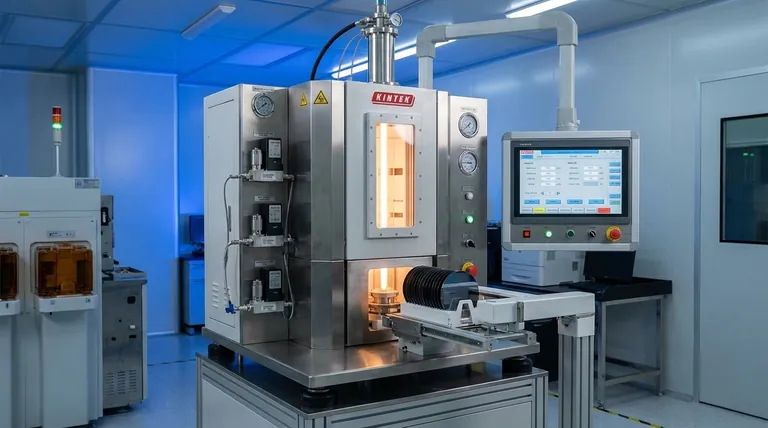
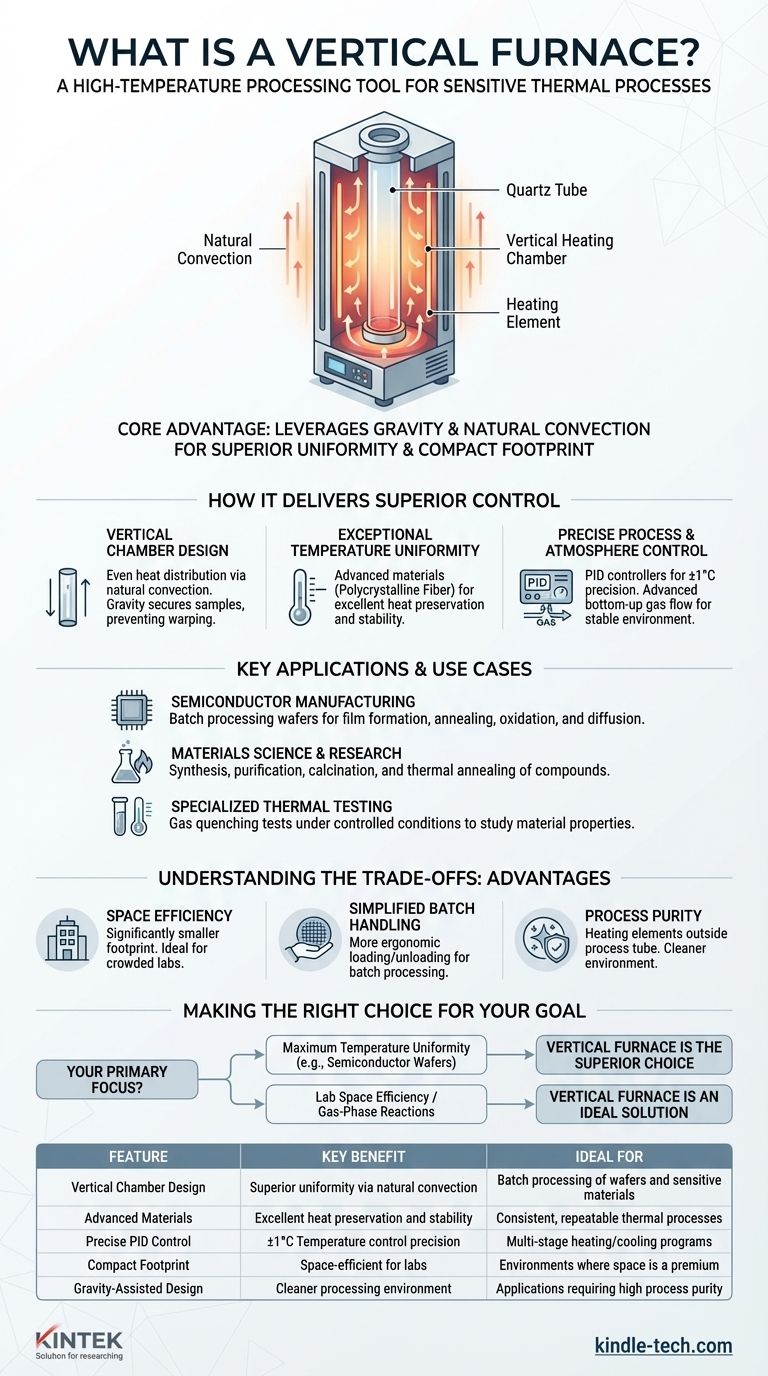
At its core, a vertical furnace is a high-temperature processing tool where the heating chamber, typically a quartz tube, is oriented vertically instead of horizontally. This design is primarily used for highly sensitive thermal processes in semiconductor manufacturing, such as film formation and annealing, as well as in advanced materials research.
