
Master the precise balancing act of quenching for your laboratory's metal components.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables you need to achieve perfect heat treatment results. Whether you are working with alloy steels requiring an oil quench or high-value aerospace parts needing controlled gas quenching, our expertise and products support your mission for superior material properties.
Contact our heat treatment experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your quenching processes, minimize distortion, and ensure repeatable success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components



















