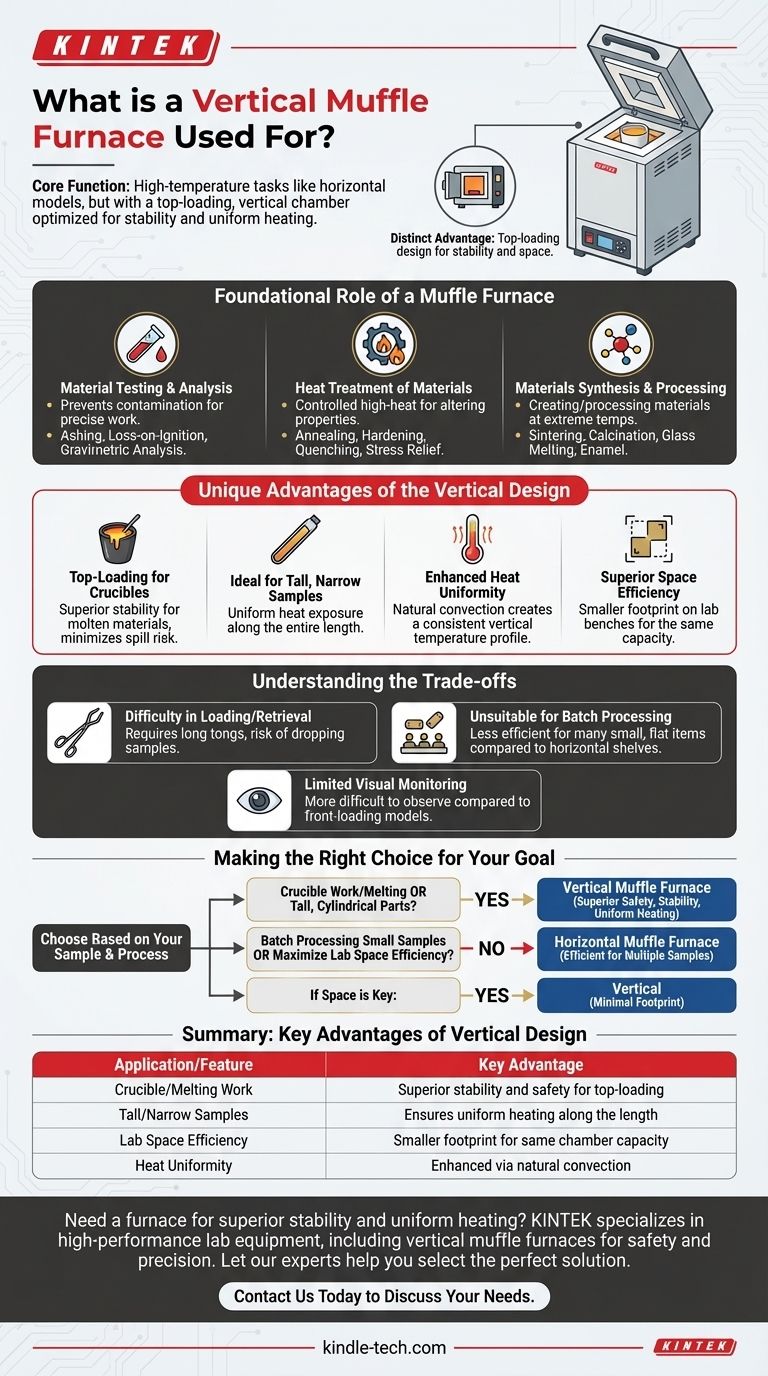
At its core, a vertical muffle furnace performs the same high-temperature tasks as its horizontal counterpart, including ashing, heat-treating, and materials synthesis. Its distinct advantage lies in its top-loading, vertical chamber, which is specifically designed for processes involving crucibles, tall samples, or molten materials where stability and uniform heating are critical.
