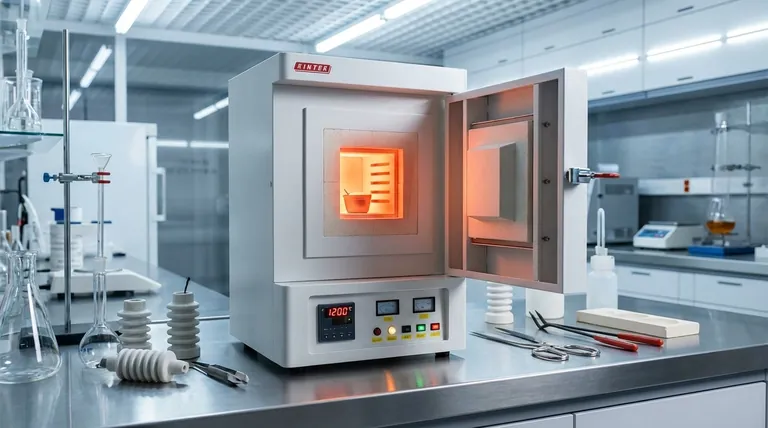
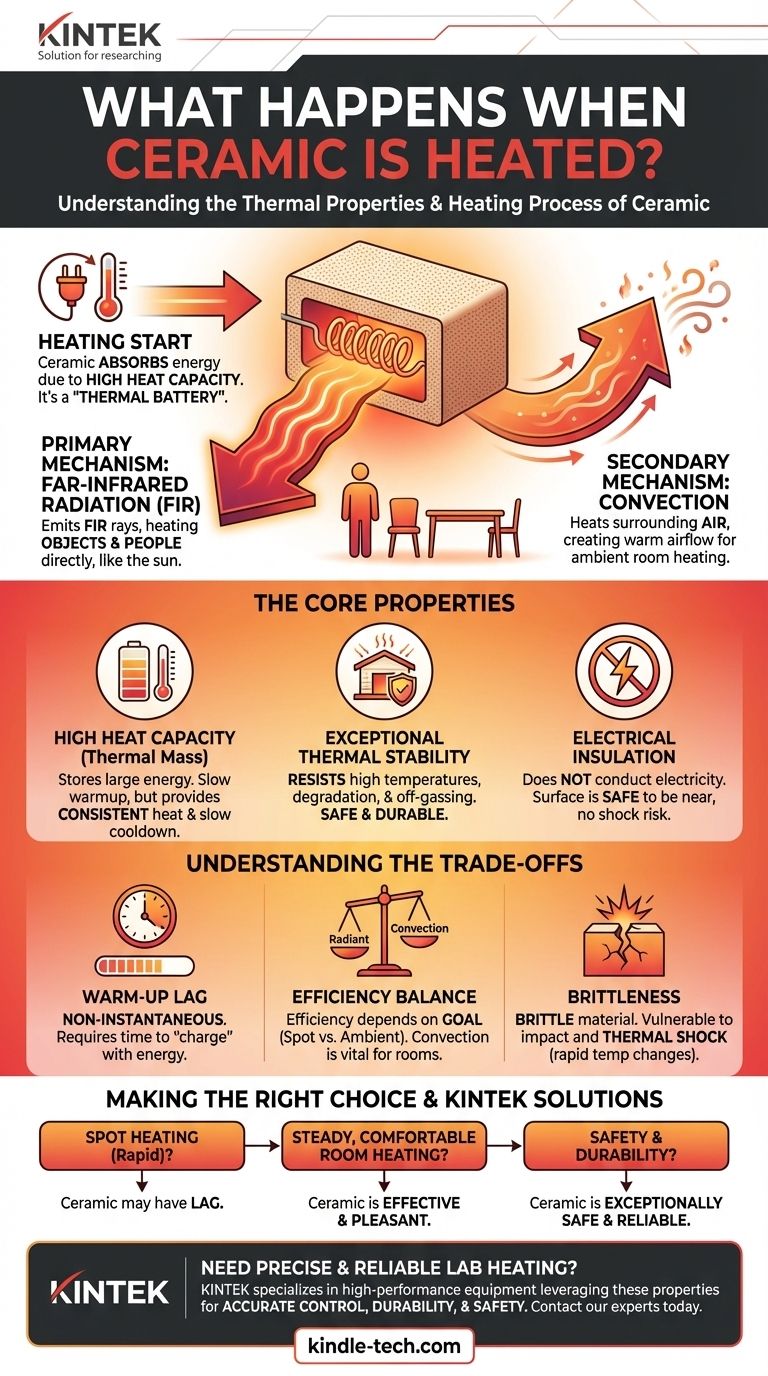
When ceramic is heated, it absorbs a significant amount of energy due to its high heat capacity, becoming a highly stable and effective radiator. Once at temperature, it primarily emits this energy as far-infrared radiation, which heats objects directly, while also transferring some heat to the surrounding air through convection.