The fundamental advantage of a vertical furnace lies in its design. By orienting the heating tube vertically, it leverages gravity and natural convection to achieve superior temperature uniformity and process consistency across multiple samples, all within a compact physical footprint.

How a Vertical Furnace Delivers Superior Control
A vertical furnace's effectiveness is not an accident; it is the direct result of a design philosophy centered on precision and repeatability. Several key elements work together to achieve this.
The Vertical Chamber Design
The heart of the system is a high-purity quartz tube surrounded by a heating element.
Placing the tube vertically allows heat to distribute more evenly through natural convection, minimizing the temperature gradients often found in horizontal furnaces.
This orientation also uses gravity to hold wafers or samples securely in place, preventing warping and ensuring consistent exposure to the controlled atmosphere.
Achieving Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
These furnaces often use advanced materials like polycrystalline fiber for the hearth.
This material provides excellent heat preservation and high reflectivity, creating a balanced and stable temperature field throughout the processing zone.
The result is extremely consistent and reliable outcomes from one batch to the next.
Precise Process and Atmosphere Control
Modern vertical furnaces integrate sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) temperature controllers.
These systems allow for precise, multi-stage heating and cooling programs, often with temperature control precision of ±1°C.
They also feature advanced gas flow control systems, which introduce gases from the bottom of the tube. This method is ideal for processes like chemical vapor deposition, as it can suspend particles uniformly within the heating zone.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The unique advantages of vertical furnaces make them indispensable in several high-stakes fields.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
This is the primary domain for vertical furnaces. They are critical for batch processing wafers for processes like film formation (deposition), annealing, oxidation, and diffusion. The exceptional uniformity is essential for device yield.
Materials Science and Research
In laboratory and industrial settings, these furnaces are used for a wide range of heat treatment applications.
This includes the synthesis, purification, calcination, and thermal annealing of both inorganic and organic compounds.
Specialized Thermal Testing
Vertical furnaces are also a preferred tool for conducting gas quenching tests under carefully controlled vacuum or atmospheric conditions, allowing researchers to study material properties after rapid cooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the choice to use a vertical furnace comes with specific considerations that make it ideal for certain applications over others.
Advantage: Space Efficiency
By building up instead of out, a vertical furnace has a significantly smaller footprint than a comparable horizontal furnace. This makes it an excellent choice for modern, often crowded, laboratories and cleanrooms.
Advantage: Simplified Batch Handling
For batch processing, loading and unloading samples (like a cassette of silicon wafers) into a vertical system is often more straightforward and ergonomic than in a long horizontal tube.
Advantage: Process Purity
In a vertical furnace, the heating elements are outside the process tube. Since particles or contaminants are more likely to fall down and away from the samples due to gravity, this design can lead to a cleaner processing environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your specific process requirements and priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity for sensitive batch processes: A vertical furnace is the superior choice for applications like semiconductor wafer fabrication.
- If your primary focus is lab space efficiency without compromising performance: The compact vertical footprint is an ideal solution for research environments where space is at a premium.
- If your primary focus involves gas-phase reactions or deposition: The vertical design with bottom-up gas flow provides an excellent, stable environment for suspending particles uniformly.
Ultimately, choosing a vertical furnace is an investment in process consistency, repeatability, and spatial efficiency for demanding thermal applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Chamber Design | Superior temperature uniformity via natural convection | Batch processing of wafers and sensitive materials |
| Advanced Materials (e.g., Polycrystalline Fiber) | Excellent heat preservation and stability | Consistent, repeatable thermal processes |
| Precise PID Control | Temperature control precision of ±1°C | Multi-stage heating/cooling programs |
| Compact Footprint | Space-efficient for labs and cleanrooms | Environments where space is a premium |
| Gravity-Assisted Design | Cleaner processing environment and secure sample holding | Applications requiring high process purity |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing capabilities?
A vertical furnace from KINTEK is an investment in precision, repeatability, and efficiency for your most demanding applications. Whether you are in semiconductor manufacturing, advanced materials research, or specialized thermal testing, our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right solution for superior temperature uniformity and process control.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK vertical furnace can meet your specific needs. Our team is ready to help you achieve your process goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry



















