In a laboratory context, the term "mixer" is not a single device but a category of equipment designed for two fundamentally different tasks. The most common is the vortex mixer, used for rapidly agitating small liquid samples. However, the term also applies to a mixer mill, a specialized instrument designed for grinding small quantities of solid material into a fine powder.
The critical distinction is the state of the sample: a vortex mixer is for agitating liquids, while a mixer mill is for pulverizing solids. Understanding your starting material and your goal—simple mixing or particle size reduction—is essential to selecting the correct instrument.
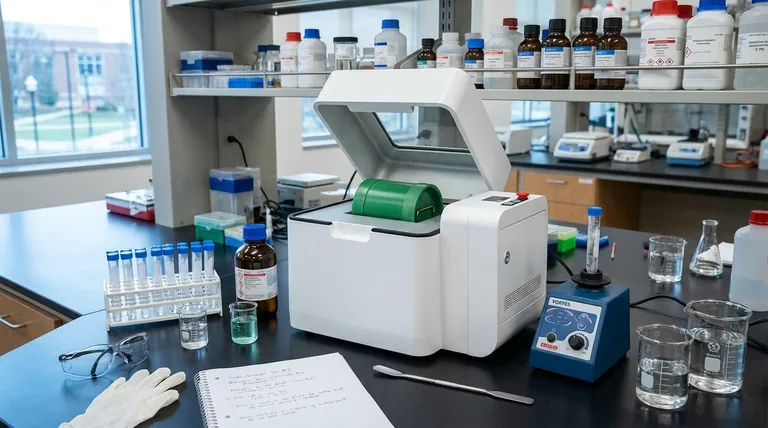

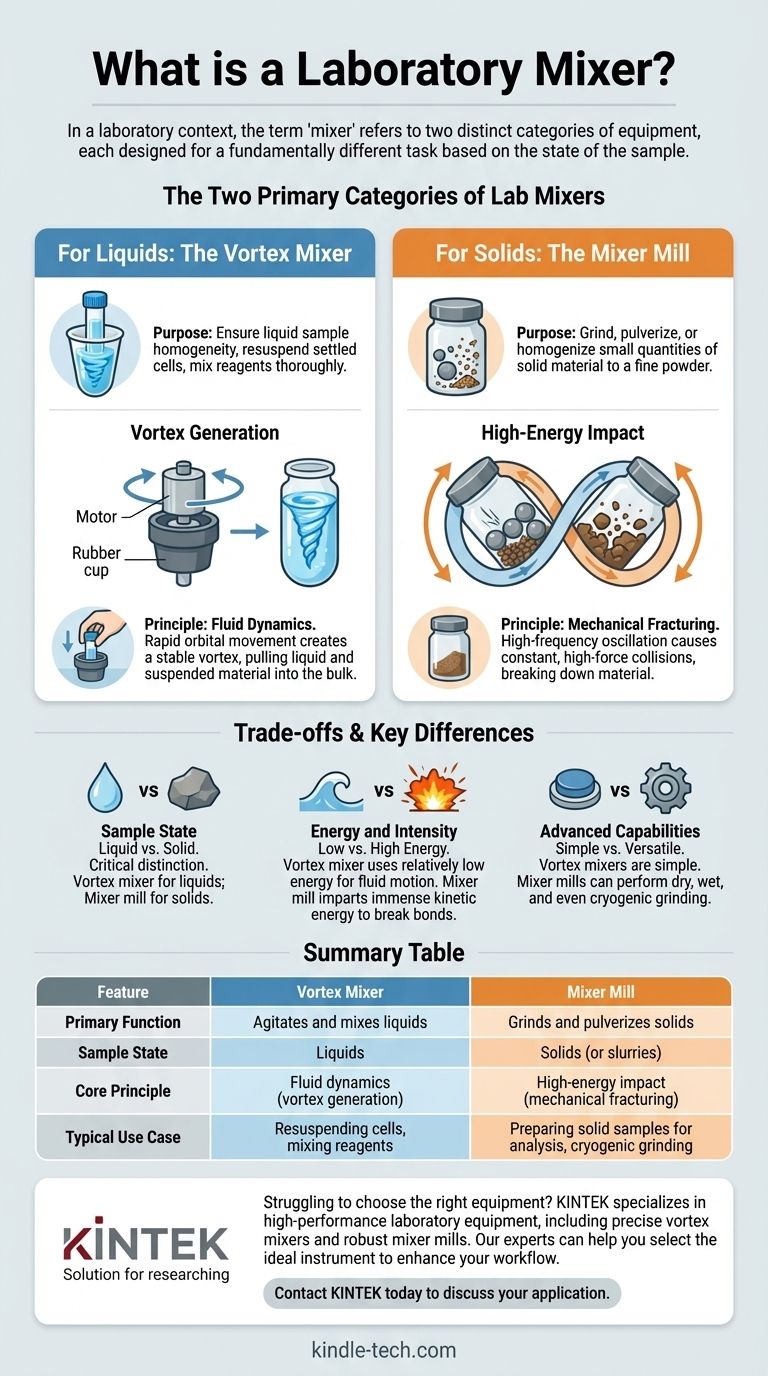
The Two Primary Categories of Lab Mixers
The function of a laboratory mixer depends entirely on its type. While both involve agitation, their mechanisms, energy levels, and intended outcomes are completely distinct.
