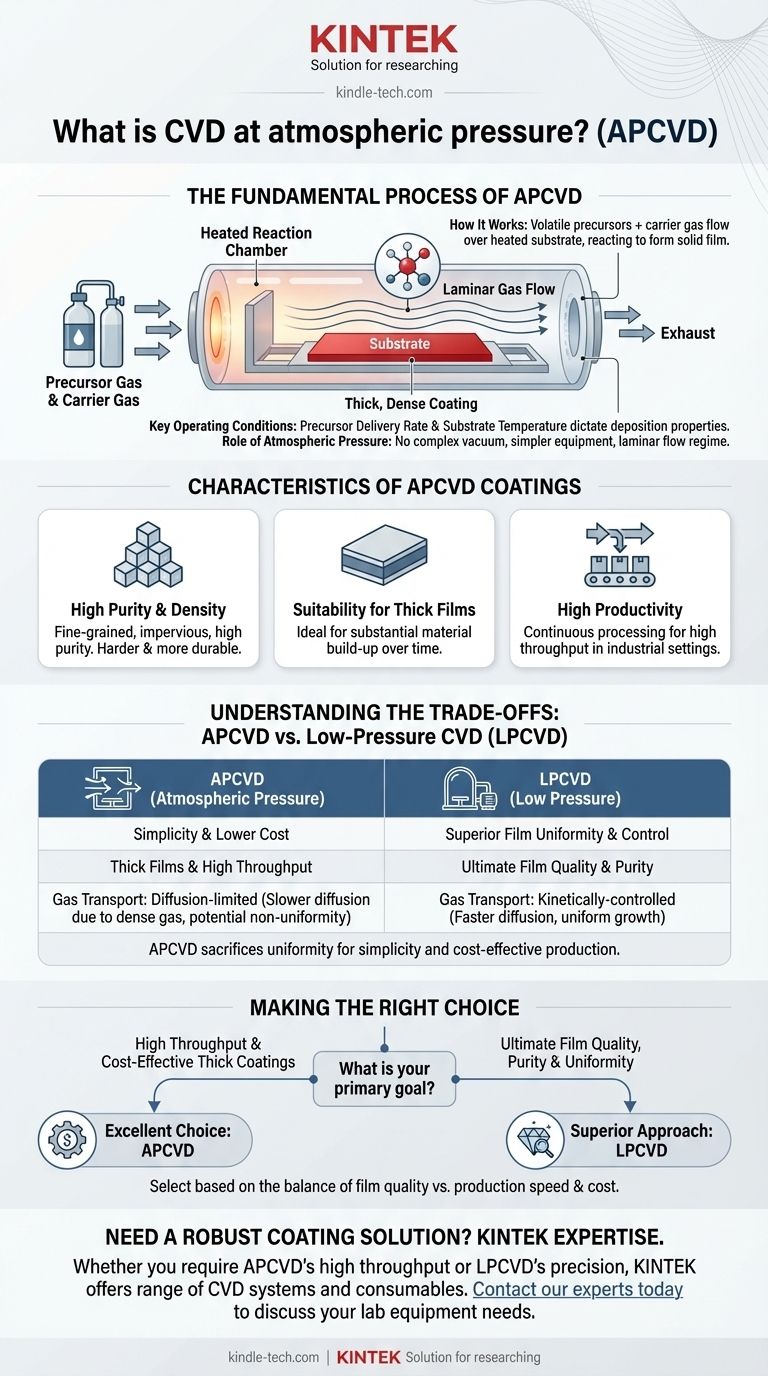
Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (APCVD) is a process for creating high-purity, dense coatings by reacting chemical precursor gases on the surface of a heated substrate under standard atmospheric conditions. Unlike other methods that require a vacuum, APCVD is valued for its operational simplicity and ability to deposit relatively thick films at a high rate of production.
APCVD is a trade-off between simplicity and precision. While it offers a straightforward, high-throughput method for producing thick coatings, it often sacrifices the superior film uniformity and control achievable with more complex low-pressure CVD techniques.
