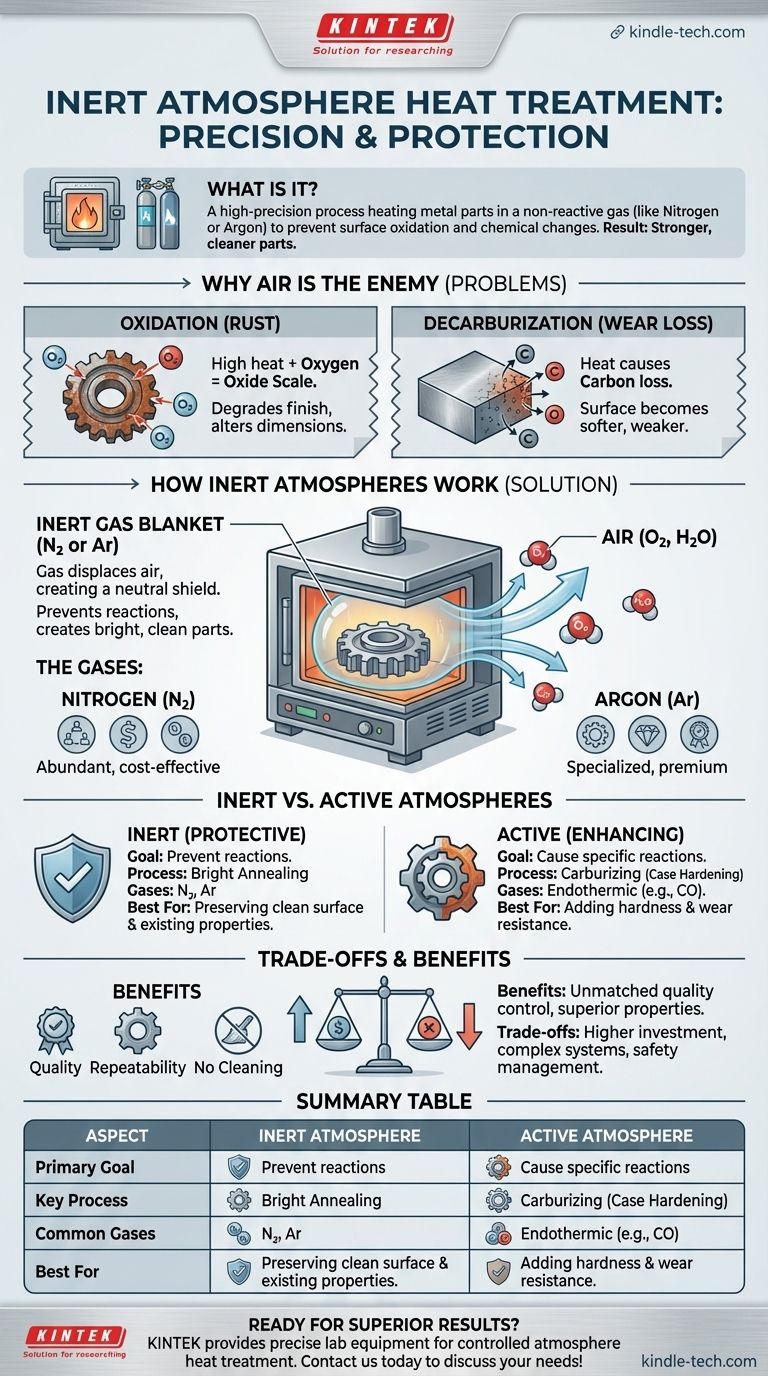
In short, inert atmosphere heat treatment is a high-precision process where metal parts are heated and cooled inside a sealed furnace filled with a non-reactive gas, most commonly nitrogen or argon. This controlled environment protects the metal's surface from oxidation (rusting) and other unwanted chemical changes that would normally occur when heated in the presence of air. The result is a stronger, cleaner part with superior material properties.
The central challenge of heat treatment is that high temperatures accelerate destructive chemical reactions with the oxygen and moisture in the air. An inert atmosphere solves this by replacing the air with a neutral gas, preserving the material's integrity and surface finish while allowing its internal structure to be precisely modified.

Why Air is the Enemy in Heat Treatment
To understand the value of an inert atmosphere, you must first understand the problems caused by heating metals in normal air. High temperatures act as a catalyst for undesirable and often irreversible surface reactions.
The Problem of Oxidation
When steel and other metals are heated to high temperatures, the oxygen in the air reacts rapidly with their surface. This creates a layer of oxide scale, which is essentially a form of rust.
This oxide layer degrades the part's surface finish, alters its precise dimensions, and can flake off, creating a messy and inconsistent product that may require costly secondary cleaning operations.
The Challenge of Decarburization
For many types of steel, the problems go deeper than just oxidation. The heat can also cause carbon atoms to diffuse out of the steel's surface and react with the oxygen in the air.
