Annealing is a foundational heat treatment process utilized across nearly every major engineering and manufacturing sector. It is employed in the aviation, automotive, military, oil and gas, energy, healthcare, tooling, and electronics industries to precisely modify a material's internal structure, making it more suitable for subsequent manufacturing steps or for its final application.
While a diverse range of industries rely on annealing, they all share a common need: to improve a material's workability, reduce its hardness, and relieve internal stresses, making it more reliable and easier to manufacture into a final product.

Why Annealing is a Critical Industrial Process
To understand why so many industries depend on annealing, you must first understand the problems it solves. Manufacturing processes like casting, forging, machining, or welding introduce significant stress and hardness into materials, making them brittle and difficult to work with.
The Core Principle: Reversing Material Stress
Annealing involves heating a material (typically metal) above its critical recrystallization temperature, holding it at that temperature for a specific time, and then cooling it at a very slow, controlled rate.
This process allows the material's internal crystalline structure, or "grain," to reform into a more uniform and stress-free state.
Primary Goal 1: Improving Ductility and Softening
The most common reason for annealing is to increase ductility (the ability to be deformed without breaking) and reduce hardness.
A softer, more ductile material is far easier to machine, stamp into a complex shape like a car door, or draw into a thin wire for electronics. This significantly reduces tool wear and the risk of component fracture during manufacturing.
Primary Goal 2: Relieving Internal Stresses
Welding, bending, and heavy machining create immense internal stresses within a material. If left untreated, these stresses can lead to warping, dimensional instability, or even catastrophic failure over time.
Annealing provides a controlled way to relax these residual stresses, ensuring the final component is stable and safe, which is non-negotiable in aerospace, automotive, and military applications.
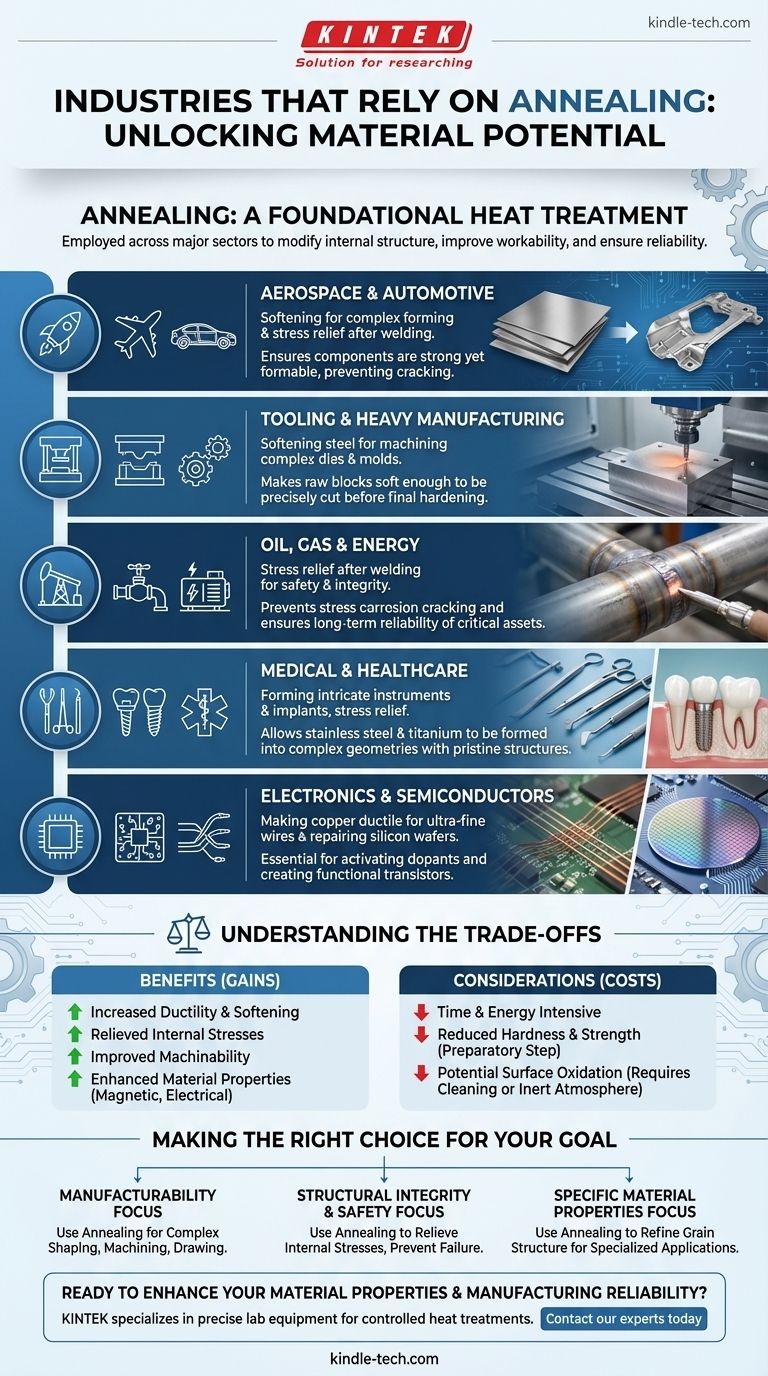
Specific Applications Across Key Industries
The general principles of annealing translate into specific, high-value applications depending on the industry's unique demands.