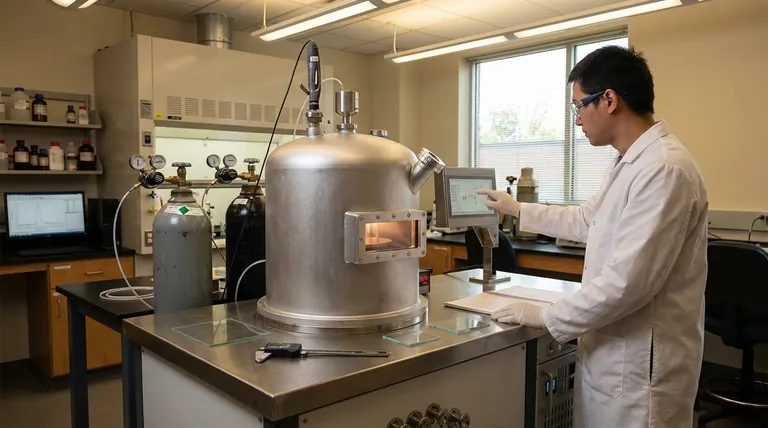

The Fundamental Process of APCVD
How It Works
The APCVD process involves heating a substrate within a reaction chamber. A mixture of volatile precursor chemicals, in gas form, is then introduced along with a carrier gas. These gases flow over the hot substrate, undergo a chemical reaction, and deposit a solid film onto the surface.
The Role of Atmospheric Pressure
Operating at atmospheric pressure is the defining characteristic of APCVD. This eliminates the need for expensive and complex vacuum systems, making the equipment simpler and more cost-effective. The process operates with gas flow rates in a laminar regime, meaning the gas moves in smooth, parallel layers.
Key Operating Conditions
The success of the deposition hinges on precise control over two main factors. The precursor delivery rate, controlled by the vaporizer's temperature, dictates the amount of reactant available. The substrate temperature determines the rate of the surface chemical reaction and influences the final properties of the deposited film.
Characteristics of APCVD Coatings
High Purity and Density
Like most CVD methods, APCVD produces coatings that are typically fine-grained, impervious, and have high purity. The resulting films are often harder and more durable than similar materials produced through conventional ceramic fabrication processes.
Suitability for Thick Films
APCVD is particularly well-suited for applications where a thick film is required. While the deposition rate might be measured in microns per minute, the continuous nature of the process allows for substantial material build-up over time.
High Productivity
Although the rate of deposition per unit area can be modest, APCVD systems are considered to have high productivity. This is because the absence of a vacuum chamber allows for continuous processing and high throughput, which is advantageous in industrial manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: APCVD vs. Low-Pressure CVD
Simplicity vs. Control
The primary advantage of APCVD is its simplicity and lower equipment cost. However, this comes at the cost of process control. Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) operates in a vacuum, which allows for much finer control over the deposition environment and film properties.
Gas Transport and Film Uniformity
This is the most critical technical difference. At atmospheric pressure, the dense concentration of gas molecules slows down the diffusion of precursor chemicals to the substrate surface. This can become the rate-limiting step, potentially leading to non-uniform film growth.
In contrast, the low pressure in LPCVD allows precursor gases to diffuse to the surface much faster. The process becomes kinetically controlled, meaning the rate is determined by the surface reaction itself, which typically results in superior film uniformity and quality.
The Precursor Challenge
A significant limitation of APCVD is the need for chemical precursors that are sufficiently volatile at atmospheric pressure. Finding precursors that are also non-toxic, non-pyrophoric, and stable poses a considerable challenge for many material systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is high throughput and cost-effective thick coatings: APCVD is an excellent and robust choice, especially for applications where perfect uniformity is not the most critical parameter.
- If your primary focus is ultimate film quality, purity, and uniformity for complex devices: A low-pressure method like LPCVD is the superior technical approach due to its enhanced control over the reaction environment.
Ultimately, selecting the right deposition method requires balancing the need for film quality against the practical demands of production speed and cost.
Summary Table:
| Feature | APCVD | LPCVD |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure | Atmospheric (No Vacuum) | Low Pressure (Vacuum Required) |
| Primary Advantage | High Throughput, Thick Films, Lower Cost | Superior Film Uniformity & Control |
| Best For | Cost-effective production where perfect uniformity is less critical | High-precision applications requiring ultimate film quality |
Need a robust coating solution for your lab?
Whether you require the high-throughput capabilities of APCVD for thick films or the precision of low-pressure methods, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific deposition needs. Our range of CVD systems and consumables ensures you get the right balance of quality, speed, and cost.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your research and production processes with the right lab equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth



















