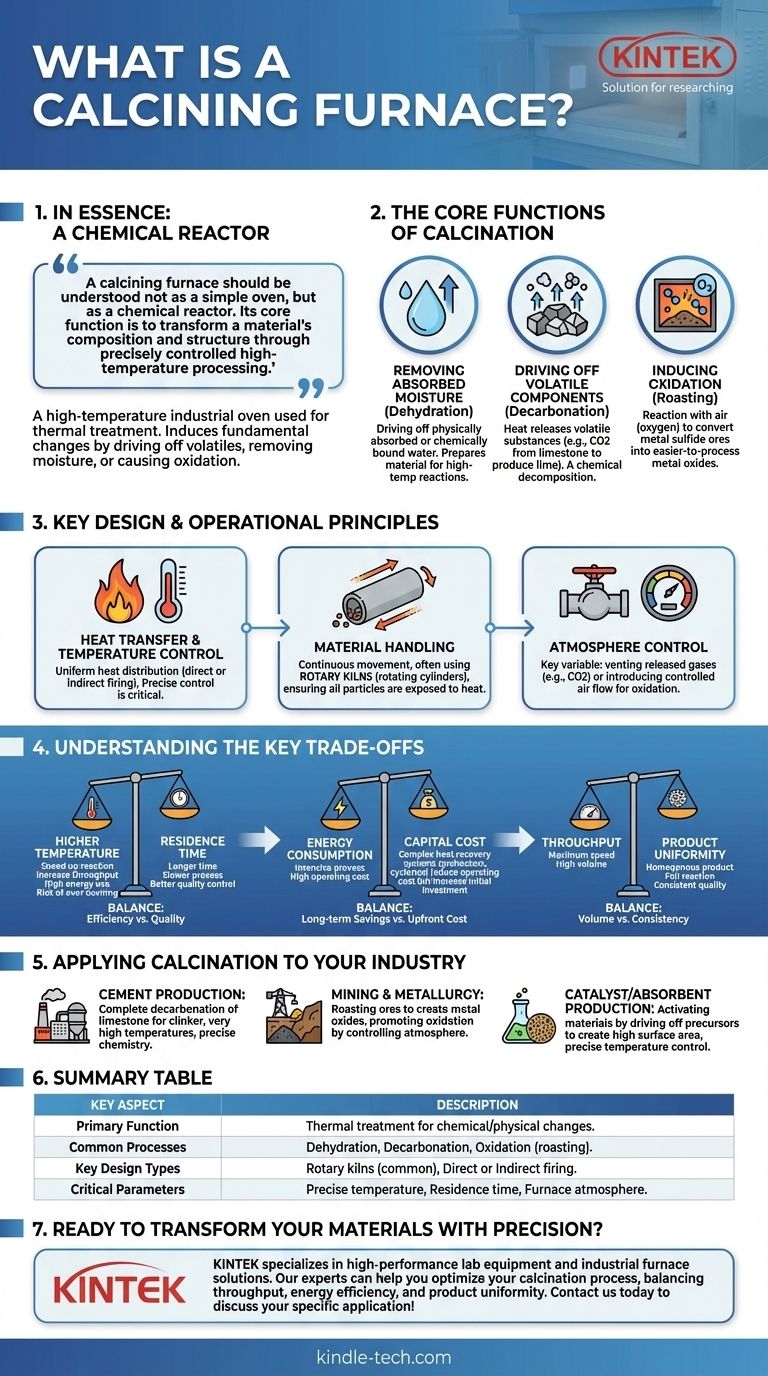
In essence, a calcining furnace is a high-temperature industrial oven used for the thermal treatment of materials. Its primary purpose is not merely to heat a substance, but to induce a fundamental change in its physical or chemical properties by driving off volatile components, removing absorbed moisture, or causing oxidation.
A calcining furnace should be understood not as a simple oven, but as a chemical reactor. Its core function is to transform a material's composition and structure through precisely controlled high-temperature processing.

The Core Functions of Calcination
The term "calcination" comes from the Latin calcinare, "to burn lime," which perfectly captures its purpose. The process uses thermal energy to trigger specific changes within a material.
