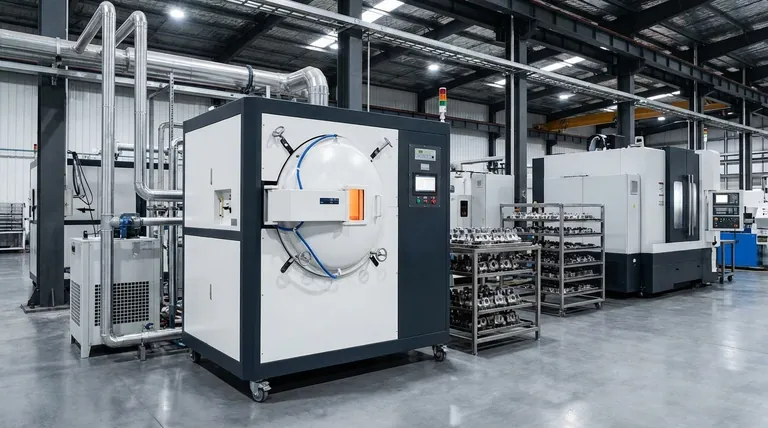
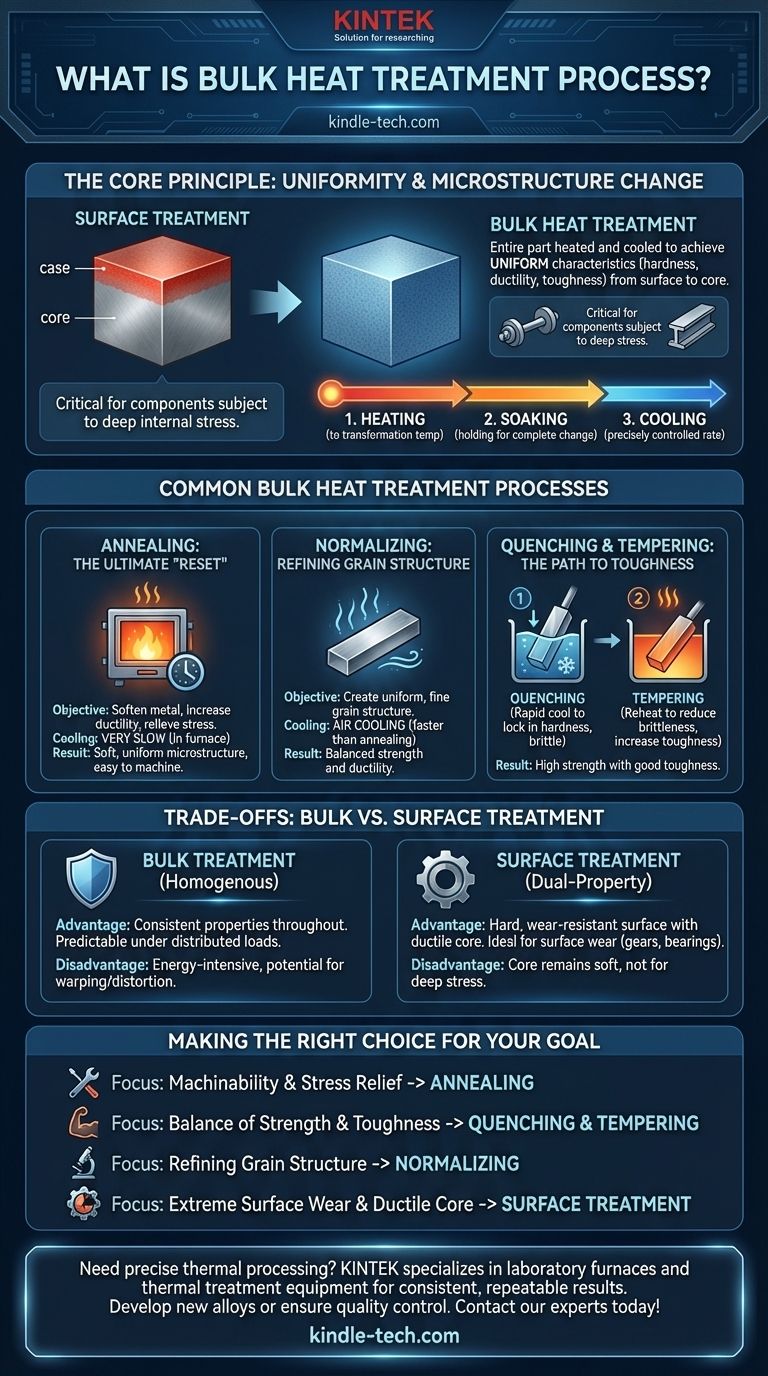
In materials science, bulk heat treatment is a process that modifies the metallurgical structure and mechanical properties of a metal component throughout its entire mass. Unlike surface treatments that only alter the outer layer, these methods heat and cool the entire part to achieve uniform characteristics, such as hardness, ductility, or toughness, from the surface all the way to the core.
