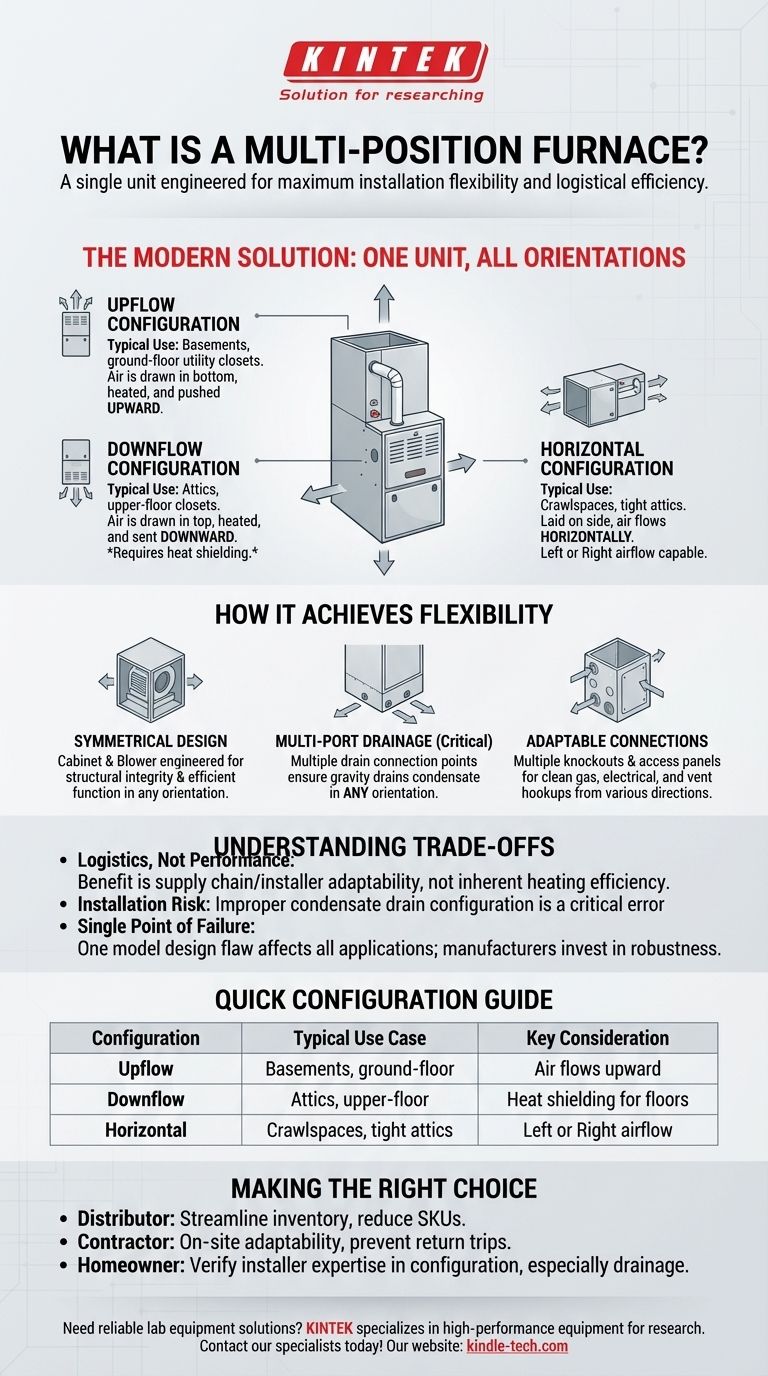
In short, a multi-position furnace is a single unit engineered for maximum installation flexibility. It is designed from the factory to be installed in any standard orientation—upflow, downflow, or horizontal (left or right)—without requiring major, on-site modifications.
The core value of a multi-position furnace is not about heating performance; it's about logistical efficiency. It solves the complex inventory and planning problems faced by distributors and contractors by creating a "one-size-fits-all" solution for different home layouts.

The Problem: One Home, Many Orientations
Before multi-position units became standard, HVAC contractors had to stock or order specific furnace models for specific installation scenarios. A furnace designed for a basement couldn't be used in an attic, creating significant logistical challenges.
The Upflow Configuration
This is the most common orientation, typically used in basements or ground-floor utility closets. Air is drawn into the bottom of the furnace, heated, and then pushed upward into the ductwork system.
The Downflow Configuration
Used in installations where the furnace is located above the living space, such as an attic or a closet on an upper floor. Air is drawn into the top of the furnace, heated, and sent downward into the ducts below. This orientation requires careful consideration of heat shielding for combustible floors.
The Horizontal Configuration
Ideal for tight spaces like crawlspaces or attics where vertical height is limited. The furnace is laid on its side, and air flows through it horizontally. A true multi-position furnace can be configured for either left-side or right-side airflow.
How a Single Furnace Achieves This
The versatility of a multi-position furnace comes from deliberate engineering choices that ensure it operates safely and effectively regardless of how it's installed.
Symmetrical Cabinet and Blower Design
The furnace's cabinet is designed to be structurally sound in any orientation. Internal components, particularly the blower motor and fan assembly, are positioned and secured to function efficiently whether they are pushing air up, down, or sideways.
Multi-Port Condensate Drainage
This is the most critical feature. High-efficiency condensing furnaces produce water (condensate) that must be drained. A multi-position furnace has multiple drain connection points or a modular trap system to ensure gravity can properly drain the water, no matter the furnace's orientation.
Adaptable Venting and Electrical Connections
The unit includes multiple knockouts and access panels for gas lines, electrical wiring, and flue pipes. This allows the installer to make the necessary connections cleanly and safely from different directions depending on the final placement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While they are the industry standard, it's important to understand what a multi-position furnace is—and what it isn't.
It's About Logistics, Not Performance
A multi-position furnace does not inherently heat better or more efficiently than a dedicated, single-position model. Its primary benefit is for the supply chain and the installer, which translates to better availability and adaptability for the customer.
Installation Error is a Critical Risk
The unit's flexibility can become a liability if the installer is not diligent. The most common error is improperly configuring the condensate drain for the chosen orientation. This mistake can lead to water pooling inside the unit, causing component failure, property damage, and safety hazards.
A Single Point of Failure
Because one model is used for all applications, any manufacturing defect or design flaw in that model has a much broader impact across all installation types. However, this also means manufacturers invest heavily in ensuring the design is robust.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a multi-position furnace is less about choice and more about understanding the modern HVAC standard.
- If your primary focus is streamlining inventory (Distributor): Multi-position furnaces are the clear choice to drastically reduce the number of SKUs you need to stock.
- If your primary focus is on-site adaptability (Contractor): Carrying a multi-position unit on your truck means you are prepared for virtually any layout you encounter, preventing return trips and project delays.
- If your primary focus is a reliable installation (Homeowner): Trust that the multi-position unit is the correct modern hardware, but verify your installer is an expert in configuring it for your specific home, paying close attention to the drain and venting setup.
Ultimately, the multi-position furnace represents a shift toward intelligent design that solves practical, real-world installation challenges.
Summary Table:
| Configuration | Typical Use Case | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Upflow | Basements, ground-floor closets | Air flows upward into ductwork |
| Downflow | Attics, upper-floor closets | Requires heat shielding for combustible floors |
| Horizontal | Crawlspaces, tight attics | Can be configured for left or right airflow |
Need reliable lab equipment solutions for your facility? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables, serving diverse research and industrial needs. Whether you're setting up a new lab or upgrading existing systems, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your specific requirements. Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a Multi-zone Tube Furnace? Enhanced Thermal Uniformity for Diffusion Research
- What is a three zone furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Uniformity
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency



















