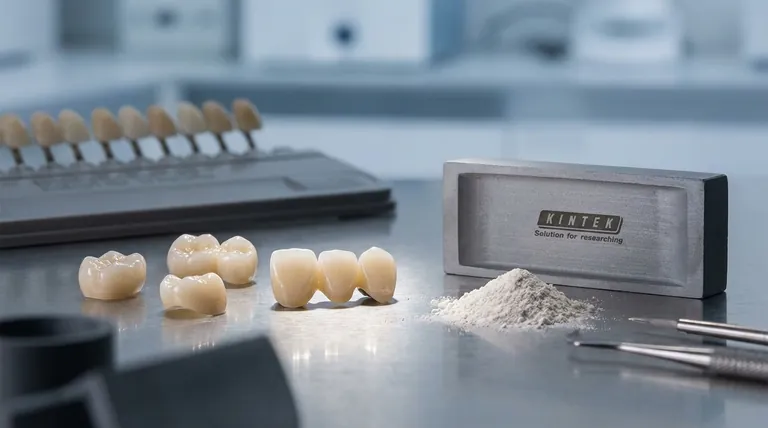
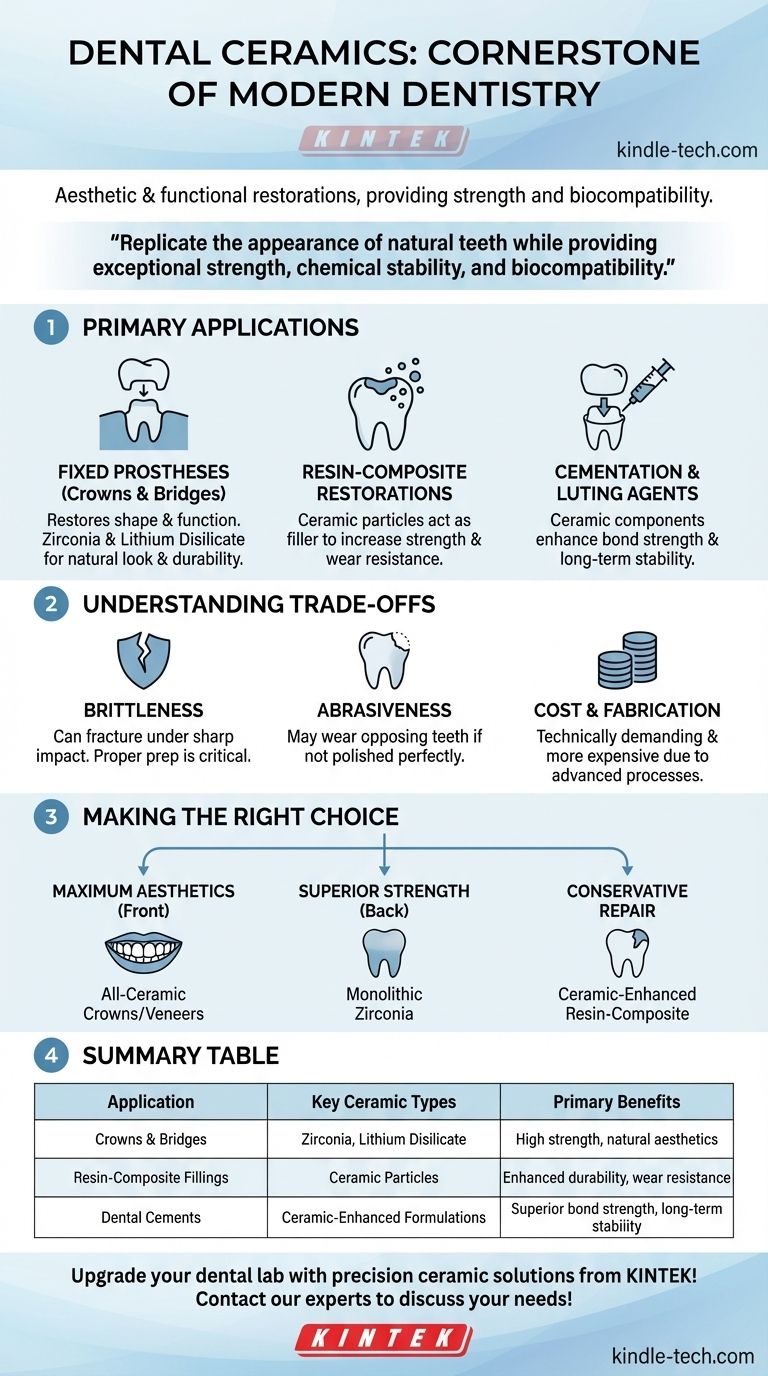
In modern dentistry, dental ceramics are a cornerstone material for aesthetic and functional restorations. They are most commonly used to create fixed prostheses such as crowns and bridges, but are also integrated as strengthening components in resin-composite filling materials and specialized dental cements.
