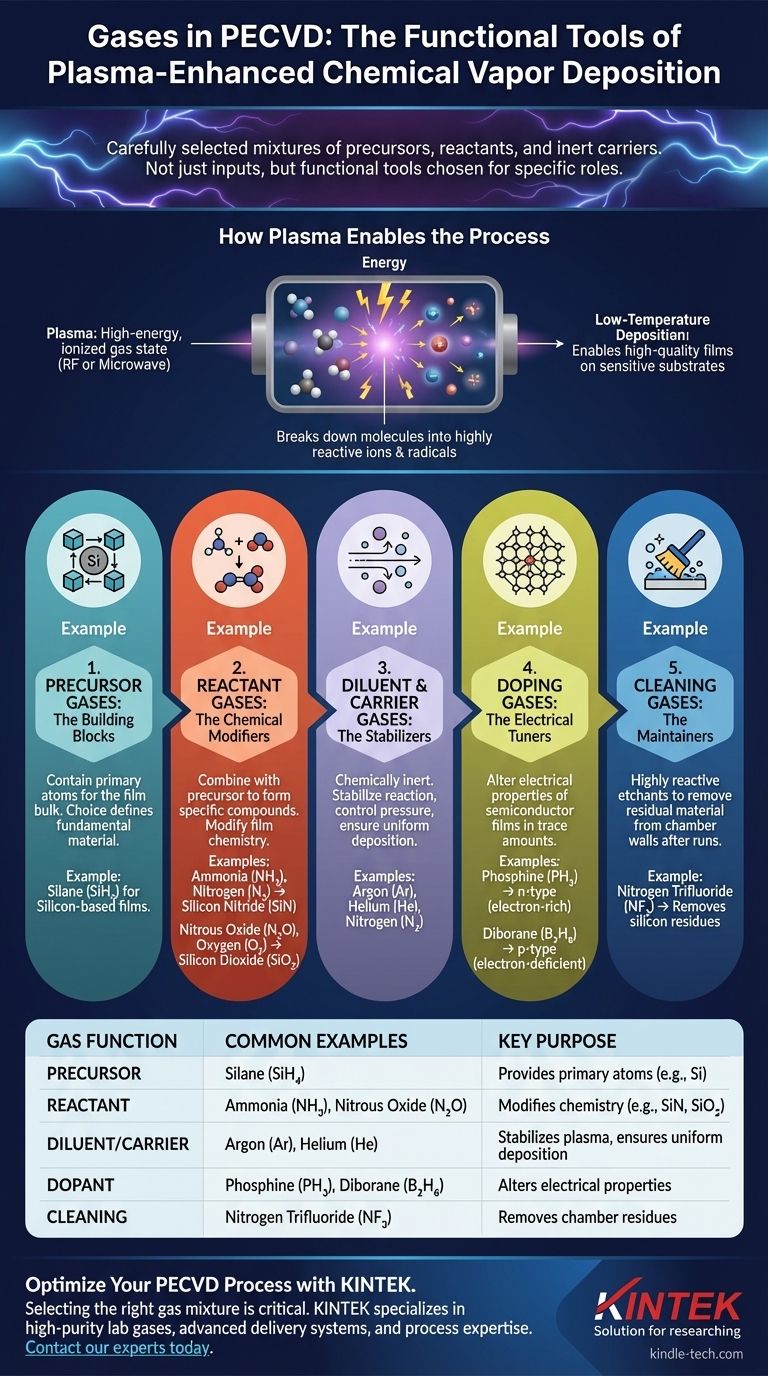
In Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), the gases used are a carefully selected mixture of precursors, reactants, and inert carriers. Common examples include silane (SiH₄) to provide silicon, ammonia (NH₃) or nitrous oxide (N₂O) to provide nitrogen or oxygen, and carrier gases like argon (Ar), helium (He), or nitrogen (N₂). Additional gases are used for specific purposes like doping or chamber cleaning.
The key to understanding PECVD is recognizing that gases are not just inputs; they are functional tools chosen for specific roles. Each gas serves as a building block (precursor), a chemical modifier (reactant), a process stabilizer (diluent), an electrical tuner (dopant), or a system maintainer (cleaning agent).

How Plasma Enables the Process
The Role of Energized Gas
PECVD relies on plasma—a high-energy, ionized state of gas. This plasma is typically generated using a radio frequency (RF) or microwave field.
The intense energy within the plasma breaks down the stable gas molecules into highly reactive ions and radicals. This allows chemical reactions to occur at much lower temperatures than in traditional thermal CVD processes.
Low-Temperature Deposition
This ability to drive reactions without extreme heat is the primary advantage of PECVD. It enables the deposition of high-quality thin films on substrates that cannot withstand high temperatures, such as plastics or fully processed semiconductor wafers.
