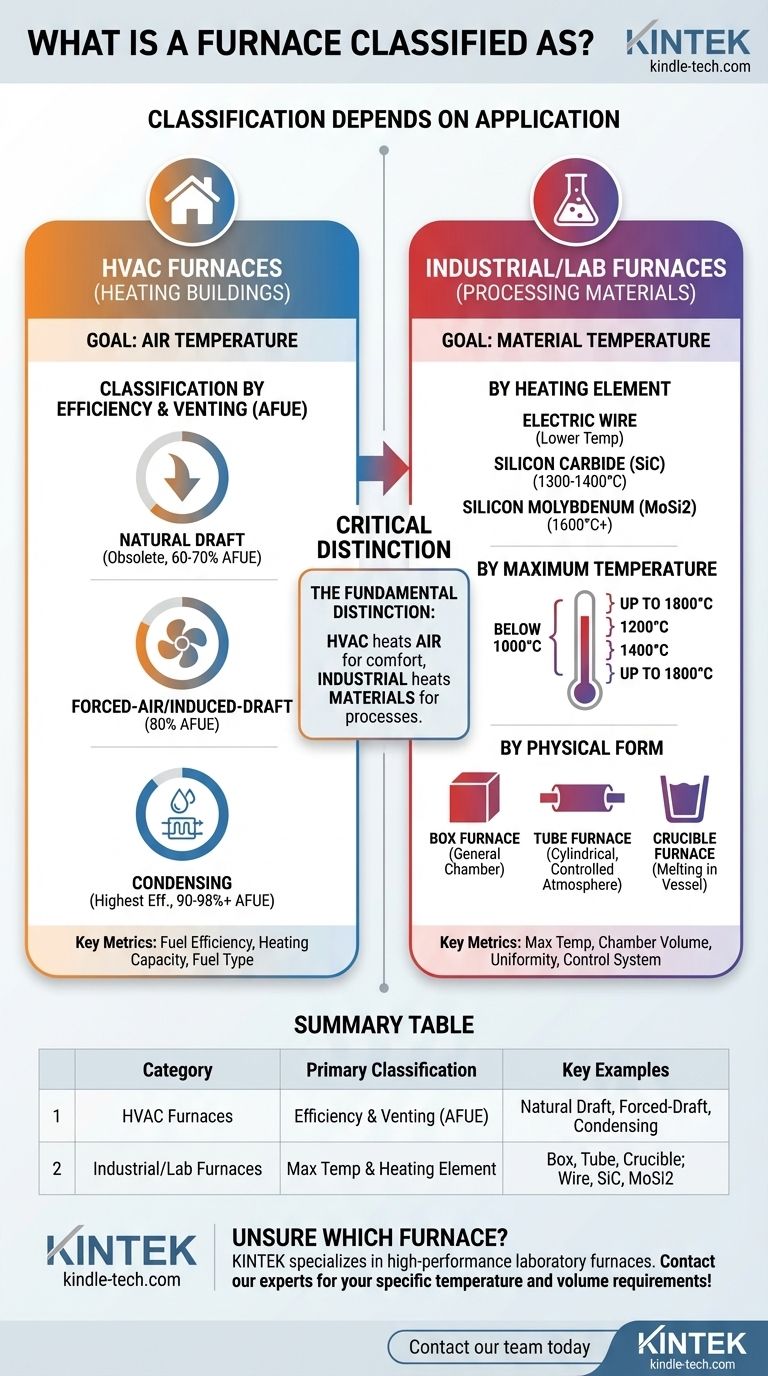
A furnace is not classified by a single, universal system. Instead, its classification depends entirely on its application, primarily falling into two major categories: HVAC systems for heating buildings and specialized furnaces for laboratory or industrial processes. For home heating, furnaces are categorized by efficiency and airflow design, while industrial furnaces are classified by factors like maximum temperature and heating element type.
The term "furnace" is broad, and its classification method changes based on its purpose. The most fundamental distinction is between HVAC furnaces designed to heat air for comfort and specialized industrial furnaces designed to heat materials to extreme temperatures for processes like metallurgy or research.
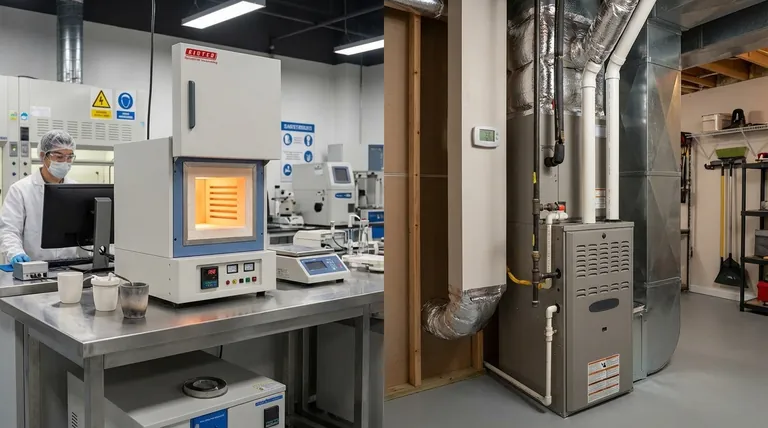

Classification for HVAC Furnaces (Home & Building Heating)
When discussing furnaces for residential or commercial buildings, the classification centers on efficiency, safety, and how the system handles air and exhaust. These are generally categorized by their venting method and overall design.
