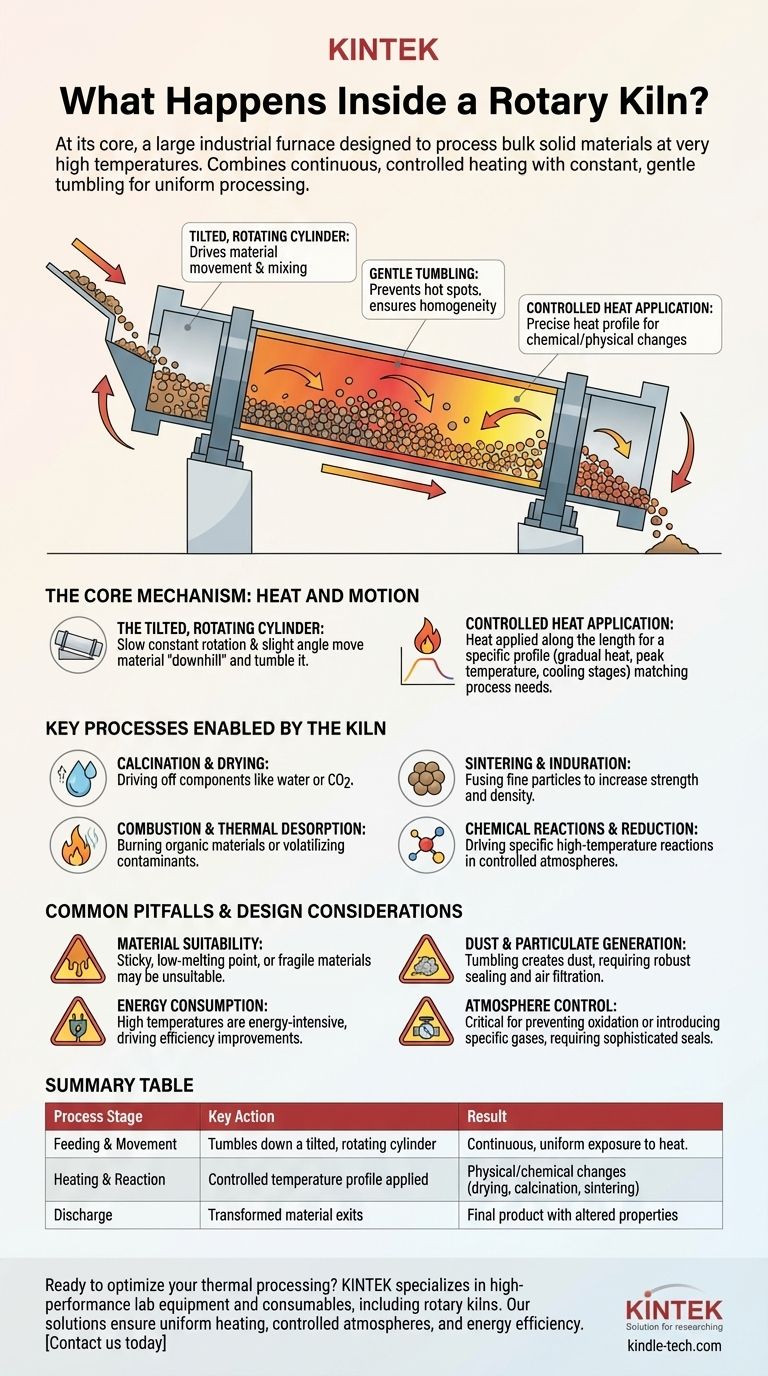
At its core, a rotary kiln is a large, industrial furnace designed to process bulk solid materials at very high temperatures. As raw material is fed into one end of a slowly rotating, tilted cylinder, it tumbles its way to the other end while being subjected to a precisely controlled heating profile, causing it to undergo fundamental physical and chemical transformations.
The essential function of a rotary kiln is to combine continuous, controlled heating with constant, gentle tumbling. This dual action ensures every particle of the material is processed uniformly, making it a highly reliable and efficient tool for industrial-scale material transformation.

