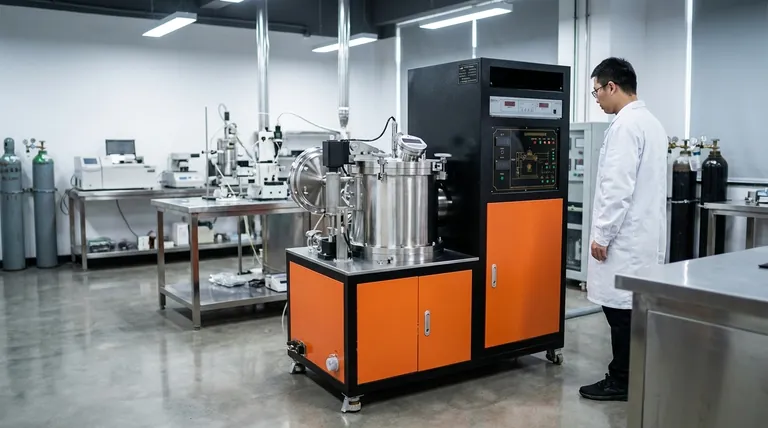
For annealing processes, the equipment of choice is not a standard furnace but one specifically designed for atmosphere control. The most common types are vacuum annealing furnaces and controlled atmosphere furnaces, such as those that use hydrogen as a protective gas. The defining feature is the ability to protect the material from oxidation and other chemical reactions at high temperatures.
The critical factor in selecting an annealing furnace is not its heating method, but its ability to control the furnace's internal atmosphere. This control is essential to prevent surface damage like oxidation and to ensure the desired metallurgical properties are achieved consistently.

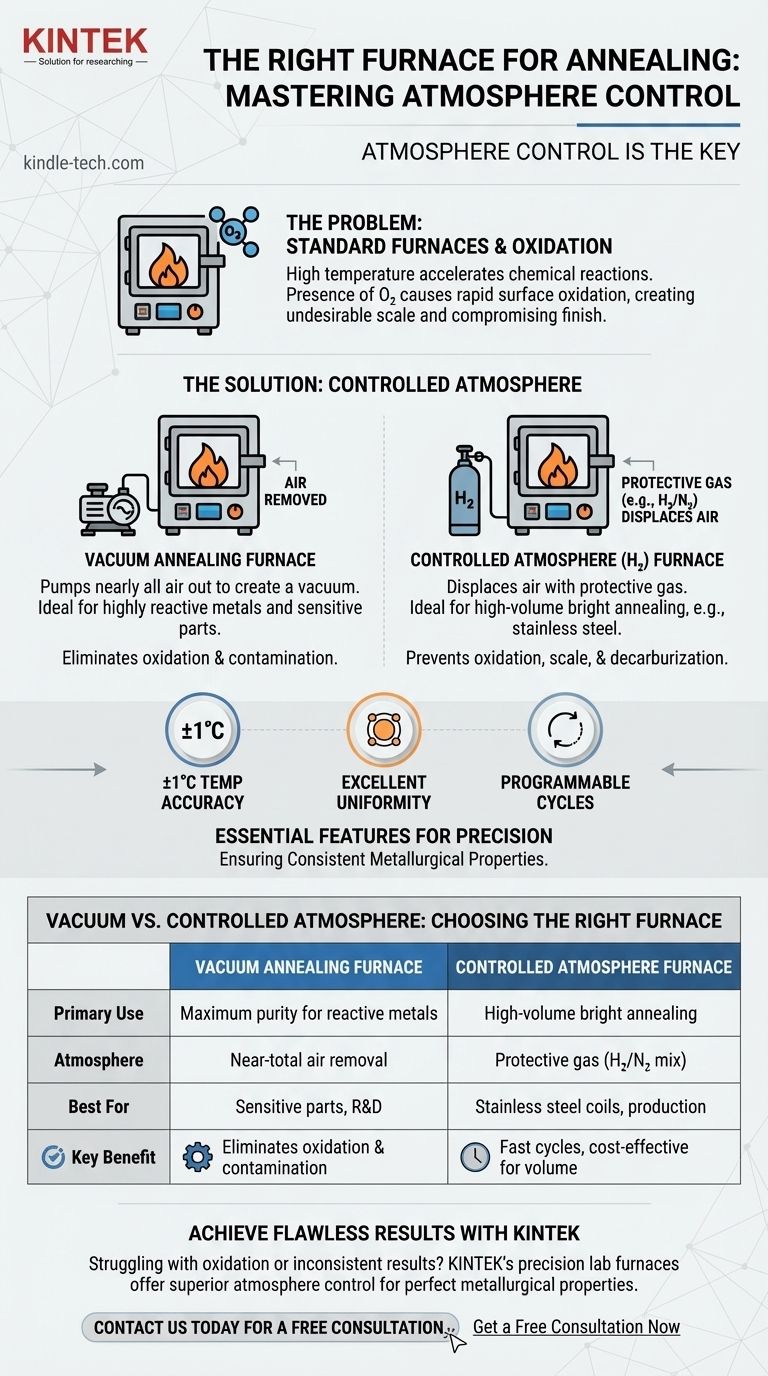
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
The primary challenge during annealing is the high temperature, which accelerates chemical reactions between the metal's surface and the surrounding air. A specialized furnace is required to manage this environment precisely.