Dental ceramics are chosen for their unique ability to replicate the appearance of natural teeth while providing exceptional strength, chemical stability, and biocompatibility, making them a gold standard for durable, long-lasting dental work.

The Primary Applications of Dental Ceramics
Dental ceramics are versatile materials that serve critical roles in both direct and indirect restorations. Their application is determined by the specific clinical need, balancing factors like strength, aesthetics, and placement.
Fixed Prostheses: Crowns and Bridges
This is the most well-known use for dental ceramics. A crown is a full-coverage restoration that encases a damaged tooth to restore its original shape, size, and function. A bridge uses crowns on adjacent teeth to support a prosthetic tooth, filling the space left by a missing one.
Ceramics like zirconia and lithium disilicate are used here because they can withstand significant biting forces while providing a natural, tooth-like appearance.
Resin-Composite Restorations
Many modern "white fillings" are resin composites. To improve their performance, manufacturers add finely milled ceramic particles as a filler.
These particles increase the material's strength, improve its resistance to wear, and reduce the amount it shrinks while hardening. This leads to a more durable and longer-lasting filling.
Cementation and Luting Agents
When a crown or bridge is permanently placed, it is bonded to the tooth structure with a dental cement, also known as a luting agent.
Some high-performance cements incorporate ceramic components to enhance their bond strength and long-term stability. This ensures the restoration remains securely attached to the tooth for years.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ceramic materials offer significant advantages, it is crucial to understand their limitations to ensure successful clinical outcomes.
Potential for Brittleness
Although ceramics are extremely hard and resistant to compression (biting down), they can be brittle. Under a sharp, focused impact, they can fracture more easily than a metallic restoration.
Proper tooth preparation and restoration design by the dentist are critical to minimize this risk.
Abrasiveness to Opposing Teeth
Some types of ceramic, particularly if not polished perfectly, can be abrasive and cause wear on the natural teeth they bite against over time.
Modern polishing techniques and the development of newer, kinder ceramic formulations have significantly reduced this concern.
Cost and Fabrication
Creating high-quality ceramic restorations is a technically demanding process that often requires advanced digital (CAD/CAM) or manual laboratory techniques.
This complexity and the cost of the raw materials typically make ceramic restorations a more expensive option compared to traditional metal or direct composite restorations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a ceramic-based material depends on balancing the clinical demands of the situation with the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics in the front of the mouth: All-ceramic crowns or veneers are the definitive choice for perfectly matching the shade and translucency of natural teeth.
- If your primary focus is superior strength for back teeth (molars): A monolithic zirconia crown provides exceptional durability to withstand heavy chewing forces.
- If your primary focus is a conservative repair of a small-to-moderate cavity: A resin-composite material enhanced with ceramic fillers offers a reliable and aesthetic direct restoration.
Ultimately, leveraging the distinct properties of dental ceramics allows for restorations that are not only functional and durable but also virtually indistinguishable from natural teeth.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Ceramic Types | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Crowns & Bridges | Zirconia, Lithium Disilicate | High strength, natural aesthetics |
| Resin-Composite Fillings | Ceramic Particles | Enhanced durability, wear resistance |
| Dental Cements | Ceramic-Enhanced Formulations | Superior bond strength, long-term stability |
Upgrade your dental lab with precision ceramic solutions from KINTEK!
Whether you're crafting durable zirconia crowns or aesthetic lithium disilicate bridges, KINTEK provides the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for superior results. Our products are designed to enhance efficiency, ensure consistency, and support the creation of long-lasting, natural-looking dental restorations.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for ceramics? Find the Right Material for Your High-Temp Application
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What are the classification of ceramic materials? A Guide to Oxides, Non-Oxides, and Composites
- What are the disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the key limitations and trade-offs.
- What is the main difference between soldering and brazing? Choose the Right Metal Joining Method