For Liquids: The Vortex Mixer
A vortex mixer is a simple, ubiquitous piece of lab equipment for mixing small volumes of liquid in test tubes or vials.
Its purpose is to ensure a liquid sample is homogenous, to resuspend settled cells or particles, or to mix reagents thoroughly.
The device consists of an electric motor connected to a rubber cup. When a vial is pressed into the cup, the motor oscillates it in a rapid circular motion, creating a vortex (a whirlpool) within the liquid that powerfully combines its contents.
For Solids: The Mixer Mill
A mixer mill is a high-energy ball mill designed for grinding, pulverizing, or homogenizing small quantities of solid material.
It is used to prepare samples for analysis by reducing them to a fine, uniform powder. This process is often called comminution.
The mill works by sealing the sample inside a grinding jar along with one or more grinding balls. The jar is then subjected to intense oscillation, causing the balls to collide with the material at high speed, pulverizing it through high-energy impact. This method is exceptionally fast and effective, even for tough materials.
Understanding the Core Principles
The "mixing" action in each device is achieved through vastly different physical principles tailored to the state of matter being processed.
Vortex Generation for Liquid Agitation
The principle behind the vortex mixer is fluid dynamics. The rapid orbital movement of the vial forces the liquid against the walls due to inertia.
This creates a stable vortex that pulls liquid and suspended material from the top surface down into the bulk of the fluid, resulting in fast and complete mixing.
High-Energy Impact for Solid Grinding
The mixer mill relies on the principle of mechanical fracturing. The motion of the grinding jars is not a simple spin but a high-frequency oscillation, often in a figure-eight pattern.
This ensures constant, high-force collisions between the heavy grinding balls and the sample material, breaking it down into smaller and smaller particles. This is a destructive physical process, not a gentle stirring action.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Differences
Confusing these two instruments can lead to failed experiments or damaged equipment. Their differences are absolute.
Sample State: Liquid vs. Solid
This is the most critical distinction. A vortex mixer is exclusively for liquids in standard vials. A mixer mill is for solids (or slurries) in specialized, sealed grinding jars. You cannot grind a rock on a vortexer, and you cannot vortex a sample inside a sealed mill.
Energy and Intensity
A vortex mixer uses relatively low energy to create fluid motion. The energy is just enough to agitate the liquid contents.
A mixer mill imparts immense kinetic energy into the system. This energy is high enough to break the chemical and physical bonds within a solid crystalline structure, reducing it to powder.
Advanced Capabilities
Vortex mixers are simple devices with one primary function.
Mixer mills, however, can perform dry grinding, wet grinding (with a solvent), and even cryogenic grinding, where the jar is cooled with liquid nitrogen. This makes them suitable for heat-sensitive or elastic samples that are otherwise difficult to pulverize.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Application
Selecting the correct instrument is not a matter of preference but of necessity based on the physical requirements of your protocol.
- If your primary focus is mixing liquid reagents or resuspending cells: A vortex mixer is the simple, correct tool for rapid agitation in vials or test tubes.
- If your primary focus is preparing a solid sample for analysis: A mixer mill is required to grind the material into a fine, homogenous powder.
- If your primary focus is processing tough, elastic, or heat-sensitive solids: A mixer mill with cryogenic grinding capability is the essential instrument for the task.
Ultimately, identifying the physical state of your sample and your desired final outcome is the only way to determine which "mixer" you truly need.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vortex Mixer | Mixer Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Agitates and mixes liquids | Grinds and pulverizes solids |
| Sample State | Liquids | Solids (or slurries) |
| Core Principle | Fluid dynamics (vortex generation) | High-energy impact (mechanical fracturing) |
| Typical Use Case | Resuspending cells, mixing reagents | Preparing solid samples for analysis, cryogenic grinding |
Struggling to choose the right equipment for your lab's mixing or grinding needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment, including vortex mixers for precise liquid agitation and robust mixer mills for efficient solid sample preparation. Our experts can help you select the ideal instrument to enhance your workflow, ensure sample homogeneity, and achieve accurate, reproducible results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover how our solutions can power your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results



















