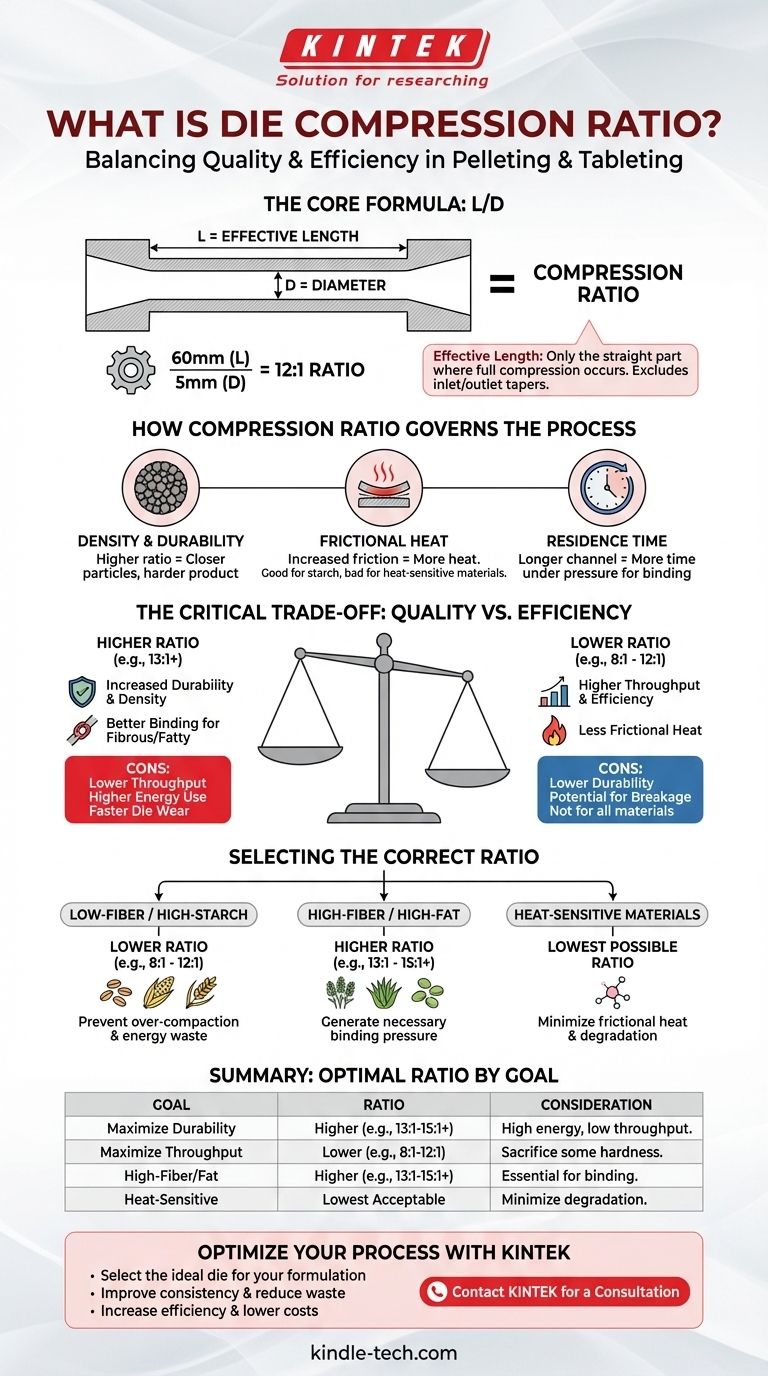
In the world of pelleting and tableting, die compression ratio is the relationship between the effective working length of the die hole and its diameter. This simple ratio is the single most influential factor in determining the final quality of the compacted product and the overall efficiency of your production line.
The challenge of compaction is not just about forming material, but about controlling a process. The die compression ratio is your primary tool for balancing the competing demands of product durability, production speed, and energy consumption.
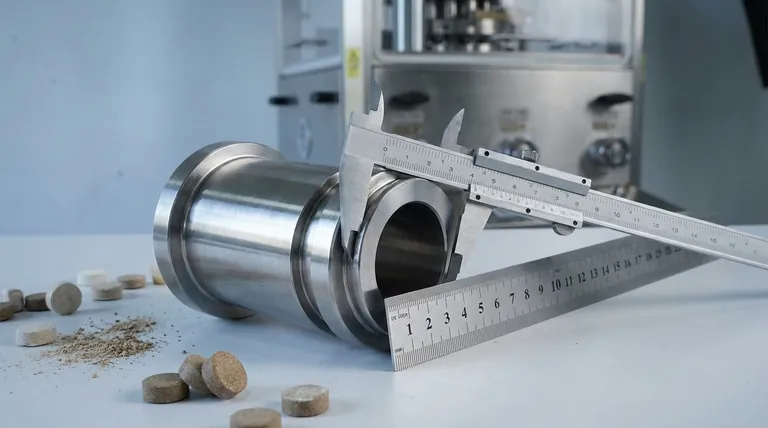

Deconstructing the Die Compression Ratio
The Core Formula: L/D
The ratio is calculated with a straightforward formula: Compression Ratio = L / D.