This loss of carbon, known as decarburization, makes the surface of the steel softer and significantly reduces its wear resistance and fatigue strength. This can be a critical failure point for components like gears and bearings.
How Inert Atmospheres Provide a Solution
By removing air from the furnace, an inert atmosphere prevents these destructive reactions from ever starting. It creates a stable, predictable environment for the heat treatment process.
Creating a Protective Shield
The inert gas, which is pumped into the sealed furnace, physically displaces the reactive oxygen and water vapor. It forms a neutral, protective blanket around the workpiece.
Because the gas is inert, it does not react with the metal even at very high temperatures. The part emerges from the furnace clean, bright, and free of scale—a process often called bright annealing or bright quenching.
The Primary Gases: Nitrogen and Argon
Nitrogen (N2) is the most common gas used for inert atmospheres. It is abundant, relatively inexpensive, and does not react with steel at most typical heat treatment temperatures.
Argon (Ar) is also used, particularly for highly reactive metals or at very high temperatures where nitrogen might form nitrides. It provides an even more inert environment but is significantly more expensive.
Beyond Inert: Understanding Controlled (Active) Atmospheres
While "inert atmosphere" is a common term, it is often used as a catch-all for a broader category known as controlled atmospheres. It is critical to understand the distinction.
The Distinction: Inert vs. Active
An inert atmosphere is purely protective. Its only job is to prevent reactions.
An active or controlled atmosphere is purposefully designed to cause a specific, desirable chemical reaction on the part's surface. These atmospheres not only protect the part but also enhance its properties.
Example: Carburizing Atmospheres
A common active process is gas carburizing. Here, an endothermic gas, often created from natural gas, is used as the atmosphere. This gas is rich in carbon monoxide (CO).
At high temperatures, the carbon monoxide reacts with the steel surface, diffusing carbon atoms into the steel. This process, called case hardening, creates a part with an extremely hard, wear-resistant surface and a softer, tougher core. This is an active process, not an inert one.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Benefits
Controlled atmospheres deliver significant quality improvements, but this comes with increased system complexity.
The Core Benefit: Unmatched Quality Control
Using a controlled atmosphere provides precise control over the final product. It prevents oxidation and decarburization, leading to improved hardness, superior wear resistance, and greater fatigue strength.
This level of control also ensures high repeatability, reduces part deformation during quenching, and often eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning, saving time and money.
The Cost of Control: Complexity and Investment
The primary trade-off is cost and complexity. These systems require sealed furnaces, gas generation or storage equipment, and sophisticated sensors to monitor and control the gas composition.
This represents a higher initial investment compared to simple air-fired furnaces.
Safety Considerations
Controlled atmospheres introduce safety challenges that must be managed. Gaseous nitrogen is an asphyxiant, while active atmospheres using natural gas are combustible. These systems require robust safety interlocks, ventilation, and operator training.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an inert or active atmosphere depends entirely on the desired outcome for the metal component.
- If your primary focus is preserving a clean surface and existing properties (e.g., bright annealing a stainless steel part): A pure inert atmosphere of nitrogen or argon is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface properties (e.g., creating a hard, wear-resistant case on a gear): You need an active controlled atmosphere, such as an endothermic gas for carburizing.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-sensitive production for less critical parts: A simpler air-fired furnace may be sufficient, but you must account for the potential need for secondary cleaning operations.
Ultimately, selecting the right atmosphere transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise and powerful manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Inert Atmosphere | Active Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prevent surface reactions (Protection) | Cause specific surface reactions (Enhancement) |
| Key Process | Bright Annealing/Quenching | Carburizing (Case Hardening) |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (N2), Argon (Ar) | Endothermic Gas (e.g., from Natural Gas) |
| Best For | Preserving clean surface & existing properties | Adding hardness/wear resistance to the surface |
Ready to achieve superior, consistent results with your heat treatment processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for controlled atmosphere applications. Whether you require a furnace for inert atmosphere bright annealing or an active atmosphere system for carburizing, our solutions are designed to protect your materials, enhance their properties, and improve your lab's efficiency.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific metal components and production goals. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover the difference precision engineering can make!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a reduction atmosphere furnace in exsolution? Precision Control for Perovskite Nanoparticles
- What is a retort furnace used for? Precise Atmosphere Control for Surface Hardening
- What is vacuum inerting? A Safer Method for Preventing Explosions and Oxidation
- What is used to provide an inert atmosphere for welding? Master the Shield for Perfect Welds
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is the role of high-temperature atmosphere control furnaces in the sintering process of 316L stainless steel?
- How does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace simulate service environments for evaluating CMAS corrosion resistance?
- What role do atmosphere furnaces or tube furnaces play in the SDS of Li-garnet electrolytes? Key to Dense Ceramic Films



