The initial energy required to heat the ceramic material is not a loss, but an investment. This "thermal battery" effect is precisely what allows ceramic to provide steady, safe, and comfortable radiant heat long after the initial warm-up period.

The Core Properties of Heated Ceramic
To understand what happens when ceramic is heated, you must first understand its fundamental material properties. These characteristics are why it's a uniquely suitable material for controlled heating applications.
High Heat Capacity (Thermal Mass)
Ceramics possess a high heat capacity, meaning they can absorb and store a large amount of thermal energy without a correspondingly high rise in temperature.
This is why a ceramic heater takes a few minutes to get hot. It's first "charging" the ceramic element with energy. The benefit is that it also cools down slowly, providing consistent heat.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Unlike metals that can warp or plastics that can melt and off-gas, most ceramics are exceptionally stable at high temperatures.
They do not easily degrade, deform, or release harmful fumes, even when subjected to the continuous heating and cooling cycles of an appliance. This makes them inherently safe and durable.
Electrical Insulation
Most technical ceramics are excellent electrical insulators. In a typical ceramic heater, an electrical resistive element (like a coiled wire) gets very hot and transfers its heat to the much larger ceramic plate.
Because the ceramic itself doesn't conduct electricity, the heater's surface remains safe to be near, preventing the risk of electric shock.
How Ceramic Transfers Heat
Once the ceramic element is saturated with thermal energy, it begins to release it into the environment through two primary methods. The balance between these two is what defines the performance of a ceramic heater.
The Primary Mechanism: Infrared Radiation
Heated ceramic is a highly efficient emitter of far-infrared (FIR) radiation. This is a specific wavelength of light that we perceive as heat.
Crucially, infrared energy travels in a straight line and heats objects and people directly, rather than just heating the air in between. This is the same type of comfortable, penetrating heat you feel from the sun.
The Secondary Mechanism: Convection
As the surface of the ceramic element heats up, it also heats the layer of air in direct contact with it. This warmer, less dense air rises, and cooler air moves in to take its place, creating a natural convection current.
This process gradually warms the ambient air temperature in a room. While the provided reference calls this a "loss," in the context of space heating, it is an essential part of warming the entire environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. The properties that make ceramic excellent for steady heating also create specific trade-offs you must consider.
The "Warm-Up" Lag
The high heat capacity that allows for steady heat output also means ceramic heaters are not instantaneous. There is a noticeable warm-up period as the ceramic element absorbs energy.
Convection vs. Radiation Efficiency
The balance of heat transfer is key. A device designed for pure radiant heating (like an outdoor patio heater) wants to minimize convection. A space heater for an enclosed room needs convection to circulate warm air. The "loss" to convection is only a negative if the goal is purely directional, spot heating.
Brittleness and Thermal Shock
While thermally stable, ceramic is a brittle material. A sharp impact can cause it to crack or shatter. Furthermore, very rapid and uneven temperature changes can create internal stresses, a phenomenon known as thermal shock, which can also lead to fractures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Heating Goal
Your specific goal determines whether the properties of heated ceramic are an advantage or a disadvantage.
- If your primary focus is rapid, spot heating: The warm-up lag of ceramic is a distinct disadvantage compared to the instant heat from a quartz or halogen heater.
- If your primary focus is steady, comfortable room heating: The combination of gentle radiant heat and natural convection from a ceramic heater is one of the most effective and pleasant solutions.
- If your primary focus is safety and durability: The high-temperature stability and non-conductive nature of ceramic make it an exceptionally safe and reliable choice for indoor environments.
Understanding these properties empowers you to select a heating technology that aligns precisely with your needs for comfort, speed, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Property | Effect When Heated |
|---|---|
| High Heat Capacity | Absorbs and stores significant energy, providing steady, consistent heat output. |
| Thermal Stability | Resists warping, degradation, and harmful fume release, even at high temperatures. |
| Electrical Insulation | Heater surface remains safe to touch, preventing electric shock risk. |
| Infrared Radiation | Emits far-infrared rays that heat objects and people directly, like the sun. |
| Convection | Warms surrounding air, contributing to ambient room temperature increase. |
Need Precise and Reliable Heating for Your Laboratory?
The unique thermal properties of ceramic are essential for controlled, safe, and efficient heating applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and heating elements that leverage these exact material advantages.
Our solutions ensure accurate temperature control, exceptional durability, and inherent safety for your most demanding processes.
Let KINTEK empower your research and development. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What can silicon carbide be used for? Solve Extreme Heat, Wear, and Purity Challenges
- How is the poor thermal-shock resistance of pure alumina typically mitigated? Improve Durability with Alumino-Silicates
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- What are the synthesis methods of SiC? From Industrial Abrasives to High-Performance Electronics
- What are the characteristics of sintering in ceramics? Unlock Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the three types of dental ceramic? A Guide to Balancing Aesthetics & Strength
- What is the process of hot isostatic pressing for making ceramic matrix composites? Achieve Near-Zero Porosity for Superior Performance
- Why is silicon carbide so important? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions



