The Core Mechanism: Heat and Motion
To understand what happens inside a rotary kiln, you must first understand its two fundamental operating principles: the controlled movement of material and the precise application of heat.
The Tilted, Rotating Cylinder
A rotary kiln is, first and foremost, a long cylindrical shell mounted on a slight angle. This tilt, combined with a slow, constant rotation, is what drives the entire process.
Material fed into the higher end automatically travels "downhill" toward the lower discharge end. The speed of this journey is carefully controlled by the kiln's angle and rotational speed.
The Role of Tumbling
The rotation does more than just move material along the kiln's length. It causes the material bed to continuously tumble and mix.
This tumbling action is critical. It prevents hot spots, exposes all surfaces of every particle to the heat source, and ensures a homogenous, consistently processed final product.
Controlled Heat Application
Heat is applied along the length of the kiln, often from a direct flame or through electric heating elements. Advanced kilns allow for a specific heat pattern or profile to be set.
This means the material can be heated gradually, held at a peak temperature, and then cooled in stages, matching the exact thermal requirements of the desired chemical reaction or physical change.
Key Processes Enabled by the Kiln
The combination of controlled movement and heating enables a wide range of industrial processes. The material that exits the kiln is fundamentally different from what went in.
Calcination and Drying
This is one of the most common uses. Calcination involves heating a material to drive off a specific component, such as removing water from hydrates or carbon dioxide from limestone to create lime.
Combustion and Thermal Desorption
Kilns are often used as incinerators to burn off organic materials or as thermal desorption units to volatilize and remove contaminants from soil or industrial waste.
Sintering and Induration
In these processes, fine powders or particles are heated to a temperature just below their melting point. This causes the particles to fuse together, dramatically increasing the material's strength and density, as seen in the production of iron ore pellets.
Chemical Reactions and Reduction
A kiln provides a high-temperature environment to drive specific chemical reactions. This can include reducing metal oxides to a more pure form by removing oxygen or creating specialized materials like battery cathodes or chemical catalysts.
Common Pitfalls and Design Considerations
While incredibly effective, the operation of a rotary kiln is not without its challenges. The design itself introduces specific considerations that must be managed for successful operation.
Material Suitability
The tumbling mechanism that makes a kiln so effective also limits the types of materials it can process. Materials that are sticky, have a very low melting point, or are extremely fragile may not be suitable.
Dust and Particulate Generation
The constant tumbling of dry materials inevitably creates dust. A properly designed kiln system must include robust sealing measures and downstream air filtration systems to capture these particulates.
Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining the high temperatures required for processes like calcination or sintering is extremely energy-intensive. This represents a significant operational cost and is a primary focus for efficiency improvements.
Atmosphere Control
For many chemical reactions, the atmosphere inside the kiln is critical. Preventing air from entering (to avoid oxidation) or introducing a specific gas requires sophisticated seals at the feed and discharge ends of the rotating cylinder.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the internal workings of a rotary kiln allows you to leverage its strengths for your specific industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is purification or removing volatiles (like in calcination): The key is the kiln's ability to apply sustained, uniform heat across the entire material bed to efficiently drive off unwanted compounds.
- If your primary focus is creating robust structures (like in sintering): The combination of a precise temperature profile and gentle tumbling is what allows fine particles to bond effectively without melting.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value, sensitive materials (like battery cathodes): The kiln's features for preventing contamination and maintaining a sealed, controlled atmosphere are the most critical factors for success.
Ultimately, a rotary kiln provides unparalleled control over the thermal processing of granular materials, making complex transformations both reliable and scalable.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding & Movement | Material tumbles down a tilted, rotating cylinder. | Continuous, uniform exposure to heat. |
| Heating & Reaction | Controlled temperature profile applied along the kiln. | Physical/chemical changes like drying, calcination, or sintering. |
| Discharge | Transformed material exits at the lower end. | Final product with altered properties (e.g., purified, strengthened). |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including rotary kilns for precise calcination, sintering, and chemical reactions. Our solutions ensure uniform heating, controlled atmospheres, and energy efficiency for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material transformation processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