The defining principle of bulk heat treatment is uniformity. While surface treatments create a hard outer "case" over a softer core, bulk processes are designed to achieve a single, consistent set of mechanical properties through the entire volume of the material.

The Core Principle: Changing the Entire Microstructure
The effectiveness of any heat treatment lies in its ability to manipulate a metal's crystalline structure. Bulk processes are designed to ensure this transformation happens completely and evenly.
From Surface to Core
The fundamental process involves three stages: heating the entire component to a specific transformation temperature, holding it at that temperature (soaking) until the change is complete, and then cooling it at a precisely controlled rate.
This holistic approach ensures that the properties are not just skin-deep. The changes penetrate through the full cross-section of the part.
Why Uniformity Matters
Consistent, through-body properties are critical for components that experience stress deep within their structure. Think of axles, structural beams, or pressure vessel walls.
In these applications, a failure at the core is just as catastrophic as a failure at the surface. Bulk treatment ensures the material is equally capable of withstanding these forces at any point.
Common Bulk Heat Treatment Processes
While all bulk treatments affect the entire part, they are tailored to achieve different outcomes. The most common processes are distinguished by their cooling rates and final objectives.
Annealing: The Ultimate "Reset"
Annealing is a process used to soften metal, increase its ductility, and relieve internal stresses. It makes the material easier to machine or form.
The process involves heating the metal, soaking it, and then cooling it very slowly, often by leaving it in the furnace to cool down. This slow cooling results in a soft, uniform microstructure.
Normalizing: Refining the Grain Structure
Normalizing is used to create a more uniform and finer grain structure than annealing. This leads to a predictable combination of strength and ductility.
The key difference is the cooling method. After heating and soaking, the part is removed from the furnace and cooled in still air. This faster cooling rate produces a harder and stronger material than one that has been annealed.
Quenching and Tempering: The Path to Toughness
This is a two-step process designed to create a combination of high strength and good toughness, a property that is often the primary goal for high-performance components.
First, quenching involves cooling the part rapidly in a medium like water, oil, or polymer. This locks in a very hard but brittle crystal structure (martensite).
Second, tempering involves reheating the quenched part to a lower temperature. This crucial step reduces the extreme hardness and brittleness, creating a more tough and durable final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Bulk vs. Surface Treatment
Choosing between a bulk and a surface heat treatment is a critical engineering decision driven entirely by the part's intended function.
The Advantage of Bulk Treatment
The primary benefit is homogenous properties. The part behaves predictably under tensile, bending, or torsional stresses that affect its entire cross-section. This is essential for components where the load is distributed throughout the material.
When to Choose Surface Treatment
Surface treatments like carburizing, nitriding, or induction hardening are superior when the primary failure mode is surface wear. They create a dual-property component: a very hard, wear-resistant surface with a softer, more ductile, and shock-resistant core.
This is the ideal combination for parts like gears, bearings, and camshafts, which must resist abrasion while also absorbing operational impacts without fracturing.
The Energy and Distortion Factor
Heating the entire volume of a large component is energy-intensive. Furthermore, the significant and uniform temperature changes in bulk treatment can sometimes lead to warping or distortion, which may require post-treatment machining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires a clear understanding of the desired end-state properties for your component.
- If your primary focus is machinability and stress relief: Annealing is the correct process to soften the material and prepare it for further manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is achieving a balance of strength and toughness throughout a component: Quenching and tempering provides the control to dial in the exact properties needed for high-stress applications.
- If your primary focus is refining grain structure for predictable performance: Normalizing creates a uniform material that eliminates inconsistencies from prior forging or casting operations.
- If your primary focus is extreme surface wear resistance with a ductile core: You should investigate surface treatments, as bulk treatment will not achieve this dual-property state.
Understanding the distinction between bulk and surface treatment is fundamental to designing components that are not just strong, but are engineered precisely for their intended function.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Objective | Cooling Method | Resulting Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften metal, relieve stress | Very slow (in furnace) | High ductility, easy machining |
| Normalizing | Refine grain structure | Air cooling | Balanced strength & ductility |
| Quenching & Tempering | Achieve toughness | Rapid quench, then reheat | High strength with good toughness |
Need precise thermal processing for your metal components? KINTEK specializes in laboratory furnaces and thermal treatment equipment designed for consistent, repeatable results. Whether you're developing new alloys or ensuring quality control in manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve the exact material properties your application demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your heat treatment requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What are vacuum furnace parts? A Guide to the Core Systems for Precision Heat Treatment



