Aerospace and Automotive
Parts like engine components, landing gear, and vehicle body panels must be strong yet formable. Annealing is used on raw metal sheets and forgings to make them soft enough to be shaped without cracking. It's also used after welding to relieve stress in the frame and structural components.
Tooling and Heavy Manufacturing
Before a high-strength piece of tool steel can become a complex die or mold, it must be machined. Annealing makes the raw steel block soft enough to be precisely cut and shaped. Only after machining is it re-hardened for its final, durable use.
Oil, Gas, and Energy
Pipelines, pressure vessels, and generator components are often welded and operate under extreme conditions. Stress-relief annealing is a mandatory step after welding to prevent stress corrosion cracking and ensure the long-term integrity and safety of these critical assets.
Medical and Healthcare
Surgical instruments and medical implants require intricate shapes and a pristine, stable material structure. Annealing allows materials like stainless steel and titanium alloys to be formed into complex geometries and ensures they are free of internal stresses that could compromise their performance in the body.
Electronics and Semiconductors
In electronics, annealing makes copper more ductile, allowing it to be drawn into the ultra-fine wires used in circuits and motors. In semiconductor manufacturing, annealing is a highly specialized process used to repair crystal lattice damage in silicon wafers after ion implantation, which is essential for activating dopants and creating functional transistors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, annealing is not without its costs and considerations. Decision-makers must weigh its benefits against these factors.
Time and Energy Consumption
Heating large components in industrial furnaces and cooling them slowly over many hours is an energy-intensive and time-consuming process. This directly translates to higher production costs and longer lead times.
Reduced Hardness and Strength
By design, annealing softens a material. While this is necessary for formability, the annealed part does not possess its final required strength. It is a preparatory step, and the component will almost always require a subsequent heat treatment, like quenching and tempering, to achieve its final desired hardness.
Potential for Surface Oxidation
Heating metals to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen can cause a layer of scale or oxidation to form on the surface. This often requires a secondary cleaning process (like sandblasting or acid pickling), adding another step and cost to production. This can be mitigated by annealing in a controlled, inert gas atmosphere, but that increases process complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use annealing is driven by the end goal for the material or component.
- If your primary focus is manufacturability: Annealing is your key to making hard materials soft enough for complex shaping, machining, or drawing.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and safety: Use annealing to relieve internal stresses from welding or forming, preventing premature failure in critical components.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: Annealing can refine a material's grain structure to enhance its magnetic or electrical performance for specialized applications.
Ultimately, understanding annealing is understanding how to unlock a material's full potential for its intended industrial purpose.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use of Annealing |
|---|---|
| Aerospace & Automotive | Softening for forming, stress relief after welding |
| Tooling & Manufacturing | Softening steel for machining complex dies/molds |
| Oil, Gas & Energy | Stress relief after welding for safety and integrity |
| Medical & Healthcare | Forming intricate instruments/implants, stress relief |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Making copper ductile for wires, repairing silicon wafers |
Ready to enhance your material properties and manufacturing reliability?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for controlled heat treatment processes like annealing. Whether you are in aerospace, medical, or electronics manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve the perfect material structure for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific annealing and material testing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