Removing Absorbed Moisture
The most basic function is dehydration, or driving off water that is physically absorbed or chemically bound within a material's structure. This is often the first stage of heating and prepares the material for higher-temperature chemical reactions.
Driving Off Volatile Components
This is the central purpose of most calcination processes. By heating a material to a specific temperature below its melting point, volatile substances are released. The most common example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate), where heat drives off carbon dioxide (CO2).
This process, known as decarbonation, is a true chemical decomposition that fundamentally alters the material.
Inducing Oxidation
A calcining furnace can also be used to intentionally react a material with the air (oxygen) inside it. This is a common step in metallurgy, where metal sulfide ores are "roasted" (a form of calcination) to convert them into metal oxides, which are easier to process and reduce to pure metal later on.
Key Design & Operational Principles
While designs vary, most industrial calcining furnaces share common operational principles focused on heat transfer, material handling, and atmosphere control.
Heat Transfer and Temperature Control
The furnace must provide uniform heat to the entire volume of material. This can be achieved through direct firing, where combustion gases are in direct contact with the material, or indirect firing, where heat is transferred through the wall of a rotating chamber (as in a rotary kiln). Precise temperature control is critical to ensure the desired reaction occurs without melting or damaging the material.
Material Handling
For continuous processing, the material must move through the furnace. Rotary kilns are the most common type of calcining furnace. They are large, rotating cylinders set at a slight incline, allowing the material to tumble and flow from the upper feed end to the lower discharge end, ensuring all particles are exposed to the heat.
Atmosphere Control
The composition of the gas inside the furnace is a key process variable. For simple decarbonation, the goal is just to vent the released CO2. For oxidation, a controlled flow of air is introduced to provide the necessary oxygen for the chemical reaction.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Operating a calcining furnace involves balancing competing operational and economic factors. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is a common source of inefficiency and poor product quality.
Temperature vs. Residence Time
There is a direct relationship between the furnace temperature and the time the material must spend inside it. Higher temperatures can speed up the reaction and increase throughput, but they also drastically increase energy consumption and can lead to "over-burning," which can damage the final product's structure.
Energy Consumption vs. Capital Cost
Calcination is an extremely energy-intensive process. Highly efficient furnaces often use complex heat recovery systems, such as preheaters or multi-stage cyclones, to capture waste heat from exhaust gases and use it to pre-heat the incoming raw material. These systems significantly reduce operating costs but add to the initial capital investment.
Throughput vs. Product Uniformity
Pushing for maximum throughput can lead to incomplete reactions if the material moves through the furnace too quickly. This results in a non-uniform product with an unreacted core, compromising its quality and performance in downstream applications. Achieving a homogenous, fully calcined product often requires a slower, more deliberate process.
Applying Calcination to Your Industry
The specific goal of calcination defines the critical process parameters.
- If your primary focus is cement production: The goal is the complete decarbonation of limestone within a blend of raw materials to form cement clinker, requiring very high temperatures and precise raw material chemistry.
- If your primary focus is mining and metallurgy: The focus is often on roasting ores to create metal oxides, where controlling the furnace atmosphere to promote oxidation is just as important as temperature.
- If your primary focus is catalyst or absorbent production: Calcination is used to activate materials by driving off precursor chemicals, creating a highly porous structure with a massive surface area, where precise temperature control is paramount to avoid structural collapse.
Ultimately, a calcining furnace is a precise instrument of material transformation, fundamental to the production of countless essential industrial materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermal treatment to induce chemical/physical changes in materials. |
| Common Processes | Dehydration, decarbonation (e.g., limestone to lime), oxidation (roasting). |
| Key Design Types | Rotary kilns (common), direct or indirect firing systems. |
| Critical Parameters | Precise temperature control, residence time, and furnace atmosphere. |
Ready to transform your materials with precision? The right calcining furnace is critical for achieving consistent, high-quality results in cement, mining, or catalyst production. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and industrial furnace solutions. Our experts can help you select the ideal system to optimize your calcination process, balancing throughput, energy efficiency, and product uniformity. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