Why a Standard Furnace Isn't Enough
In a standard furnace, the presence of oxygen in the air will cause the metal's surface to oxidize rapidly when heated. This creates an undesirable layer of scale, which can compromise the component's finish, dimensions, and properties.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburisation
The purpose of a controlled atmosphere is to protect the material. By either removing the air entirely (vacuum) or replacing it with a non-reactive gas, the furnace prevents oxidation, scale formation, and other unwanted reactions like decarburisation (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel).
Achieving a "Bright" Finish
Processes like bright annealing, particularly for stainless steel, rely entirely on a protective atmosphere. The goal is to produce a finished product that is clean, bright, and free of oxides, eliminating the need for post-treatment cleaning or pickling.
Key Types of Annealing Furnaces
Annealing furnaces are best categorized by how they achieve atmosphere control. The two primary methods are creating a vacuum or introducing a specific protective gas.
The Vacuum Annealing Furnace
A vacuum furnace works by pumping nearly all of the air out of the heating chamber. By creating a vacuum, it removes the oxygen and other gases that could react with the workpiece. This method is highly effective for solution treatment and aging processes for sensitive parts.
The Controlled Atmosphere (Hydrogen) Furnace
This type of furnace displaces the air with a protective gas. A common choice is hydrogen or a non-flammable mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen. This "blanket" of gas is chemically inert to the workpiece, preventing oxidation during the heat treatment cycle.
Essential Features for Precision
High-performance annealing furnaces are defined by their precision. Key features include automatic temperature controllers with an accuracy of ±1℃, excellent temperature uniformity across the chamber, and programmable heating and cooling cycles. They often include paperless recorders to log process data for quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between a vacuum and a controlled gas atmosphere is driven by the specific material, the desired outcome, and operational considerations. There is no single "best" option for all scenarios.
Vacuum vs. Gas Atmosphere
A vacuum furnace provides the purest possible environment, making it ideal for highly reactive metals or applications where even trace contamination is unacceptable. However, they can have longer cycle times due to pumping and cooling requirements.
A gas atmosphere furnace often allows for faster processing and can be more cost-effective for high-volume production, such as the bright annealing of stainless steel coils. However, it requires careful management of gas flow and safety protocols, especially when using hydrogen.
Material and Process Compatibility
The specific metal being annealed is a critical factor. Some metals may react negatively with certain protective gases, even if they are intended to be inert. The end goal—whether it's simple stress relief or achieving a mirror-like bright finish—will heavily influence which furnace and atmosphere is most appropriate.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Choosing the correct furnace comes down to aligning the equipment's capabilities with your material and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for highly reactive metals: A vacuum annealing furnace is the definitive choice, as it removes virtually all atmospheric contaminants.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput bright annealing of stainless steel: A controlled atmosphere furnace using a hydrogen-nitrogen mixture is an industry-standard and highly effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific metallurgical properties with minimal surface reaction: Both vacuum and controlled atmosphere furnaces are excellent options, with the choice depending on material compatibility and production volume.
Ultimately, selecting the right annealing furnace is about mastering the component's environment to protect its integrity and achieve a flawless result.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Annealing Furnace | Controlled Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Maximum purity for reactive metals | High-volume bright annealing |
| Atmosphere | Near-total air removal | Protective gas (e.g., H₂/N₂ mix) |
| Best For | Sensitive parts, R&D | Stainless steel coils, production |
| Key Benefit | Eliminates oxidation & contamination | Fast cycles, cost-effective for volume |
Achieve Flawless Annealing Results with KINTEK
Struggling with oxidation, decarburization, or inconsistent results in your heat treatment processes? The right annealing furnace is the key to protecting your materials and achieving perfect metallurgical properties every time.
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment, including high-performance vacuum and controlled atmosphere annealing furnaces designed for laboratories and production facilities. Our solutions offer:
- ±1°C Temperature Accuracy: Ensure precise and repeatable results.
- Superior Atmosphere Control: Choose from vacuum or gas systems to perfectly match your material needs.
- Programmable Cycles: Automate complex heating and cooling profiles for consistency.
Whether you are working with reactive metals requiring ultra-high purity or need efficient bright annealing for stainless steel, we have the expertise and equipment to meet your challenge.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application. Our experts will help you select the ideal furnace to enhance your lab's capabilities, improve product quality, and boost your efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering



