By Efficiency and Venting Method
The most common way to classify modern HVAC furnaces is by their Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating, which is closely tied to their design.
A Natural Draft Furnace is an older, low-efficiency design (typically 60-70% AFUE). It relies on the natural buoyancy of hot exhaust gases to vent them up a chimney, similar to a traditional fireplace. These are largely obsolete due to their inefficiency.
A Forced-Air / Induced-Draft Furnace is a significant improvement (typically 80% AFUE). It uses a small fan to actively pull exhaust gases out, which improves efficiency and safety over natural draft systems.
A Forced-Draft / Sealed-Combustion Furnace also operates around 80% AFUE but enhances safety. It draws combustion air from the outside directly into a sealed chamber, preventing it from consuming oxygen from inside the living space.
A Condensing Furnace represents the highest efficiency category (90-98%+ AFUE). It features a second heat exchanger that captures additional heat from the exhaust vapor, causing it to condense into water. This design extracts the maximum possible energy from the fuel.
Classification for Laboratory & Industrial Furnaces
In scientific and industrial settings, the term "furnace" usually refers to a high-temperature oven, often called a muffle furnace. These are not used for heating buildings but for processing materials. Their classification is based on their technical capabilities.
By Heating Element
The type of heating element dictates the furnace's maximum achievable temperature and longevity.
- Electric Wire Muffle Furnace: Uses a resistance wire element. These are common for lower-temperature applications.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rod Muffle Furnace: Employs SiC rods to achieve higher temperatures, typically in the 1300°C to 1400°C range.
- Silicon Molybdenum (MoSi2) Rod Muffle Furnace: Uses specialized MoSi2 elements to reach very high temperatures, often 1600°C or more.
By Maximum Temperature
This is a critical specification for industrial use. Furnaces are grouped into brackets based on the highest temperature they can safely sustain, such as below 1000°C, 1200°C, 1400°C, and up to 1800°C.
By Physical Form
The shape of the furnace is designed around the material it will heat.
- Box Furnace: A standard chamber for general-purpose heating of objects or materials in crucibles.
- Tube Furnace: Features a cylindrical chamber for heating samples within a tube, often used for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere.
- Crucible Furnace: Designed specifically to heat materials contained within a vessel called a crucible, common in metallurgy for melting metals.
By Control System
The controller determines the precision and automation of the heating process, ranging from simple pointer tables and digital displays to sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers that provide precise temperature stability and programmable controllers for complex heating cycles.
Understanding the Critical Distinction
The most common point of confusion arises from not distinguishing between the goals of these two broad furnace categories. Failing to do so can make technical specifications seem irrelevant or contradictory.
HVAC: The Goal is Air Temperature
For an HVAC furnace, the entire system is designed to heat air and distribute it throughout a structure. The key metrics are fuel efficiency (AFUE), heating capacity (BTUs), and the type of fuel used (natural gas, propane, oil). Safety and emissions are also primary concerns.
Industrial/Lab: The Goal is Material Temperature
For an industrial or laboratory furnace, the goal is to heat a material inside a controlled chamber to a specific, often extreme, temperature. The key metrics are maximum temperature, chamber volume, temperature uniformity, and the precision of the control system. Fuel efficiency is a secondary concern to process accuracy.
How to Identify the Right Classification for Your Needs
To make sense of furnace classifications, start by identifying the application.
- If your primary focus is residential or commercial heating: You should concentrate on HVAC classifications, particularly the efficiency tiers (non-condensing at ~80% AFUE vs. condensing at 90%+ AFUE).
- If your primary focus is laboratory research or industrial manufacturing: You need to use the industrial classifications, starting with the required maximum temperature, which will then determine the necessary heating element and furnace type.
- If you are simply trying to understand the term: The key is to recognize that "furnace" is context-dependent and always ask whether it is being used for comfort heating or material processing.
Ultimately, understanding the intended purpose of the furnace is the first and most critical step in its classification.
Summary Table:
| Category | Primary Classification Method | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| HVAC Furnaces | Efficiency & Venting (AFUE Rating) | Natural Draft, Forced-Draft, Condensing |
| Industrial/Lab Furnaces | Maximum Temperature & Heating Element | Box, Tube, Crucible; Wire, SiC, MoSi2 |
Unsure which furnace type is right for your process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces for research and industry. Whether you need a box furnace for general heating or a high-temperature tube furnace for specialized applications, our experts can help you select the perfect equipment. Contact our team today to discuss your specific temperature and volume requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of the sintering process in ceramic manufacturing? Achieve High Density and Structural Integrity
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating
- How to cool a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Maximize Equipment Lifespan
- What are the risks associated with the sintering process? Key Strategies to Prevent Failure & Maximize Quality
- What is the objective of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing



