The choice between a vertical and horizontal muffle furnace is not about the type of thermal process, but about the shape, container, and handling requirements of your sample. The vertical design excels where gravity, stability, and a smaller footprint are primary concerns.

The Foundational Role of a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is fundamentally a high-temperature oven. Its key feature is an insulated chamber—the "muffle"—that isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements.
For Material Testing and Analysis
This isolation prevents contamination, which is critical for precise analytical work. Common applications include ashing to determine the non-combustible content of a sample, loss-on-ignition analysis, and gravimetric analysis.
It's also used for sample pretreatment in fields like environmental analysis, drug testing, and quality control.
For Heat Treatment of Materials
Muffle furnaces provide the controlled, high-heat environment needed for altering the physical and chemical properties of materials.
This includes heat-treating processes like annealing, hardening, quenching, and stress relief for metals and alloys.
For Materials Synthesis and Processing
These furnaces are central to creating new materials or processing existing ones at extreme temperatures.
Key uses are sintering of ceramics and powdered metals, calcination, creating technical ceramics, melting glass, and developing specialized enamel coatings.
The Unique Advantages of the Vertical Design
While the fundamental applications are the same, the vertical orientation offers specific benefits that make it the superior choice for certain tasks.
Top-Loading for Crucibles and Unstable Samples
The primary advantage is its top-loading design. Lowering a sample into the chamber from above is inherently more stable than placing it on a shelf.
This is ideal for crucibles containing molten materials or powders, as it minimizes the risk of tipping and spilling, which can be a major hazard in a front-loading furnace.
Ideal for Tall, Narrow Samples
A vertical chamber is perfectly suited for samples that are taller than they are wide. It ensures more uniform heat exposure along the entire length of the object, which can be difficult to achieve for a tall sample lying on its side in a horizontal furnace.
Enhanced Heat Uniformity via Natural Convection
In a vertical tube furnace, natural heat convection creates a more uniform temperature profile along the central vertical axis. This can be critical for processes where precise temperature consistency throughout the sample is paramount.
Superior Space Efficiency
Vertical furnaces typically have a much smaller footprint on a lab bench or production floor compared to a horizontal model with the same internal capacity, making them valuable in crowded spaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The vertical design is not universally superior. Its advantages come with practical limitations that must be considered.
Difficulty in Loading and Retrieval
Placing and retrieving samples often requires long tongs and a steady hand. There is a greater risk of accidentally dropping a sample to the bottom of the chamber, which can be difficult and dangerous to recover.
Unsuitable for Batch Processing of Small Items
The design is poorly suited for processing many small, flat items simultaneously. A horizontal furnace with shelves is far more efficient for laying out multiple samples for a single run.
Limited Visual Monitoring
It is often more difficult to visually monitor the sample during a process in a top-loading vertical furnace compared to a front-loading model with a viewing window.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, focus on the nature of your sample and process, not just the temperature you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is crucible work or melting: A vertical furnace offers superior safety and stability, making it the clear choice.
- If your primary focus is processing tall, cylindrical parts: The vertical orientation provides more uniform heating for this specific geometry.
- If your primary focus is batch processing multiple small samples: A traditional horizontal muffle furnace with shelves is far more practical and efficient.
- If your primary focus is lab space efficiency: A vertical furnace provides maximum heating capacity for a minimal benchtop footprint.
Ultimately, the vertical muffle furnace is a specialized tool engineered to solve specific material handling challenges in high-temperature environments.
Summary Table:
| Application/Feature | Key Advantage of Vertical Design |
|---|---|
| Crucible/Melting Work | Superior stability and safety for top-loading |
| Tall/Narrow Samples | Ensures uniform heating along the length |
| Lab Space Efficiency | Smaller footprint for the same chamber capacity |
| Heat Uniformity | Enhanced via natural convection |
Need a furnace that provides superior stability for your crucible work or uniform heating for tall samples? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vertical muffle furnaces designed for safety, efficiency, and precise thermal processing. Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Purity



