- L represents the effective length of the die channel.
- D represents the diameter of the die channel.
A die with a 60mm effective length and a 5mm diameter hole would have a compression ratio of 12:1 (or simply 12).
What is "Effective" Length?
This is a critical distinction. The effective length is only the part of the die channel where full compression occurs.
It does not include any relief, taper, or countersink at the inlet or outlet of the hole. These features are designed to ease material flow and reduce initial pressure, so the true compressive work happens only in the straight portion of the channel.
The Purpose of the Ratio
The compression ratio directly dictates the amount of pressure, friction, and residence time the material experiences as it's forced through the die. A higher ratio means more pressure and more time under compression.
How Compression Ratio Governs the Process
Controlling Density and Durability
A higher compression ratio increases the friction and pressure exerted on the material. This forces particles closer together, resulting in a denser, harder, and more durable pellet or tablet that can better withstand handling and transportation.
Generating Frictional Heat
This increased friction also generates significant heat. For materials like animal feed, this heat can be beneficial as it helps gelatinize starches, which act as a natural binder. For other materials, like pharmaceuticals or certain chemicals, this heat can be detrimental, causing degradation.
Determining Residence Time
A longer die channel (a higher ratio for a given diameter) means the material spends more time under pressure. This "residence time" is critical for achieving the necessary binding and heat transfer throughout the material.
The Critical Trade-off: Quality vs. Efficiency
Choosing a compression ratio is always an exercise in balancing competing factors. A higher ratio is not inherently better.
Production Throughput
A very high compression ratio creates more resistance. This can slow down the rate at which material can be forced through the die, directly reducing your tons-per-hour throughput.
Energy Consumption
Overcoming this higher resistance requires more work from the mill's motor. This leads to increased amperage draw and higher energy costs per ton of product produced. A die that is "too tight" for the formulation will cause the mill to plug or overload.
Die Life and Wear
Constant high pressure and friction accelerate the wear on the inside of the die channels. Choosing an unnecessarily high compression ratio will lead to more frequent and costly die replacements.
Selecting the Correct Ratio for Your Material
The ideal compression ratio is entirely dependent on the characteristics of your raw material formulation.
Low-Fiber, High-Starch Formulations
Formulations with a high starch content and low fiber (e.g., some poultry or swine feeds) are often easy to compact. They typically require a lower compression ratio (e.g., 8:1 to 12:1) to prevent over-compaction, burning, and excessive energy use.
High-Fiber or High-Fat Formulations
Fibrous materials (e.g., cattle feed, alfalfa, biomass) or formulations with high fat content naturally resist compaction. They require a higher compression ratio (e.g., 13:1 to 15:1 or even higher) to generate the necessary friction and pressure to form a durable pellet.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
For materials that can be damaged by heat, the goal is to use the lowest compression ratio possible that still achieves the required tablet or pellet integrity. This minimizes frictional heat generation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal die compression ratio is not a single number; it is a function of your material and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum product durability: Opt for a higher compression ratio, but be prepared for lower throughput and higher energy consumption.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Use the lowest compression ratio that still produces an acceptable quality product for your specific application.
- If you are processing a difficult, fibrous material: A higher compression ratio is necessary to create the binding pressure required for a quality pellet.
- If you are processing a heat-sensitive formulation: Your main goal is to minimize friction, which means selecting the lowest possible compression ratio that meets quality standards.
Understanding and mastering the die compression ratio transforms pelleting from a brute-force process into a precisely controlled manufacturing operation.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Recommended Compression Ratio | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Maximize Durability | Higher Ratio (e.g., 13:1 - 15:1+) | Higher energy use, lower throughput, increased die wear |
| Maximize Throughput | Lower Ratio (e.g., 8:1 - 12:1) | May sacrifice some pellet hardness and durability |
| High-Fiber/Fat Materials | Higher Ratio (e.g., 13:1 - 15:1+) | Necessary to generate sufficient binding pressure |
| Heat-Sensitive Materials | Lowest Possible Acceptable Ratio | Minimizes frictional heat to prevent degradation |
Optimize Your Pelleting or Tableting Process with KINTEK
Are you struggling with pellet quality, low throughput, or high energy costs? The die compression ratio is often the key. Selecting the right die is critical for balancing product durability with operational efficiency.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. Our expertise can help you:
- Select the ideal die for your specific material formulation.
- Improve product consistency and reduce waste.
- Increase production efficiency and lower operational costs.
Don't let the wrong compression ratio hinder your process. Let our experts help you achieve superior results.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover the right solution for your lab's pelleting and tableting needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- How does a rotary tablet press work? A Guide to High-Speed Tablet Manufacturing
- What is the difference between single punch and rotary tablet press? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production
- How fast is the rotary tablet press? Unlock Peak Production Speeds for Your Tablets
- What is the use of tablet press? Transforming Powder into Precise, Uniform Tablets
- What are the disadvantages of press working? High Costs and Design Limits for Mass Production



