The Core Roles of Gases in PECVD
The specific gas mixture, or "recipe," is determined entirely by the desired properties of the final thin film. Each gas has a distinct function.
Precursor Gases: The Building Blocks
Precursor gases contain the primary atoms that will make up the bulk of the deposited film. The choice of precursor defines the fundamental material being created.
For silicon-based films, the most common precursor is Silane (SiH₄).
Reactant Gases: The Chemical Modifiers
Reactant gases are introduced to combine with the precursor to form a specific compound film. They modify the chemistry of the final material.
Common examples include:
- Ammonia (NH₃) or Nitrogen (N₂) to create silicon nitride (SiN).
- Nitrous Oxide (N₂O) or Oxygen (O₂) to create silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Diluent and Carrier Gases: The Stabilizers
These are chemically inert gases that do not become part of the final film. Their purpose is to stabilize the reaction, control pressure, and ensure a uniform deposition rate across the substrate.
The most common diluent gases are Argon (Ar), Helium (He), and Nitrogen (N₂).
Doping Gases: The Electrical Tuners
To alter the electrical properties of a semiconductor film, small, controlled amounts of dopant gases are added.
Typical dopants include:
- Phosphine (PH₃) to create n-type (electron-rich) silicon.
- Diborane (B₂H₆) to create p-type (electron-deficient) silicon.
Cleaning Gases: The Maintainers
After deposition runs, residual material can build up on the chamber walls. A plasma-enhanced cleaning cycle is often performed using highly reactive etchant gases.
A common cleaning gas is Nitrogen Trifluoride (NF₃), which effectively removes silicon-based residues.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Gas Purity vs. Cost
The quality of the final film is directly tied to the purity of the source gases. While ultra-high purity gases produce superior results, they come at a significant cost, which must be balanced against the application's requirements.
Safety and Handling
Many gases used in PECVD are highly hazardous. Silane is pyrophoric (ignites on contact with air), while phosphine and diborane are extremely toxic. This necessitates complex and costly safety, storage, and gas delivery systems.
Process Complexity
Managing the precise flow rates, ratios, and pressures of multiple gases is a significant engineering challenge. Minor deviations in the gas recipe can drastically alter the properties of the deposited film, requiring sophisticated process control systems.
Selecting the Right Gas Mixture for Your Film
Your choice of gases is a direct translation of your desired material outcome.
- If your primary focus is a dielectric insulator (e.g., SiO₂): You will need a silicon precursor like SiH₄ and an oxygen source like N₂O, often diluted with He or N₂.
- If your primary focus is a passivation layer (e.g., SiN): You will combine a silicon precursor like SiH₄ with a nitrogen source like NH₃, typically in a nitrogen or argon carrier gas.
- If your primary focus is doped amorphous silicon (e.g., for solar cells): You will use SiH₄ as the precursor, potentially H₂ for structural control, and add trace amounts of PH₃ (n-type) or B₂H₆ (p-type).
- If your primary focus is chamber maintenance: You will run a plasma process using only an etchant gas like NF₃ to clean the chamber between deposition cycles.
Ultimately, mastering a PECVD process means mastering the precise control and interaction of these functional gases.
Summary Table:
| Gas Function | Common Examples | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor | Silane (SiH₄) | Provides primary atoms for the film (e.g., silicon) |
| Reactant | Ammonia (NH₃), Nitrous Oxide (N₂O) | Modifies chemistry to form compounds (e.g., SiN, SiO₂) |
| Diluent/Carrier | Argon (Ar), Helium (He) | Stabilizes plasma, ensures uniform deposition |
| Dopant | Phosphine (PH₃), Diborane (B₂H₆) | Alters electrical properties of semiconductor films |
| Cleaning | Nitrogen Trifluoride (NF₃) | Removes chamber residues between runs |
Optimize Your PECVD Process with KINTEK
Selecting the right gas mixture is critical for achieving high-quality thin films with precise electrical and structural properties. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab gases, advanced gas delivery systems, and process expertise for PECVD applications. Whether you are depositing silicon nitride for passivation, doped amorphous silicon for solar cells, or silicon dioxide for insulation, our solutions ensure safety, consistency, and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific PECVD requirements and discover how we can support your research or production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the benefits of plasma enhanced CVD? Achieve High-Quality, Low-Temperature Film Deposition
- What gas is used in PECVD? A Guide to Precursor, Carrier, and Doping Gas Mixtures
- What is plasma assisted physical vapor deposition? Enhance Your Coating Performance with Advanced PA-PVD
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced vapor deposition work? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Coating
- Why do PECVD systems operate at low pressure and low temperature? Protect Sensitive Substrates with Plasma Energy



















